Ruiqing Sun
Decoupling Constraint from Two Direction in Evolutionary Constrained Multi-objective Optimization
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Real-world Constrained Multi-objective Optimization Problems (CMOPs) often contain multiple constraints, and understanding and utilizing the coupling between these constraints is crucial for solving CMOPs. However, existing Constrained Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms (CMOEAs) typically ignore these couplings and treat all constraints as a single aggregate, which lacks interpretability regarding the specific geometric roles of constraints. To address this limitation, we first analyze how different constraints interact and show that the final Constrained Pareto Front (CPF) depends not only on the Pareto fronts of individual constraints but also on the boundaries of infeasible regions. This insight implies that CMOPs with different coupling types must be solved from different search directions. Accordingly, we propose a novel algorithm named Decoupling Constraint from Two Directions (DCF2D). This method periodically detects constraint couplings and spawns an auxiliary population for each relevant constraint with an appropriate search direction. Extensive experiments on seven challenging CMOP benchmark suites and on a collection of real-world CMOPs demonstrate that DCF2D outperforms five state-of-the-art CMOEAs, including existing decoupling-based methods.
Evolutionary training-free guidance in diffusion model for 3D multi-objective molecular generation
May 16, 2025Abstract:Discovering novel 3D molecular structures that simultaneously satisfy multiple property targets remains a central challenge in materials and drug design. Although recent diffusion-based models can generate 3D conformations, they require expensive retraining for each new property or property-combination and lack flexibility in enforcing structural constraints. We introduce EGD (Evolutionary Guidance in Diffusion), a training-free framework that embeds evolutionary operators directly into the diffusion sampling process. By performing crossover on noise-perturbed samples and then denoising them with a pretrained Unconditional diffusion model, EGD seamlessly blends structural fragments and steers generation toward user-specified objectives without any additional model updates. On both single- and multi-target 3D conditional generation tasks-and on multi-objective optimization of quantum properties EGD outperforms state-of-the-art conditional diffusion methods in accuracy and runs up to five times faster per generation. In the single-objective optimization of protein ligands, EGD enables customized ligand generation. Moreover, EGD can embed arbitrary 3D fragments into the generated molecules while optimizing multiple conflicting properties in one unified process. This combination of efficiency, flexibility, and controllable structure makes EGD a powerful tool for rapid, guided exploration of chemical space.
Batch-FPM: Random batch-update multi-parameter physical Fourier ptychography neural network
Aug 25, 2024Abstract:Fourier Ptychographic Microscopy (FPM) is a computational imaging technique that enables high-resolution imaging over a large field of view. However, its application in the biomedical field has been limited due to the long image reconstruction time and poor noise robustness. In this paper, we propose a fast and robust FPM reconstruction method based on physical neural networks with batch update stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimization strategy, capable of achieving attractive results with low single-to-noise ratio and correcting multiple system parameters simultaneously. Our method leverages a random batch optimization approach, breaks away from the fixed sequential iterative order and gives greater attention to high-frequency information. The proposed method has better convergence performance even for low signal-to-noise ratio data sets, such as low exposure time dark-field images. As a result, it can greatly increase the image recording and result reconstruction speed without any additional hardware modifications. By utilizing advanced deep learning optimizers and perform parallel computational scheme, our method enhances GPU computational efficiency, significantly reducing reconstruction costs. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves near real-time digital refocusing of a 1024 x 1024 pixels region of interest on consumer-grade GPUs. This approach significantly improves temporal resolution (by reducing the exposure time of dark-field images), noise resistance, and reconstruction speed, and therefore can efficiently promote the practical application of FPM in clinical diagnostics, digital pathology, and biomedical research, etc. In addition, we believe our algorithm scheme can help researchers quickly validate and implement FPM-related ideas. We invite requests for the full code via email.
Teach model to answer questions after comprehending the document
Jul 18, 2023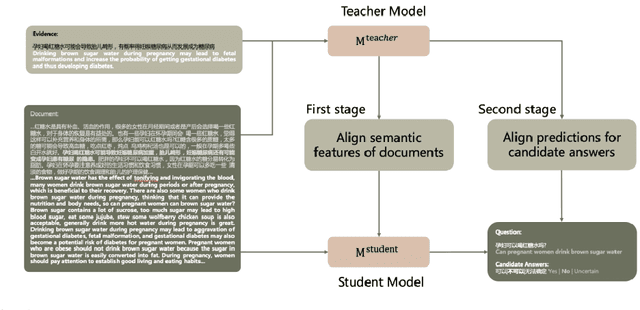
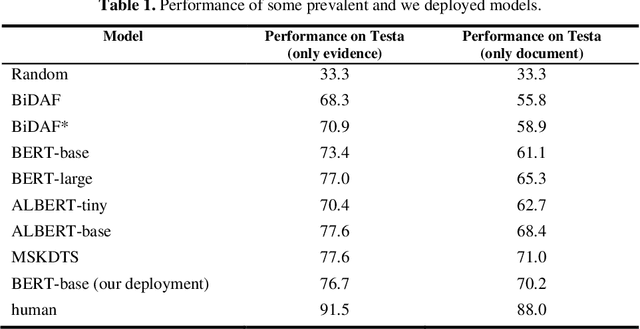
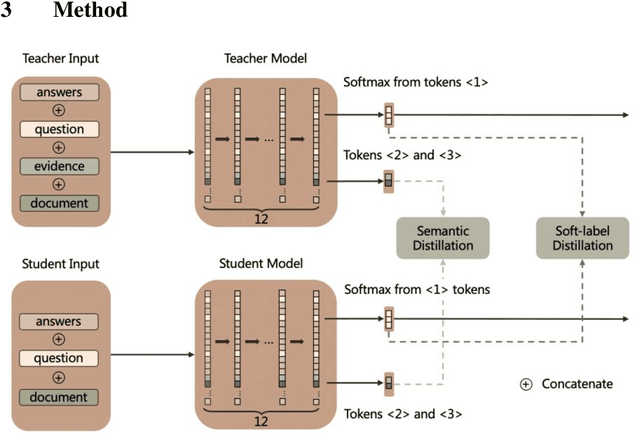

Abstract:Multi-choice Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) is a challenging extension of Natural Language Processing (NLP) that requires the ability to comprehend the semantics and logical relationships between entities in a given text. The MRC task has traditionally been viewed as a process of answering questions based on the given text. This single-stage approach has often led the network to concentrate on generating the correct answer, potentially neglecting the comprehension of the text itself. As a result, many prevalent models have faced challenges in performing well on this task when dealing with longer texts. In this paper, we propose a two-stage knowledge distillation method that teaches the model to better comprehend the document by dividing the MRC task into two separate stages. Our experimental results show that the student model, when equipped with our method, achieves significant improvements, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method.
Adaptive coded illumination Fourier ptychography microscopy based on physical neural network
Apr 20, 2023



Abstract:Fourier Ptychographic Microscopy (FPM) is a computational technique that achieves a large space-bandwidth product imaging. It addresses the challenge of balancing a large field of view and high resolution by fusing information from multiple images taken with varying illumination angles. Nevertheless, conventional FPM framework always suffers from long acquisition time and a heavy computational burden. In this paper, we propose a novel physical neural network that generates an adaptive illumination mode by incorporating temporally-encoded illumination modes as a distinct layer, aiming to improve the acquisition and calculation efficiency. Both simulations and experiments have been conducted to validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method. It is worth mentioning that, unlike previous works that obtain the intensity of a multiplexed illumination by post-combination of each sequentially illuminated and obtained low-resolution images, our experimental data is captured directly by turning on multiple LEDs with a coded illumination pattern. Our method has exhibited state-of-the-art performance in terms of both detail fidelity and imaging velocity when assessed through a multitude of evaluative aspects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge