Robert Lewis
Improving Domain Generalization in Contrastive Learning using Adaptive Temperature Control
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training with contrastive learning is a powerful method for learning from sparsely labeled data. However, performance can drop considerably when there is a shift in the distribution of data from training to test time. We study this phenomenon in a setting in which the training data come from multiple domains, and the test data come from a domain not seen at training that is subject to significant covariate shift. We present a new method for contrastive learning that incorporates domain labels to increase the domain invariance of learned representations, leading to improved out-of-distribution generalization. Our method adjusts the temperature parameter in the InfoNCE loss -- which controls the relative weighting of negative pairs -- using the probability that a negative sample comes from the same domain as the anchor. This upweights pairs from more similar domains, encouraging the model to discriminate samples based on domain-invariant attributes. Through experiments on a variant of the MNIST dataset, we demonstrate that our method yields better out-of-distribution performance than domain generalization baselines. Furthermore, our method maintains strong in-distribution task performance, substantially outperforming baselines on this measure.
Computational Empathy Counteracts the Negative Effects of Anger on Creative Problem Solving
Aug 15, 2022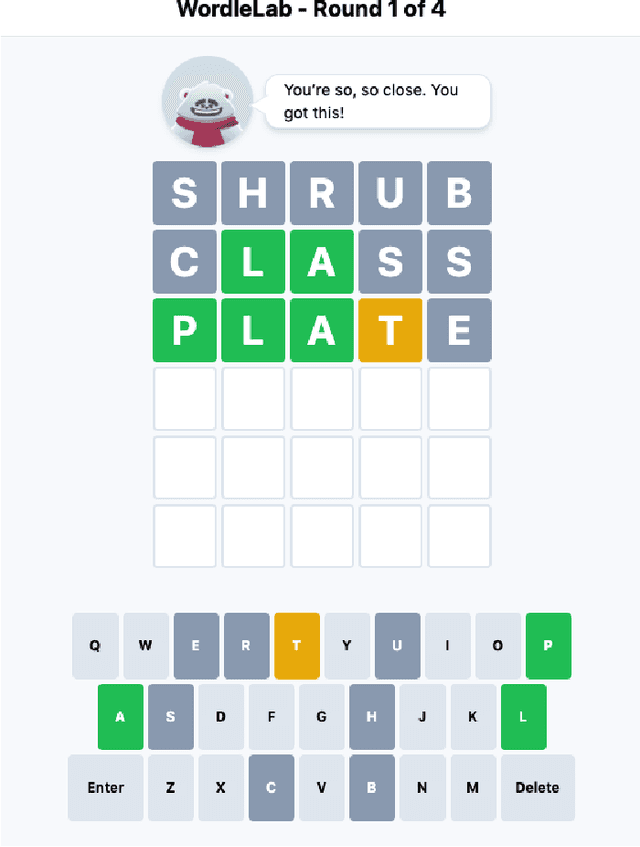

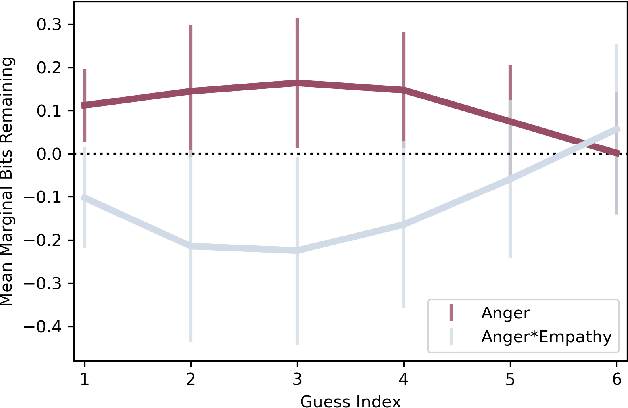
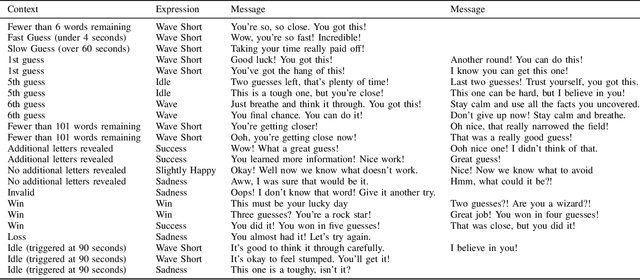
Abstract:How does empathy influence creative problem solving? We introduce a computational empathy intervention based on context-specific affective mimicry and perspective taking by a virtual agent appearing in the form of a well-dressed polar bear. In an online experiment with 1,006 participants randomly assigned to an emotion elicitation intervention (with a control elicitation condition and anger elicitation condition) and a computational empathy intervention (with a control virtual agent and an empathic virtual agent), we examine how anger and empathy influence participants' performance in solving a word game based on Wordle. We find participants who are assigned to the anger elicitation condition perform significantly worse on multiple performance metrics than participants assigned to the control condition. However, we find the empathic virtual agent counteracts the drop in performance induced by the anger condition such that participants assigned to both the empathic virtual agent and the anger condition perform no differently than participants in the control elicitation condition and significantly better than participants assigned to the control virtual agent and the anger elicitation condition. While empathy reduces the negative effects of anger, we do not find evidence that the empathic virtual agent influences performance of participants who are assigned to the control elicitation condition. By introducing a framework for computational empathy interventions and conducting a two-by-two factorial design randomized experiment, we provide rigorous, empirical evidence that computational empathy can counteract the negative effects of anger on creative problem solving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge