Robert J. Full
Ultra-fast, programmable, and electronics-free soft robots enabled by snapping metacaps
Oct 28, 2022Abstract:Soft robots have a myriad of potentials because of their intrinsically compliant bodies, enabling safe interactions with humans and adaptability to unpredictable environments. However, most of them have limited actuation speeds, require complex control systems, and lack sensing capabilities. To address these challenges, here we geometrically design a class of metacaps whose rich nonlinear mechanical behaviors can be harnessed to create soft robots with unprecedented functionalities. Specifically, we demonstrate a sensor-less metacap gripper that can grasp objects in 3.75 ms upon physical contact and a pneumatically actuated gripper with tunable actuation behaviors that have little dependence on the rate of input. Both grippers can be readily integrated into a robotic platform for practical applications. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the metacap enables propelling of a swimming robot, exhibiting amplified swimming speed as well as untethered, electronics-free swimming with tunable speeds. Our metacaps provide new strategies to design the next-generation soft robots that require high transient output energy and are capable of autonomous and electronics-free maneuvering.
Mechanical principles of dynamic terrestrial self-righting using wings
Mar 17, 2021Abstract:Terrestrial animals and robots are susceptible to flipping-over during rapid locomotion in complex terrains. However, small robots are less capable of self-righting from an upside-down orientation compared to small animals like insects. Inspired by the winged discoid cockroach, we designed a new robot that opens its wings to self-right by pushing against the ground. We used this robot to systematically test how self-righting performance depends on wing opening magnitude, speed, and asymmetry, and modeled how kinematic and energetic requirements depend on wing shape and body/wing mass distribution. We discovered that the robot self-rights dynamically using kinetic energy to overcome potential energy barriers, that larger and faster symmetric wing opening increases self-righting performance, and that opening wings asymmetrically increases righting probability when wing opening is small. Our results suggested that the discoid cockroach's winged self-righting is a dynamic maneuver. While the thin, lightweight wings of the discoid cockroach and our robot are energetically sub-optimal for self-righting compared to tall, heavy ones, their ability to open wings saves them substantial energy compared to if they had static shells. Analogous to biological exaptations, our study provided a proof-of-concept for terrestrial robots to use existing morphology in novel ways to overcome new locomotor challenges.
Comparative Design, Scaling, and Control of Appendages for Inertial Reorientation
Feb 18, 2017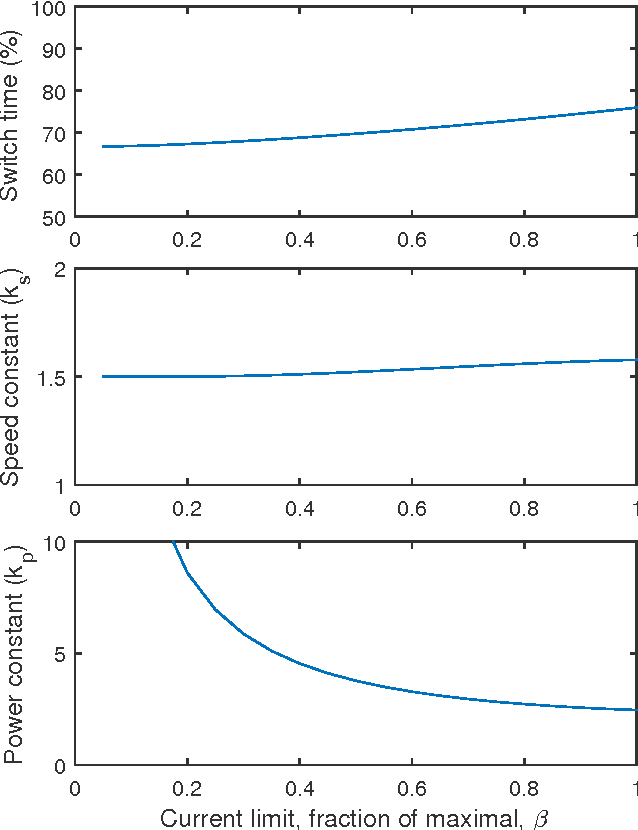
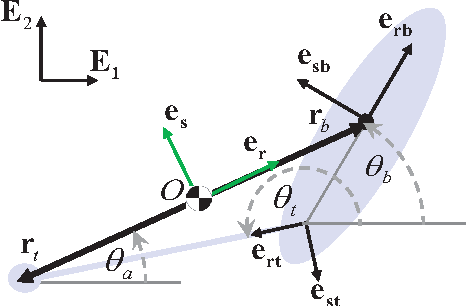
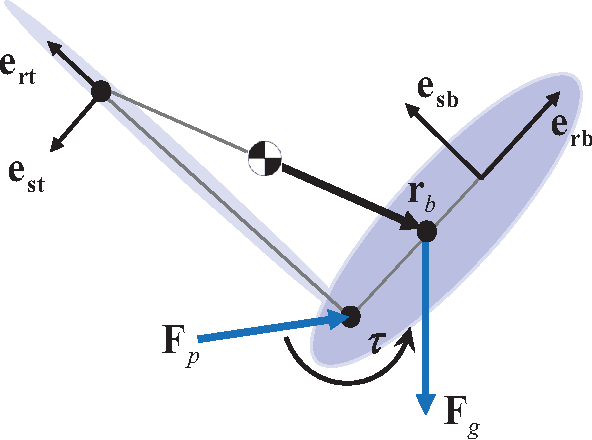
Abstract:This paper develops a comparative framework for the design of actuated inertial appendages for planar, aerial reorientation. We define the Inertial Reorientation template, the simplest model of this behavior, and leverage its linear dynamics to reveal the design constraints linking a task with the body designs capable of completing it. As practicable inertial appendage designs lead to morphology that is generally more complex, we advance a notion of "anchoring" whereby a judicious choice of physical design in concert with an appropriate control policy yields a system whose closed loop dynamics are sufficiently captured by the template as to permit all further design to take place in its far simpler parameter space. This approach is effective and accurate over the diverse design spaces afforded by existing platforms, enabling performance comparison through the shared task space. We analyze examples from the literature and find advantages to each body type, but conclude that tails provide the highest potential performance for reasonable designs. Thus motivated, we build a physical example by retrofitting a tail to a RHex robot and present empirical evidence of its efficacy.
* Technical report included at the end of this file
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge