Ruichen Xu
Kolmogorov-Arnold Representation for Symplectic Learning: Advancing Hamiltonian Neural Networks
Aug 26, 2025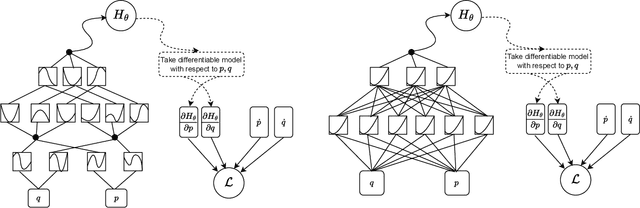
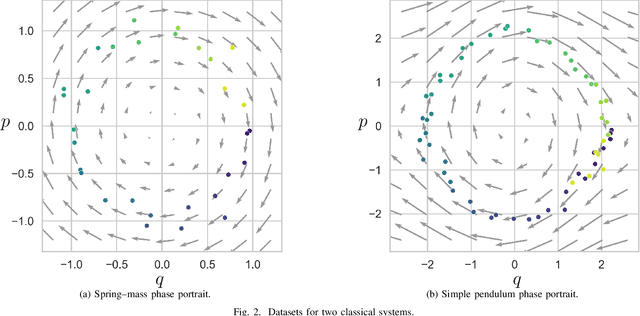
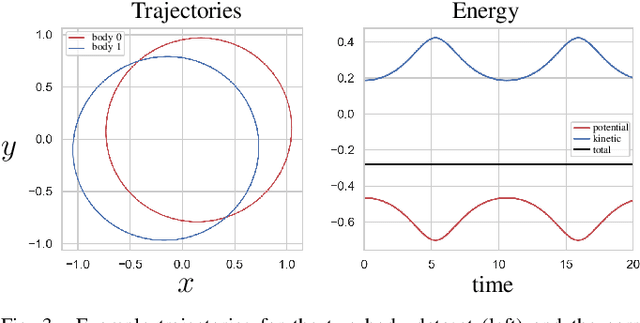
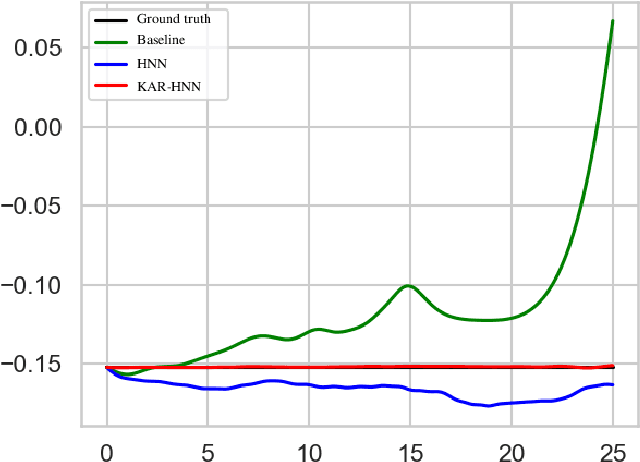
Abstract:We propose a Kolmogorov-Arnold Representation-based Hamiltonian Neural Network (KAR-HNN) that replaces the Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) with univariate transformations. While Hamiltonian Neural Networks (HNNs) ensure energy conservation by learning Hamiltonian functions directly from data, existing implementations, often relying on MLPs, cause hypersensitivity to the hyperparameters while exploring complex energy landscapes. Our approach exploits the localized function approximations to better capture high-frequency and multi-scale dynamics, reducing energy drift and improving long-term predictive stability. The networks preserve the symplectic form of Hamiltonian systems, and thus maintain interpretability and physical consistency. After assessing KAR-HNN on four benchmark problems including spring-mass, simple pendulum, two- and three-body problem, we foresee its effectiveness for accurate and stable modeling of realistic physical processes often at high dimensions and with few known parameters.
An Iterative Framework for Generative Backmapping of Coarse Grained Proteins
May 23, 2025Abstract:The techniques of data-driven backmapping from coarse-grained (CG) to fine-grained (FG) representation often struggle with accuracy, unstable training, and physical realism, especially when applied to complex systems such as proteins. In this work, we introduce a novel iterative framework by using conditional Variational Autoencoders and graph-based neural networks, specifically designed to tackle the challenges associated with such large-scale biomolecules. Our method enables stepwise refinement from CG beads to full atomistic details. We outline the theory of iterative generative backmapping and demonstrate via numerical experiments the advantages of multistep schemes by applying them to proteins of vastly different structures with very coarse representations. This multistep approach not only improves the accuracy of reconstructions but also makes the training process more computationally efficient for proteins with ultra-CG representations.
Rethinking Benign Overfitting in Two-Layer Neural Networks
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Recent theoretical studies (Kou et al., 2023; Cao et al., 2022) have revealed a sharp phase transition from benign to harmful overfitting when the noise-to-feature ratio exceeds a threshold-a situation common in long-tailed data distributions where atypical data is prevalent. However, harmful overfitting rarely happens in overparameterized neural networks. Further experimental results suggested that memorization is necessary for achieving near-optimal generalization error in long-tailed data distributions (Feldman & Zhang, 2020). We argue that this discrepancy between theoretical predictions and empirical observations arises because previous feature-noise data models overlook the heterogeneous nature of noise across different data classes. In this paper, we refine the feature-noise data model by incorporating class-dependent heterogeneous noise and re-examine the overfitting phenomenon in neural networks. Through a comprehensive analysis of the training dynamics, we establish test loss bounds for the refined model. Our findings reveal that neural networks can leverage "data noise", previously deemed harmful, to learn implicit features that improve the classification accuracy for long-tailed data. Experimental validation on both synthetic and real-world datasets supports our theoretical results.
Safe Hybrid-Action Reinforcement Learning-Based Decision and Control for Discretionary Lane Change
Mar 01, 2024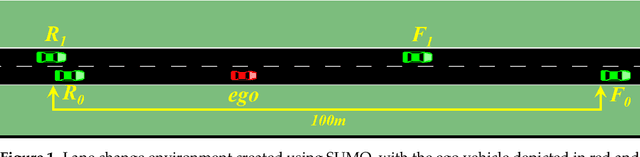
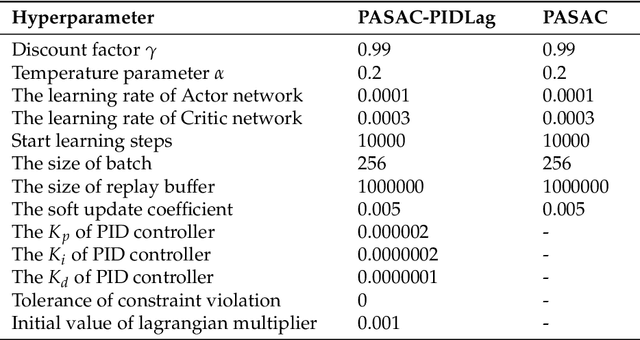
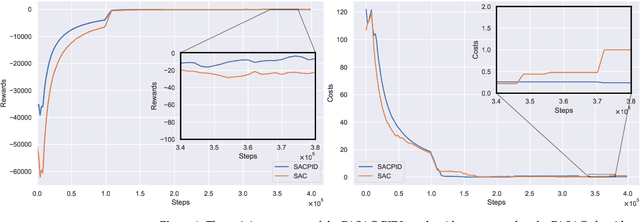
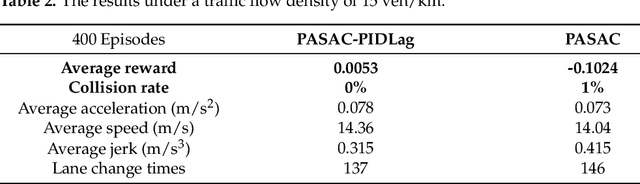
Abstract:Autonomous lane-change, a key feature of advanced driver-assistance systems, can enhance traffic efficiency and reduce the incidence of accidents. However, safe driving of autonomous vehicles remains challenging in complex environments. How to perform safe and appropriate lane change is a popular topic of research in the field of autonomous driving. Currently, few papers consider the safety of reinforcement learning in autonomous lane-change scenarios. We introduce safe hybrid-action reinforcement learning into discretionary lane change for the first time and propose Parameterized Soft Actor-Critic with PID Lagrangian (PASAC-PIDLag) algorithm. Furthermore, we conduct a comparative analysis of the Parameterized Soft Actor-Critic (PASAC), which is an unsafe version of PASAC-PIDLag. Both algorithms are employed to train the lane-change strategy of autonomous vehicles to output discrete lane-change decision and longitudinal vehicle acceleration. Our simulation results indicate that at a traffic density of 15 vehicles per kilometer (15 veh/km), the PASAC-PIDLag algorithm exhibits superior safety with a collision rate of 0%, outperforming the PASAC algorithm, which has a collision rate of 1%. The outcomes of the generalization assessments reveal that at low traffic density levels, both the PASAC-PIDLag and PASAC algorithms are proficient in attaining a 0% collision rate. Under conditions of high traffic flow density, the PASAC-PIDLag algorithm surpasses PASAC in terms of both safety and optimality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge