Ruichen Zheng
LLMs as Scalable, General-Purpose Simulators For Evolving Digital Agent Training
Oct 16, 2025
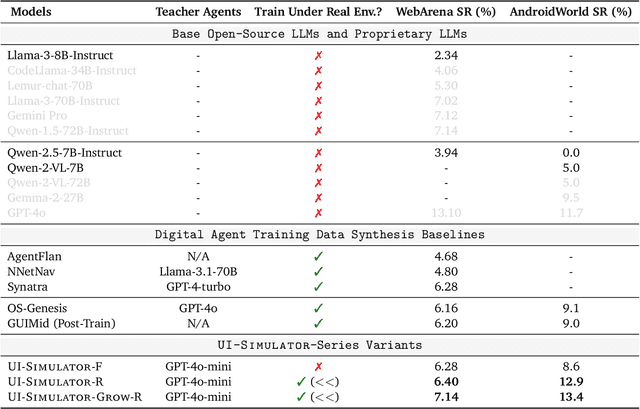
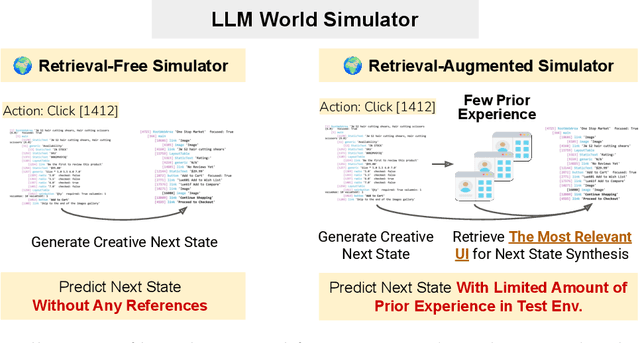
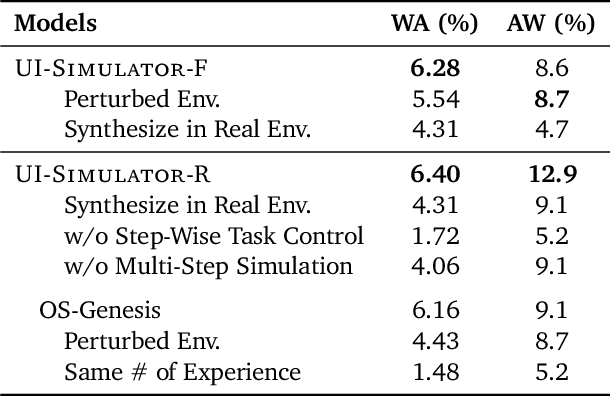
Abstract:Digital agents require diverse, large-scale UI trajectories to generalize across real-world tasks, yet collecting such data is prohibitively expensive in both human annotation, infra and engineering perspectives. To this end, we introduce $\textbf{UI-Simulator}$, a scalable paradigm that generates structured UI states and transitions to synthesize training trajectories at scale. Our paradigm integrates a digital world simulator for diverse UI states, a guided rollout process for coherent exploration, and a trajectory wrapper that produces high-quality and diverse trajectories for agent training. We further propose $\textbf{UI-Simulator-Grow}$, a targeted scaling strategy that enables more rapid and data-efficient scaling by prioritizing high-impact tasks and synthesizes informative trajectory variants. Experiments on WebArena and AndroidWorld show that UI-Simulator rivals or surpasses open-source agents trained on real UIs with significantly better robustness, despite using weaker teacher models. Moreover, UI-Simulator-Grow matches the performance of Llama-3-70B-Instruct using only Llama-3-8B-Instruct as the base model, highlighting the potential of targeted synthesis scaling paradigm to continuously and efficiently enhance the digital agents.
Multimodal Cultural Safety: Evaluation Frameworks and Alignment Strategies
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) are increasingly deployed in globally distributed applications, such as tourism assistants, yet their ability to produce culturally appropriate responses remains underexplored. Existing multimodal safety benchmarks primarily focus on physical safety and overlook violations rooted in cultural norms, which can result in symbolic harm. To address this gap, we introduce CROSS, a benchmark designed to assess the cultural safety reasoning capabilities of LVLMs. CROSS includes 1,284 multilingual visually grounded queries from 16 countries, three everyday domains, and 14 languages, where cultural norm violations emerge only when images are interpreted in context. We propose CROSS-Eval, an intercultural theory-based framework that measures four key dimensions: cultural awareness, norm education, compliance, and helpfulness. Using this framework, we evaluate 21 leading LVLMs, including mixture-of-experts models and reasoning models. Results reveal significant cultural safety gaps: the best-performing model achieves only 61.79% in awareness and 37.73% in compliance. While some open-source models reach GPT-4o-level performance, they still fall notably short of proprietary models. Our results further show that increasing reasoning capacity improves cultural alignment but does not fully resolve the issue. To improve model performance, we develop two enhancement strategies: supervised fine-tuning with culturally grounded, open-ended data and preference tuning with contrastive response pairs that highlight safe versus unsafe behaviors. These methods substantially improve GPT-4o's cultural awareness (+60.14%) and compliance (+55.2%), while preserving general multimodal capabilities with minimal performance reduction on general multimodal understanding benchmarks.
Neural Octahedral Field: Octahedral prior for simultaneous smoothing and sharp edge regularization
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Neural implicit representation, the parameterization of distance function as a coordinate neural field, has emerged as a promising lead in tackling surface reconstruction from unoriented point clouds. To enforce consistent orientation, existing methods focus on regularizing the gradient of the distance function, such as constraining it to be of the unit norm, minimizing its divergence, or aligning it with the eigenvector of Hessian that corresponds to zero eigenvalue. However, under the presence of large scanning noise, they tend to either overfit the noise input or produce an excessively smooth reconstruction. In this work, we propose to guide the surface reconstruction under a new variant of neural field, the octahedral field, leveraging the spherical harmonics representation of octahedral frames originated in the hexahedral meshing. Such field automatically snaps to geometry features when constrained to be smooth, and naturally preserves sharp angles when interpolated over creases. By simultaneously fitting and smoothing the octahedral field alongside the implicit geometry, it behaves analogously to bilateral filtering, resulting in smooth reconstruction while preserving sharp edges. Despite being operated purely pointwise, our method outperforms various traditional and neural approaches across extensive experiments, and is very competitive with methods that require normal and data priors. Our full implementation is available at: https://github.com/Ankbzpx/frame-field.
Learning Visibility Field for Detailed 3D Human Reconstruction and Relighting
Apr 24, 2023Abstract:Detailed 3D reconstruction and photo-realistic relighting of digital humans are essential for various applications. To this end, we propose a novel sparse-view 3d human reconstruction framework that closely incorporates the occupancy field and albedo field with an additional visibility field--it not only resolves occlusion ambiguity in multiview feature aggregation, but can also be used to evaluate light attenuation for self-shadowed relighting. To enhance its training viability and efficiency, we discretize visibility onto a fixed set of sample directions and supply it with coupled geometric 3D depth feature and local 2D image feature. We further propose a novel rendering-inspired loss, namely TransferLoss, to implicitly enforce the alignment between visibility and occupancy field, enabling end-to-end joint training. Results and extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, as it surpasses state-of-the-art in terms of reconstruction accuracy while achieving comparably accurate relighting to ray-traced ground truth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge