Robert Gieselmann
Fast-dRRT*: Efficient Multi-Robot Motion Planning for Automated Industrial Manufacturing
Sep 19, 2023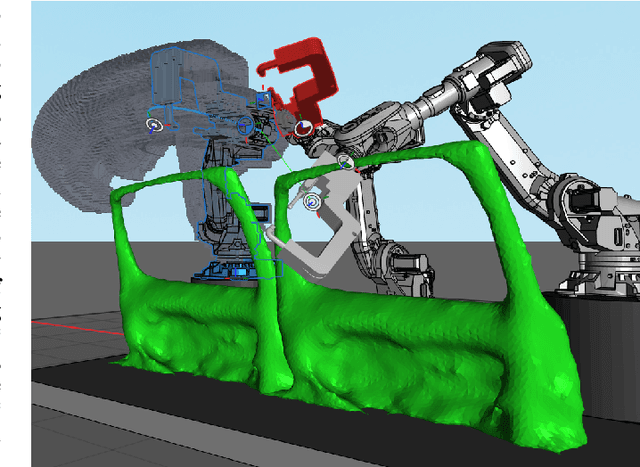
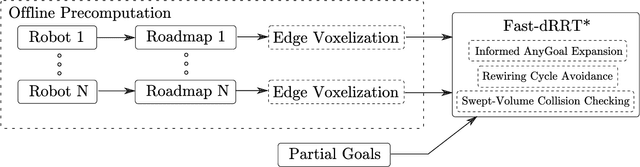
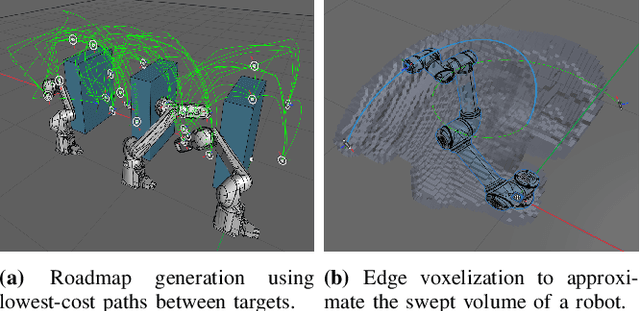
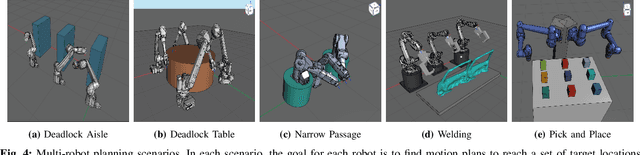
Abstract:We present Fast-dRRT*, a sampling-based multi-robot planner, for real-time industrial automation scenarios. Fast-dRRT* builds upon the discrete rapidly-exploring random tree (dRRT*) planner, and extends dRRT* by using pre-computed swept volumes for efficient collision detection, deadlock avoidance for partial multi-robot problems, and a simplified rewiring strategy. We evaluate Fast-dRRT* on five challenging multi-robot scenarios using two to four industrial robot arms from various manufacturers. The scenarios comprise situations involving deadlocks, narrow passages, and close proximity tasks. The results are compared against dRRT*, and show Fast-dRRT* to outperform dRRT* by up to 94% in terms of finding solutions within given time limits, while only sacrificing up to 35% on initial solution cost. Furthermore, Fast-dRRT* demonstrates resilience against noise in target configurations, and is able to solve challenging welding, and pick and place tasks with reduced computational time. This makes Fast-dRRT* a promising option for real-time motion planning in industrial automation.
Experience-Based Heuristic Search: Robust Motion Planning with Deep Q-Learning
Feb 05, 2021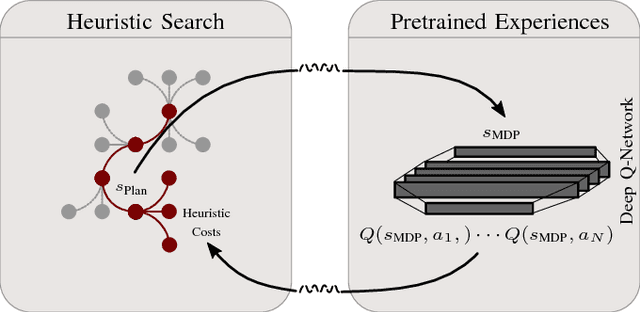
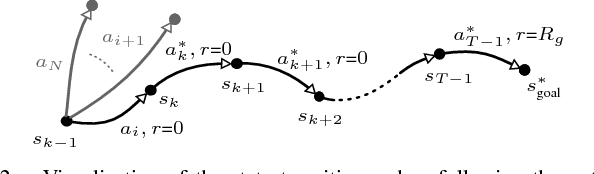
Abstract:Interaction-aware planning for autonomous driving requires an exploration of a combinatorial solution space when using conventional search- or optimization-based motion planners. With Deep Reinforcement Learning, optimal driving strategies for such problems can be derived also for higher-dimensional problems. However, these methods guarantee optimality of the resulting policy only in a statistical sense, which impedes their usage in safety critical systems, such as autonomous vehicles. Thus, we propose the Experience-Based-Heuristic-Search algorithm, which overcomes the statistical failure rate of a Deep-reinforcement-learning-based planner and still benefits computationally from the pre-learned optimal policy. Specifically, we show how experiences in the form of a Deep Q-Network can be integrated as heuristic into a heuristic search algorithm. We benchmark our algorithm in the field of path planning in semi-structured valet parking scenarios. There, we analyze the accuracy of such estimates and demonstrate the computational advantages and robustness of our method. Our method may encourage further investigation of the applicability of reinforcement-learning-based planning in the field of self-driving vehicles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge