Rong Xiang
VIALM: A Survey and Benchmark of Visually Impaired Assistance with Large Models
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:Visually Impaired Assistance (VIA) aims to automatically help visually impaired (VI) handle daily activities. The advancement of VIA primarily depends on developments in Computer Vision (CV) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), both of which exhibit cutting-edge paradigms with large models (LMs). Furthermore, LMs have shown exceptional multimodal abilities to tackle challenging physically-grounded tasks such as embodied robots. To investigate the potential and limitations of state-of-the-art (SOTA) LMs' capabilities in VIA applications, we present an extensive study for the task of VIA with LMs (\textbf{VIALM}). In this task, given an \textit{image} illustrating the physical environments and a \textit{linguistic request} from a VI user, VIALM aims to output step-by-step \textit{guidance} to assist the VI user in fulfilling the request grounded in the environment. The study consists of a survey reviewing recent LM research and benchmark experiments examining selected LMs' capabilities in VIA. The results indicate that while LMs can augment VIA, their output cannot be well \textit{grounded} in reality (i.e., 25.7\% GPT-4's responses) and lacks \textit{fine-grained} guidance (i.e., 32.1\% GPT-4's responses).
UniPoll: A Unified Social Media Poll Generation Framework via Multi-Objective Optimization
Jun 12, 2023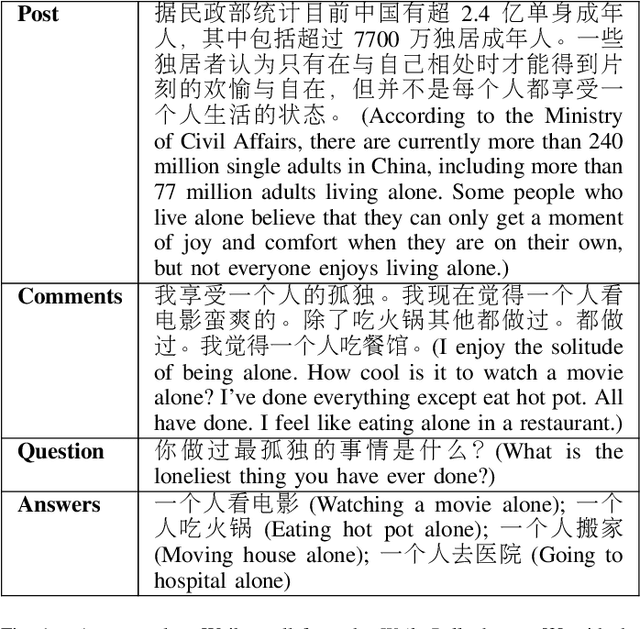
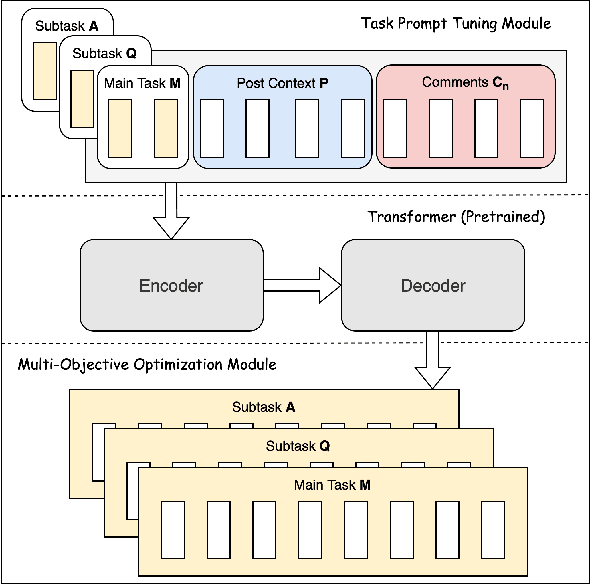

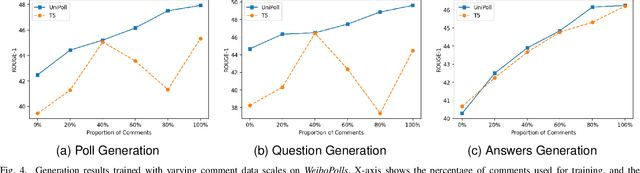
Abstract:Social media platforms are essential outlets for expressing opinions, providing a valuable resource for capturing public viewpoints via text analytics. However, for many users, passive browsing is their preferred mode of interaction, leading to their perspectives being overlooked by text analytics methods. Meanwhile, social media polls have emerged as a practical feature for gathering public opinions, allowing post authors to pose questions with pre-defined answer options for readers to vote on. To broaden the benefits of polls for posts without them, this article explores the automatic generation of a poll from a social media post by leveraging cutting-edge natural language generation (NLG) techniques. However, existing NLG techniques, primarily developed for general-domain texts, may be ineffective when applied to noisy social media data, which often feature implicit context-question-answer relations. To tackle these challenges, we enrich a post context with its comments and propose a novel unified poll generation framework called UniPoll. It employs prompt tuning with multi-objective optimization to bolster the connection exploration between contexts (posts and comments) and polls (questions and answers). Experimental comparisons on a large-scale Chinese Weibo dataset show that UniPoll significantly outperforms T5, the state-of-the-art NLG model, which generates question and answer separately. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative analyses further underscore the superiority of UniPoll through various evaluation lenses.
Dual Memory Network Model for Biased Product Review Classification
Sep 16, 2018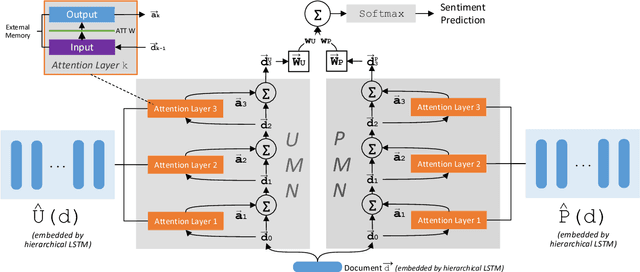
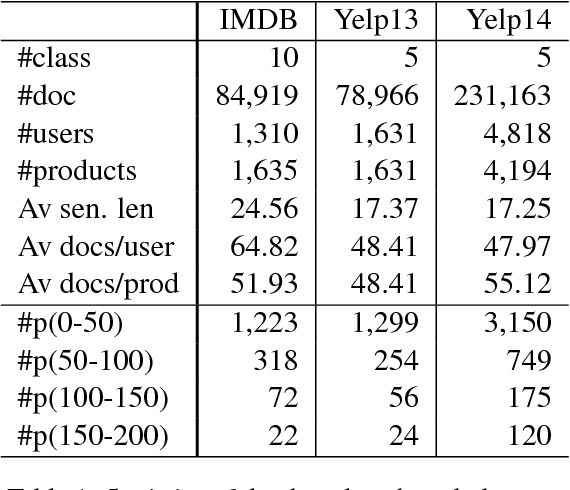
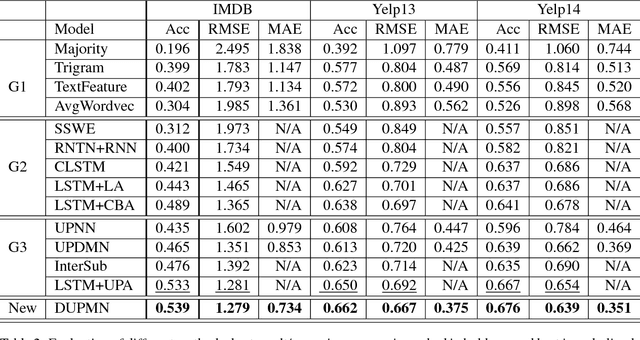

Abstract:In sentiment analysis (SA) of product reviews, both user and product information are proven to be useful. Current tasks handle user profile and product information in a unified model which may not be able to learn salient features of users and products effectively. In this work, we propose a dual user and product memory network (DUPMN) model to learn user profiles and product reviews using separate memory networks. Then, the two representations are used jointly for sentiment prediction. The use of separate models aims to capture user profiles and product information more effectively. Compared to state-of-the-art unified prediction models, the evaluations on three benchmark datasets, IMDB, Yelp13, and Yelp14, show that our dual learning model gives performance gain of 0.6%, 1.2%, and 0.9%, respectively. The improvements are also deemed very significant measured by p-values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge