Rogerio Schmidt Feris
Dialog-based Interactive Image Retrieval
Nov 01, 2018
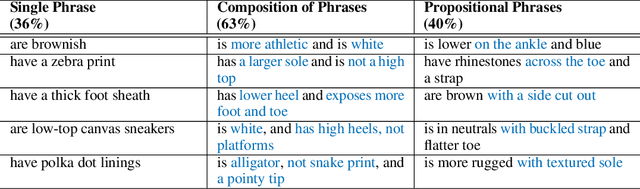
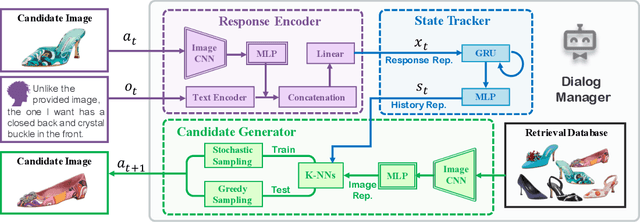
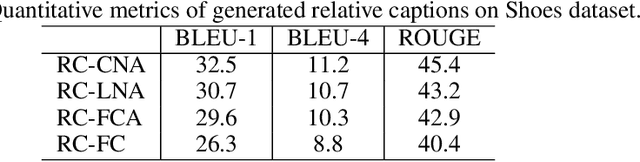
Abstract:Existing methods for interactive image retrieval have demonstrated the merit of integrating user feedback, improving retrieval results. However, most current systems rely on restricted forms of user feedback, such as binary relevance responses, or feedback based on a fixed set of relative attributes, which limits their impact. In this paper, we introduce a new approach to interactive image search that enables users to provide feedback via natural language, allowing for more natural and effective interaction. We formulate the task of dialog-based interactive image retrieval as a reinforcement learning problem, and reward the dialog system for improving the rank of the target image during each dialog turn. To mitigate the cumbersome and costly process of collecting human-machine conversations as the dialog system learns, we train our system with a user simulator, which is itself trained to describe the differences between target and candidate images. The efficacy of our approach is demonstrated in a footwear retrieval application. Experiments on both simulated and real-world data show that 1) our proposed learning framework achieves better accuracy than other supervised and reinforcement learning baselines and 2) user feedback based on natural language rather than pre-specified attributes leads to more effective retrieval results, and a more natural and expressive communication interface.
Walk and Learn: Facial Attribute Representation Learning from Egocentric Video and Contextual Data
Jun 22, 2016
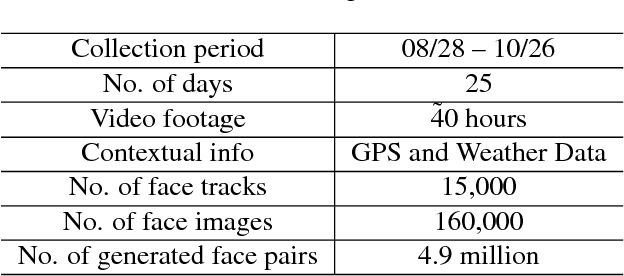
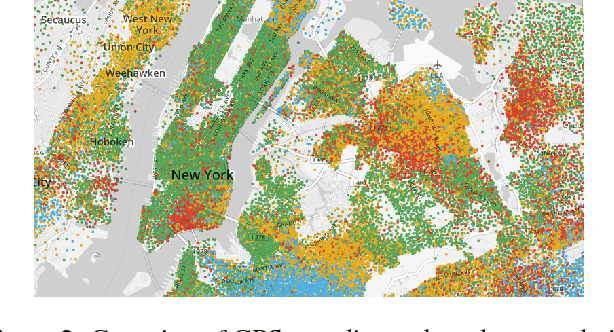
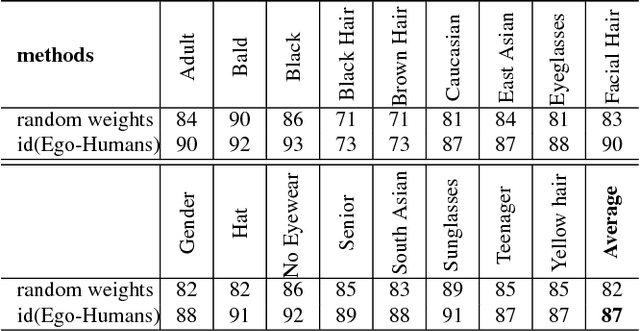
Abstract:The way people look in terms of facial attributes (ethnicity, hair color, facial hair, etc.) and the clothes or accessories they wear (sunglasses, hat, hoodies, etc.) is highly dependent on geo-location and weather condition, respectively. This work explores, for the first time, the use of this contextual information, as people with wearable cameras walk across different neighborhoods of a city, in order to learn a rich feature representation for facial attribute classification, without the costly manual annotation required by previous methods. By tracking the faces of casual walkers on more than 40 hours of egocentric video, we are able to cover tens of thousands of different identities and automatically extract nearly 5 million pairs of images connected by or from different face tracks, along with their weather and location context, under pose and lighting variations. These image pairs are then fed into a deep network that preserves similarity of images connected by the same track, in order to capture identity-related attribute features, and optimizes for location and weather prediction to capture additional facial attribute features. Finally, the network is fine-tuned with manually annotated samples. We perform an extensive experimental analysis on wearable data and two standard benchmark datasets based on web images (LFWA and CelebA). Our method outperforms by a large margin a network trained from scratch. Moreover, even without using manually annotated identity labels for pre-training as in previous methods, our approach achieves results that are better than the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge