Robert Calderbank
Duke University
A Universal Neural Receiver that Learns at the Speed of Wireless
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:Today we design wireless networks using mathematical models that govern communication in different propagation environments. We rely on measurement campaigns to deliver parametrized propagation models, and on the 3GPP standards process to optimize model-based performance, but as wireless networks become more complex this model-based approach is losing ground. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are counting on Artificial Intelligence (AI) to transform wireless by increasing spectral efficiency, reducing signaling overhead, and enabling continuous network innovation through software upgrades. They may also be interested in new use cases like integrated sensing and communications (ISAC). All we need is an AI-native physical layer, so why not simply tailor the offline AI algorithms that have revolutionized image and natural language processing to the wireless domain? We argue that these algorithms rely on off-line training that is precluded by the sub-millisecond speeds at which the wireless interference environment changes. We present an alternative architecture, a universal neural receiver based on convolution, which governs transmit and receive signal processing of any signal in any part of the wireless spectrum. Our neural receiver is designed to invert convolution, and we separate the question of which convolution to invert from the actual deconvolution. The neural network that performs deconvolution is very simple, and we configure this network by setting weights based on domain knowledge. By telling our neural network what we know, we avoid extensive offline training. By developing a universal receiver, we hope to simplify discussions about the proper choice of waveform for different use cases in the international standards. Since the receiver architecture is largely independent of technologies introduced at the base station, we hope to increase the rate of innovation in wireless.
Does 6G Need a New Waveform: Comparing Zak-OTFS with CP-OFDM
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Across the world, there is growing interest in new waveforms, Zak-OTFS in particular, and over-the-air implementations are starting to appear. The choice between OFDM and Zak-OTFS is not so much a choice between waveforms as it is an architectural choice between preventing inter-carrier interference (ICI) and embracing ICI. In OFDM, once the Input-Output (I/O) relation is known, equalization is relatively simple, at least when there is no ICI. However, in the presence of ICI the I/O relation is non-predictable and its acquisition is non-trivial. In contrast, equalization is more involved in Zak-OTFS due to inter-symbol-interference (ISI), however the I/O relation is predictable and its acquisition is simple. {Zak-OTFS exhibits superior performance in doubly-spread 6G use cases with high delay/Doppler channel spreads (i.e., high mobility and/or large cells), but architectural choice is governed by the typical use case, today and in the future. What is typical depends to some degree on geography, since large delay spread is a characteristic of large cells which are the rule rather than the exception in many important wireless markets.} This paper provides a comprehensive performance comparison of cyclic prefix OFDM (CP-OFDM) and Zak-OTFS across the full range of 6G propagation environments. The performance results provide insights into the fundamental architectural choice.
Equivalence of Several 6G Modulation Schemes for Doubly-Selective Channels
Nov 12, 2025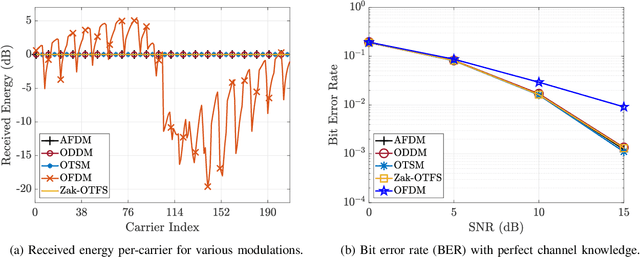
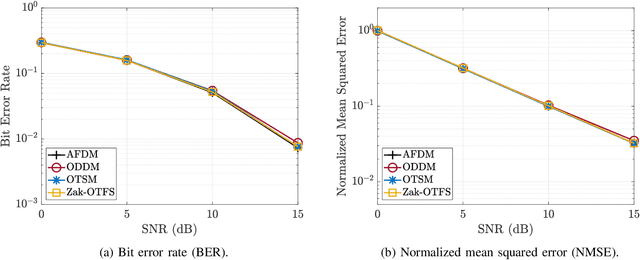
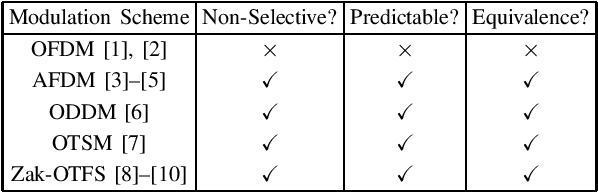
Abstract:There is significant recent interest in designing new modulation schemes for doubly-selective channels with large delay and Doppler spreads, where legacy modulation schemes based on time-frequency signal representations do not perform well. In this paper, we develop a framework for analyzing such modulations using two characteristics -- non-selectivity and predictability -- which directly relate to the diversity and spectral efficiency that the modulations achieve. We show that modulations in the delay-Doppler, chirp and time-sequency domains are non-selective, predictable and equivalent to one another, whereas time-frequency modulations are selective and non-predictable.
Over-the-Air Transmission of Zak-OTFS on mmWave Communications Testbed
Nov 10, 2025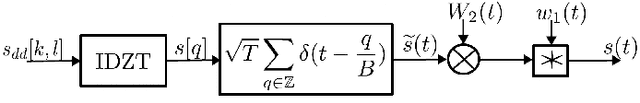
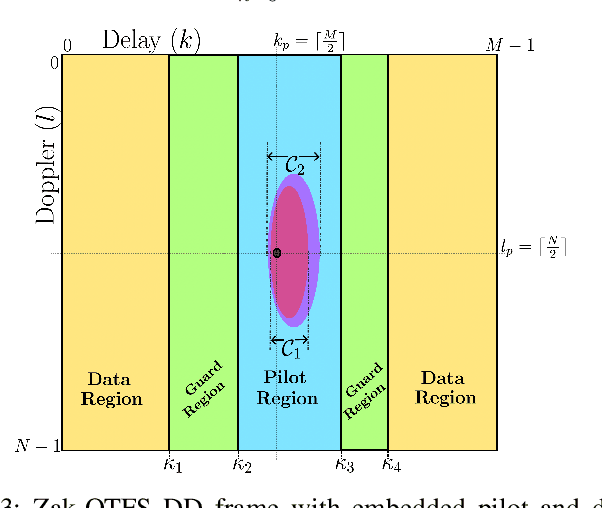
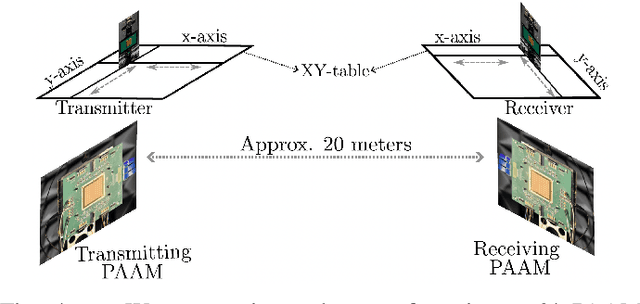
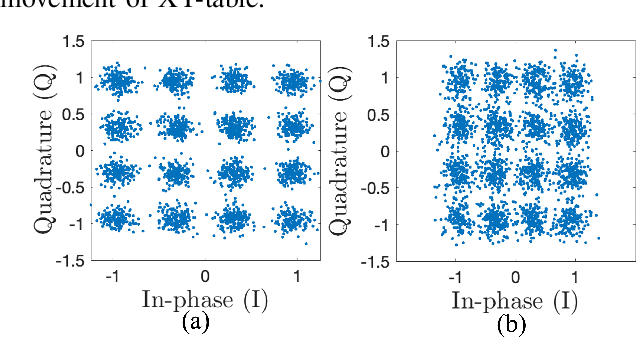
Abstract:Millimeter-wave (mmWave) communication offers vast bandwidth for next-generation wireless systems but faces severe path loss, Doppler effects, and hardware impairments. Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a robust waveform for high-mobility and doubly dispersive channels, outperforming OFDM under strong Doppler. However, the most studied multicarrier OTFS (MC-OTFS) is not easily predictable because the input-output (I$/$O) relation is not given by (twisted) convolution. Recently, the Zak-transform based OTFS (Zak-OTFS or OTFS 2$.$0) was proposed, which provides a single domain delay Doppler (DD) processing framework with predictable I$/$O behavior. This paper presents one of the first over-the-air (OTA) demonstrations of Zak-OTFS at mmWave frequencies. We design a complete Zak-OTFS based mmWave OTA system featuring root-raised-cosine (RRC) filtering for enhanced DD-domain predictability, higher-order modulations up to 16-QAM, and a low-overhead preamble for synchronization. A comprehensive signal model incorporating carrier frequency offset (CFO) and timing impairments is developed, showing these effects can be jointly captured within the effective DD-domain channel. Experimental validation on the COSMOS testbed confirms the feasibility and robustness of Zak-OTFS under realistic mmWave conditions, highlighting its potential for efficient implementations in beyond-5G and 6G systems.
Instantaneous Polarimetry with Zak-OTFS
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Polarimetry, which is the ability to measure the scattering response of the environment across orthogonal polarizations, is fundamental to enhancing wireless communication and radar system performance. In this paper, we utilize the Zak-OTFS modulation to enable instantaneous polarimetry within a single transmission frame. We transmit a Zak-OTFS carrier waveform and a spread carrier waveform mutually unbiased to it simultaneously over orthogonal polarizations. The mutual unbiasedness of the two waveforms enables the receiver to estimate the full polarimetric response of the scattering environment from a single received frame. Unlike existing methods for instantaneous polarimetry with computational complexity quadratic in the time-bandwidth product, the proposed method enables instantaneous polarimetry at complexity that is only sublinear in the time-bandwidth product. Via numerical simulations, we show ideal polarimetric target detection and parameter estimation results with the proposed method, with improvements in performance and computational complexity over comparable baselines.
Low-Complexity Equalization of Zak-OTFS in the Frequency Domain
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:4G/5G wireless standards use orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) which is robust to frequency selectivity. Equalization is possible with a single tap filter, and low-complexity equalization makes OFDM an attractive physical layer. However the performance of OFDM degrades with mobility, since Doppler spreads introduce inter-carrier interference (ICI) between subcarriers and they are no longer orthogonal. Zak-transform based orthogonal time frequency space (Zak-OTFS) modulation has been shown to be robust to doubly selective channels. Zak-OTFS signals are formed in the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, converted to time domain (TD) for transmission and reception, then returned to the DD domain for processing. The received signal is a superposition of many attenuated copies since the doubly selective channel introduces delay and Doppler shifts. The received symbols are more difficult to equalize since they are subject to interference along both delay and Doppler axes. In this paper, we propose a new low-complexity method of equalizing Zak-OTFS in the frequency domain (FD). We derive the FD system model and show that it is unitarily equivalent to the DD system model. We show that the channel matrix in the FD is banded, making it possible to apply conjugate gradient methods to reduce the complexity of equalization. We show that complexity of FD equalization is linear in the dimension of a Zak-OTFS frame. For comparison the complexity of naive MMSE equalization is cubic in the frame dimension. Through numerical simulations we show that FD equalization of Zak-OTFS achieves similar performance as equalization in DD domain.
Zak-OTFS over CP-OFDM
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Zak-Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (Zak-OTFS) modulation has been shown to achieve significantly better performance compared to the standardized Cyclic-Prefix Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (CP-OFDM), in high delay/Doppler spread scenarios envisaged in next generation communication systems. Zak-OTFS carriers are quasi-periodic pulses in the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, characterized by two parameters, (i) the pulse period along the delay axis (``delay period") (Doppler period is related to the delay period), and (ii) the pulse shaping filter. An important practical challenge is enabling support for Zak-OTFS modulation in existing CP-OFDM based modems. In this paper we show that Zak-OTFS modulation with pulse shaping constrained to sinc filtering (filter bandwidth equal to the communication bandwidth $B$) followed by time-windowing with a rectangular window of duration $(T + T_{cp})$ ($T$ is the symbol duration and $T_{cp}$ is the CP duration), can be implemented as a low-complexity precoder over standard CP-OFDM. We also show that the Zak-OTFS de-modulator with matched filtering constrained to sinc filtering (filter bandwidth $B$) followed by rectangular time windowing over duration $T$ can be implemented as a low-complexity post-processing of the CP-OFDM de-modulator output. This proposed ``Zak-OTFS over CP-OFDM" architecture enables us to harness the benefits of Zak-OTFS in existing network infrastructure. We also show that the proposed Zak-OTFS over CP-OFDM is a family of modulations, with CP-OFDM being a special case when the delay period takes its minimum possible value equal to the inverse bandwidth, i.e., Zak-OTFS over CP-OFDM with minimum delay period.
Zak-OTFS Based Coded Random Access for Uplink mMTC
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a grant-free coded random access (CRA) scheme for uplink massive machine-type communications (mMTC), based on Zak-orthogonal time frequency space (Zak-OTFS) modulation in the delay-Doppler domain. The scheme is tailored for doubly selective wireless channels, where conventional orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)-based CRA suffers from unreliable inter-slot channel prediction due to time-frequency variability. By exploiting the predictable nature of Zak-OTFS, the proposed approach enables accurate channel estimation across slots, facilitating reliable successive interference cancellation across user packet replicas. A fair comparison with an OFDM-based CRA baseline shows that the proposed scheme achieves significantly lower packet loss rates under high mobility and user density. Extensive simulations over the standardized Veh-A channel confirm the robustness and scalability of Zak-OTFS-based CRA, supporting its applicability to future mMTC deployments.
Waveform for Next Generation Communication Systems: Comparing Zak-OTFS with OFDM
May 20, 2025

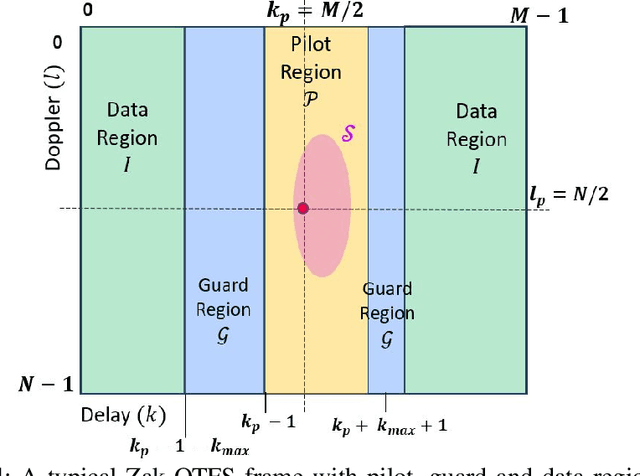
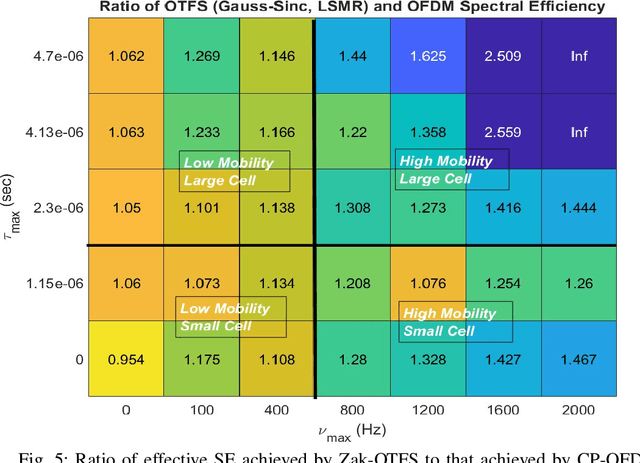
Abstract:Across the world, there is growing interest in new waveforms, Zak-OTFS in particular, and over-the-air implementations are starting to appear. The choice between OFDM and Zak-OTFS is not so much a choice between waveforms as it is an architectural choice between preventing inter-carrier interference (ICI) and embracing ICI. In OFDM, once the Input-Output (I/O) relation is known, equalization is relatively simple, at least when there is no ICI. However, in the presence of ICI the I/O relation is non-predictable and its acquisition is non-trivial. In contrast, equalization is more involved in Zak-OTFS due to inter-symbol-interference (ISI), however the I/O relation is predictable and its acquisition is simple. {Zak-OTFS exhibits superior performance in doubly-spread 6G use cases with high delay/Doppler channel spreads (i.e., high mobility and/or large cells), but architectural choice is governed by the typical use case, today and in the future. What is typical depends to some degree on geography, since large delay spread is a characteristic of large cells which are the rule rather than the exception in many important wireless markets.} This paper provides a comprehensive performance comparison of cyclic prefix OFDM (CP-OFDM) and Zak-OTFS across the full range of 6G propagation environments. The performance results provide insights into the fundamental architectural choice.
Zak-OTFS for Spread Spectrum Communication
May 12, 2025Abstract:An attractive feature of spread spectrum technologies such as code division multiple access (CDMA) is that it is harder to intercept or jam signals, and this feature was lost when orthogonal frequency domain modulation prevailed over CDMA in wireless standards. Legacy spread carrier waveforms are not matched to delay and Doppler shifts characteristic of 6G wireless environments, and this makes equalization very challenging. Zak-OTFS modulation is a communication framework that parameterizes the wireless channel in the delay-Doppler (DD) domain, where the parameters map directly to physical attributes of the scatterers that comprise the scattering environment. Hence, the channel can be efficiently acquired and equalized. The Zak-OTFS carrier is a pulse in the DD domain, and the Zak transform converts it to a pulse train modulated by a tone (pulsone) in the time domain. The pulsone waveform is localized rather than spread, and it suffers from high PAPR. We describe how to transform Zak-OTFS into a spread spectrum communication system, where the spread carrier waveforms have low PAPR and are matched to the delay and Doppler characteristics of the wireless channel. This transformation is realized by a unitary transform that is a generalization of the discrete affine Fourier transform. The transform maps a pulsone to a time domain waveform which yields a CAZAC sequence after sampling. The family of CAZAC sequences includes the Zadoff-Chu sequences incorporated in LTE and 5G-NR standards. We describe the end-to-end time-domain transceiver signal processing, comprising channel estimation and data demodulation, for the proposed system. We quantify system performance through BER simulations using a six-path Veh-A channel model, showing that the proposed system achieves similar uncoded BER as pulsone-based Zak-OTFS, where the PAPR of each spread carrier waveform is only 3.58 dB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge