Rostyslav Hryniv
Towards realistic symmetry-based completion of previously unseen point clouds
Jan 05, 2022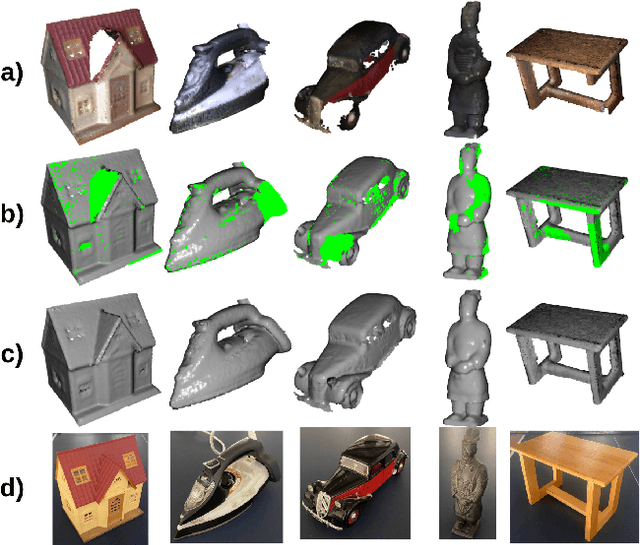
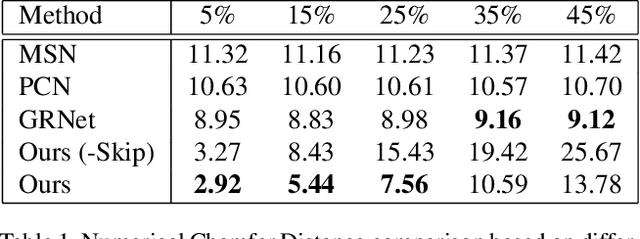
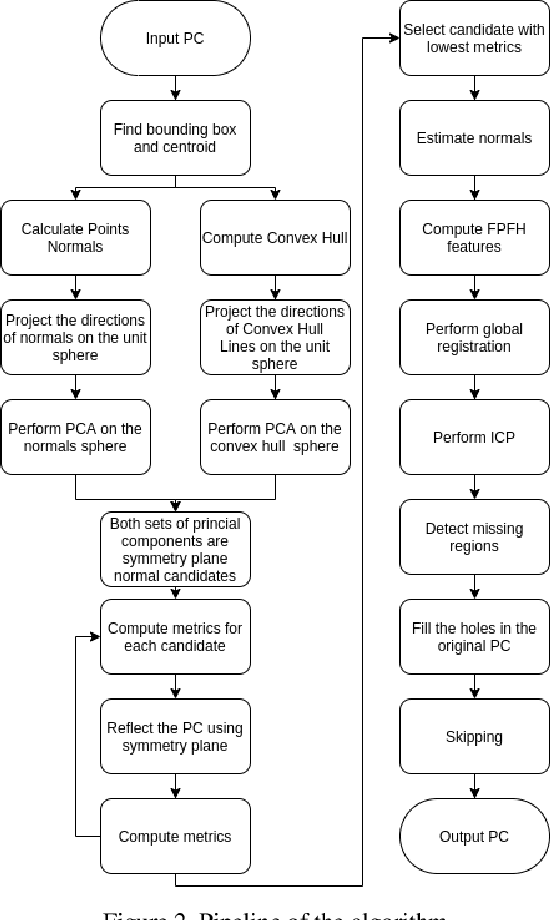
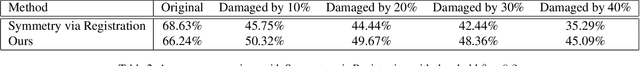
Abstract:3D scanning is a complex multistage process that generates a point cloud of an object typically containing damaged parts due to occlusions, reflections, shadows, scanner motion, specific properties of the object surface, imperfect reconstruction algorithms, etc. Point cloud completion is specifically designed to fill in the missing parts of the object and obtain its high-quality 3D representation. The existing completion approaches perform well on the academic datasets with a predefined set of object classes and very specific types of defects; however, their performance drops significantly in the real-world settings and degrades even further on previously unseen object classes. We propose a novel framework that performs well on symmetric objects, which are ubiquitous in man-made environments. Unlike learning-based approaches, the proposed framework does not require training data and is capable of completing non-critical damages occurring in customer 3D scanning process using e.g. Kinect, time-of-flight, or structured light scanners. With thorough experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art efficiency in point cloud completion of real-world customer scans. We benchmark the framework performance on two types of datasets: properly augmented existing academic dataset and the actual 3D scans of various objects.
Minimal Solvers for Single-View Lens-Distorted Camera Auto-Calibration
Nov 17, 2020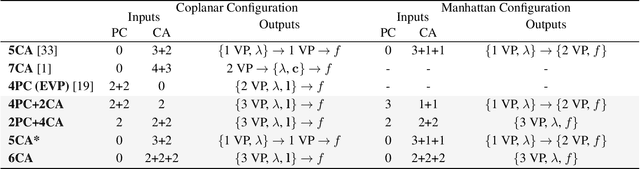
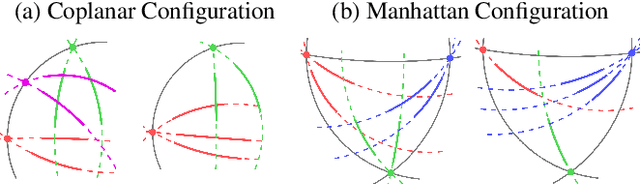
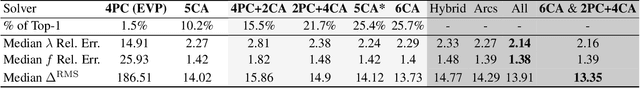
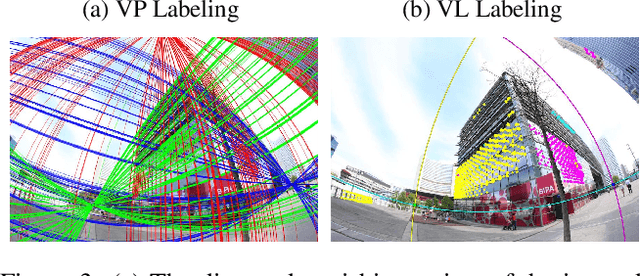
Abstract:This paper proposes minimal solvers that use combinations of imaged translational symmetries and parallel scene lines to jointly estimate lens undistortion with either affine rectification or focal length and absolute orientation. We use constraints provided by orthogonal scene planes to recover the focal length. We show that solvers using feature combinations can recover more accurate calibrations than solvers using only one feature type on scenes that have a balance of lines and texture. We also show that the proposed solvers are complementary and can be used together in a RANSAC-based estimator to improve auto-calibration accuracy. State-of-the-art performance is demonstrated on a standard dataset of lens-distorted urban images. The code is available at https://github.com/ylochman/single-view-autocalib.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge