Ruicong Yao
Unlocking the Value of Decentralized Data: A Federated Dual Learning Approach for Model Aggregation
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies have revolutionized numerous fields, yet their applications often rely on costly and time-consuming data collection processes. Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising alternative by enabling AI models to be trained on decentralized data where data is scattered across clients (distributed nodes). However, existing FL approaches struggle to match the performance of centralized training due to challenges such as heterogeneous data distribution and communication delays, limiting their potential for breakthroughs. We observe that many real-world use cases involve hybrid data regimes, in which a server (center node) has access to some data while a large amount of data is distributed across associated clients. To improve the utilization of decentralized data under this regime, address data heterogeneity issue, and facilitate asynchronous communication between the server and clients, we propose a dual learning approach that leverages centralized data at the server to guide the merging of model updates from clients. Our method accommodates scenarios where server data is out-of-domain relative to decentralized client data, making it applicable to a wide range of use cases. We provide theoretical analysis demonstrating the faster convergence of our method compared to existing methods. Furthermore, experimental results across various scenarios show that our approach significantly outperforms existing technologies, highlighting its potential to unlock the value of large amounts of decentralized data.
Surrogate Model Extension : A Fast and Accurate Weight Update Attack on Federated Learning
May 31, 2023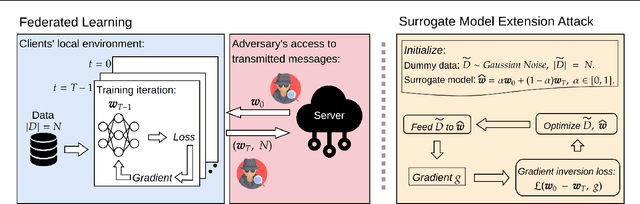
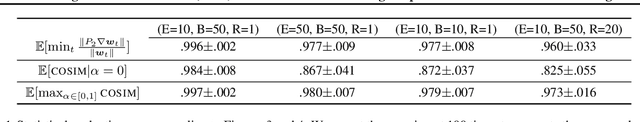
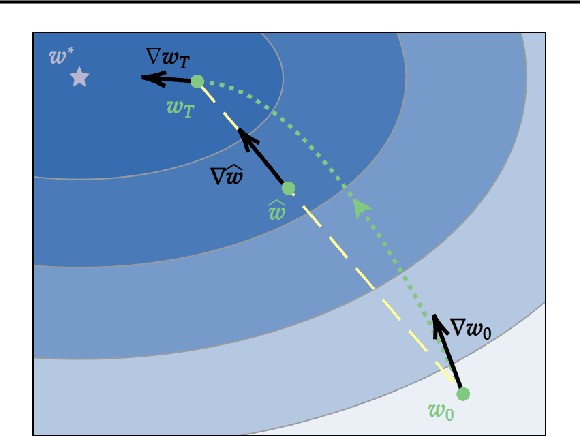
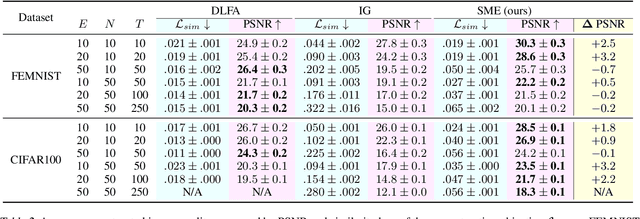
Abstract:In Federated Learning (FL) and many other distributed training frameworks, collaborators can hold their private data locally and only share the network weights trained with the local data after multiple iterations. Gradient inversion is a family of privacy attacks that recovers data from its generated gradients. Seemingly, FL can provide a degree of protection against gradient inversion attacks on weight updates, since the gradient of a single step is concealed by the accumulation of gradients over multiple local iterations. In this work, we propose a principled way to extend gradient inversion attacks to weight updates in FL, thereby better exposing weaknesses in the presumed privacy protection inherent in FL. In particular, we propose a surrogate model method based on the characteristic of two-dimensional gradient flow and low-rank property of local updates. Our method largely boosts the ability of gradient inversion attacks on weight updates containing many iterations and achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Additionally, our method runs up to $100\times$ faster than the SOTA baseline in the common FL scenario. Our work re-evaluates and highlights the privacy risk of sharing network weights. Our code is available at https://github.com/JunyiZhu-AI/surrogate_model_extension.
Fast Linear Model Trees by PILOT
Feb 08, 2023Abstract:Linear model trees are regression trees that incorporate linear models in the leaf nodes. This preserves the intuitive interpretation of decision trees and at the same time enables them to better capture linear relationships, which is hard for standard decision trees. But most existing methods for fitting linear model trees are time consuming and therefore not scalable to large data sets. In addition, they are more prone to overfitting and extrapolation issues than standard regression trees. In this paper we introduce PILOT, a new algorithm for linear model trees that is fast, regularized, stable and interpretable. PILOT trains in a greedy fashion like classic regression trees, but incorporates an $L^2$ boosting approach and a model selection rule for fitting linear models in the nodes. The abbreviation PILOT stands for $PI$ecewise $L$inear $O$rganic $T$ree, where `organic' refers to the fact that no pruning is carried out. PILOT has the same low time and space complexity as CART without its pruning. An empirical study indicates that PILOT tends to outperform standard decision trees and other linear model trees on a variety of data sets. Moreover, we prove its consistency in an additive model setting under weak assumptions. When the data is generated by a linear model, the convergence rate is polynomial.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge