Ruizhou Sun
Occlusion-Aware Detection and Re-ID Calibrated Network for Multi-Object Tracking
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) is a crucial computer vision task that aims to predict the bounding boxes and identities of objects simultaneously. While state-of-the-art methods have made remarkable progress by jointly optimizing the multi-task problems of detection and Re-ID feature learning, yet, few approaches explore to tackle the occlusion issue, which is a long-standing challenge in the MOT field. Generally, occluded objects may hinder the detector from estimating the bounding boxes, resulting in fragmented trajectories. And the learned occluded Re-ID embeddings are less distinct since they contain interferer. To this end, we propose an occlusion-aware detection and Re-ID calibrated network for multi-object tracking, termed as ORCTrack. Specifically, we propose an Occlusion-Aware Attention (OAA) module in the detector that highlights the object features while suppressing the occluded background regions. OAA can serve as a modulator that enhances the detector for some potentially occluded objects. Furthermore, we design a Re-ID embedding matching block based on the optimal transport problem, which focuses on enhancing and calibrating the Re-ID representations through different adjacent frames complementarily. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted on two challenging VisDrone2021-MOT and KITTI benchmarks. Experimental evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our approach, which can achieve new state-of-the-art performance and enjoy high run-time efficiency.
A Unified Transformer Framework for Group-based Segmentation: Co-Segmentation, Co-Saliency Detection and Video Salient Object Detection
Mar 11, 2022



Abstract:Humans tend to mine objects by learning from a group of images or several frames of video since we live in a dynamic world. In the computer vision area, many researches focus on co-segmentation (CoS), co-saliency detection (CoSD) and video salient object detection (VSOD) to discover the co-occurrent objects. However, previous approaches design different networks on these similar tasks separately, and they are difficult to apply to each other, which lowers the upper bound of the transferability of deep learning frameworks. Besides, they fail to take full advantage of the cues among inter- and intra-feature within a group of images. In this paper, we introduce a unified framework to tackle these issues, term as UFO (Unified Framework for Co-Object Segmentation). Specifically, we first introduce a transformer block, which views the image feature as a patch token and then captures their long-range dependencies through the self-attention mechanism. This can help the network to excavate the patch structured similarities among the relevant objects. Furthermore, we propose an intra-MLP learning module to produce self-mask to enhance the network to avoid partial activation. Extensive experiments on four CoS benchmarks (PASCAL, iCoseg, Internet and MSRC), three CoSD benchmarks (Cosal2015, CoSOD3k, and CocA) and four VSOD benchmarks (DAVIS16, FBMS, ViSal and SegV2) show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-arts on three different tasks in both accuracy and speed by using the same network architecture , which can reach 140 FPS in real-time.
Context Decoupling Augmentation for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Mar 02, 2021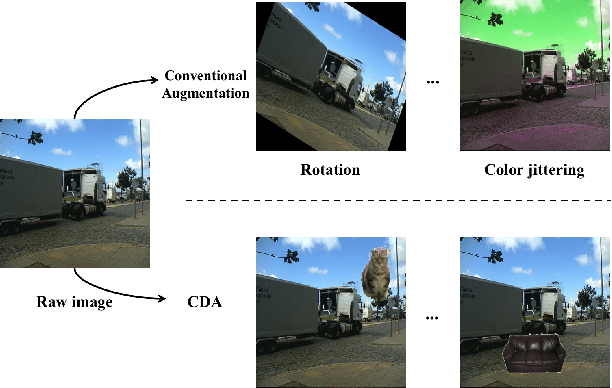
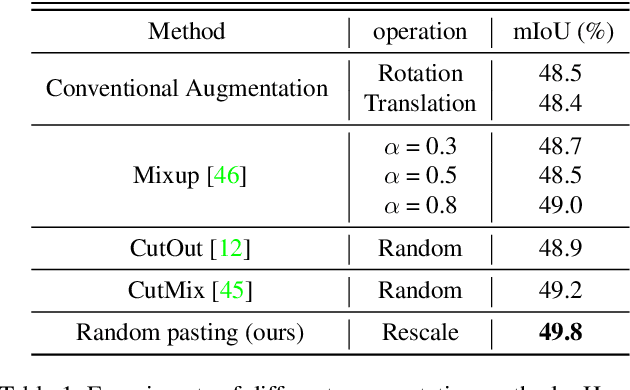
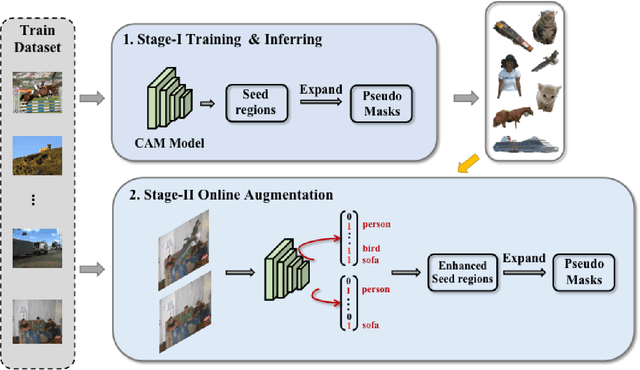
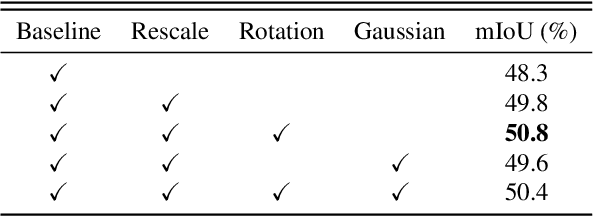
Abstract:Data augmentation is vital for deep learning neural networks. By providing massive training samples, it helps to improve the generalization ability of the model. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) is a challenging problem that has been deeply studied in recent years, conventional data augmentation approaches for WSSS usually employ geometrical transformations, random cropping and color jittering. However, merely increasing the same contextual semantic data does not bring much gain to the networks to distinguish the objects, e.g., the correct image-level classification of "aeroplane" may be not only due to the recognition of the object itself, but also its co-occurrence context like "sky", which will cause the model to focus less on the object features. To this end, we present a Context Decoupling Augmentation (CDA) method, to change the inherent context in which the objects appear and thus drive the network to remove the dependence between object instances and contextual information. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset with several alternative network architectures demonstrate that CDA can boost various popular WSSS methods to the new state-of-the-art by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge