Reyhan Kevser Keser
Focus-and-Detect: A Small Object Detection Framework for Aerial Images
Mar 24, 2022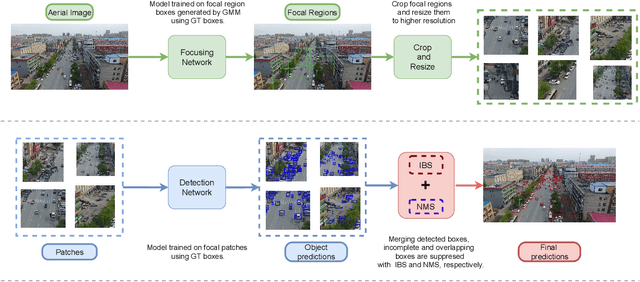
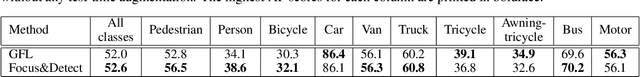
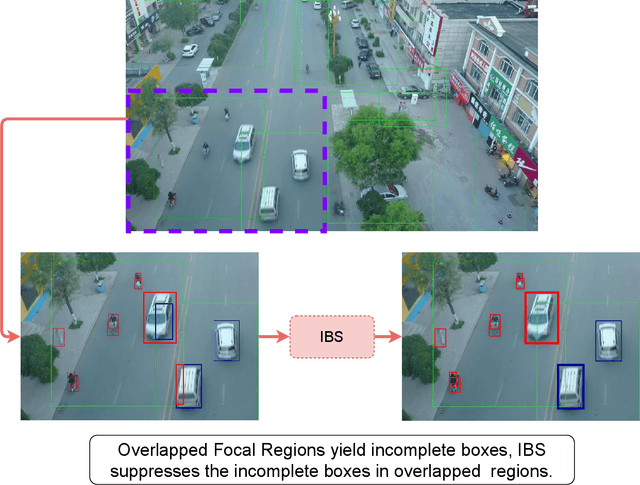
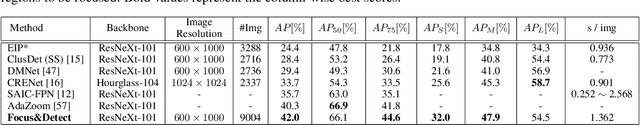
Abstract:Despite recent advances, object detection in aerial images is still a challenging task. Specific problems in aerial images makes the detection problem harder, such as small objects, densely packed objects, objects in different sizes and with different orientations. To address small object detection problem, we propose a two-stage object detection framework called "Focus-and-Detect". The first stage which consists of an object detector network supervised by a Gaussian Mixture Model, generates clusters of objects constituting the focused regions. The second stage, which is also an object detector network, predicts objects within the focal regions. Incomplete Box Suppression (IBS) method is also proposed to overcome the truncation effect of region search approach. Results indicate that the proposed two-stage framework achieves an AP score of 42.06 on VisDrone validation dataset, surpassing all other state-of-the-art small object detection methods reported in the literature, to the best of authors' knowledge.
* 12 pages, 6 figures
Representation Learning using Graph Autoencoders with Residual Connections
May 03, 2021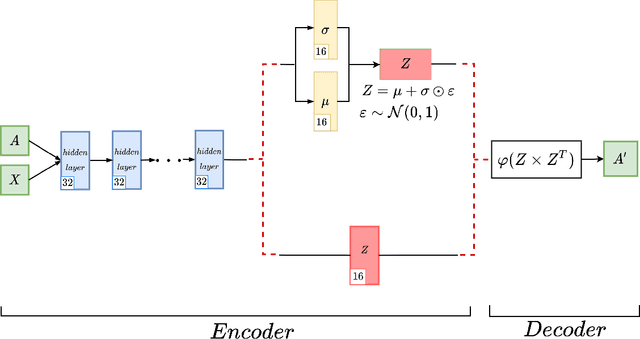
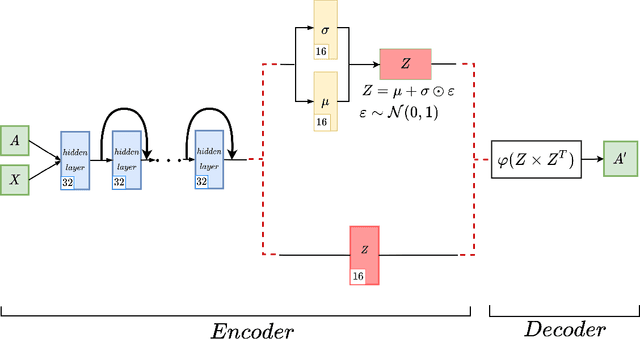
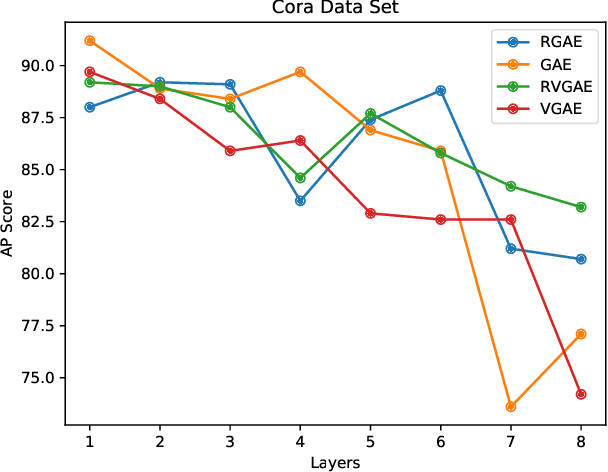
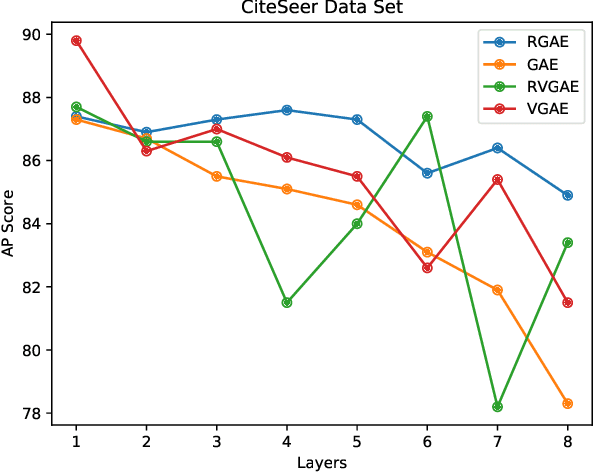
Abstract:Graph autoencoders are very efficient at embedding graph-based complex data sets. However, most of the autoencoders have shallow depths and their efficiency tends to decrease with the increase of layer depth. In this paper, we study the effect of adding residual connections to shallow and deep graph variational and vanilla autoencoders. We show that residual connections improve the accuracy of the deep graph-based autoencoders. Furthermore, we propose Res-VGAE, a graph variational autoencoder with different residual connections. Our experiments show that our model achieves superior results when compared with other autoencoder-based models for the link prediction task.
PURSUhInT: In Search of Informative Hint Points Based on Layer Clustering for Knowledge Distillation
Feb 26, 2021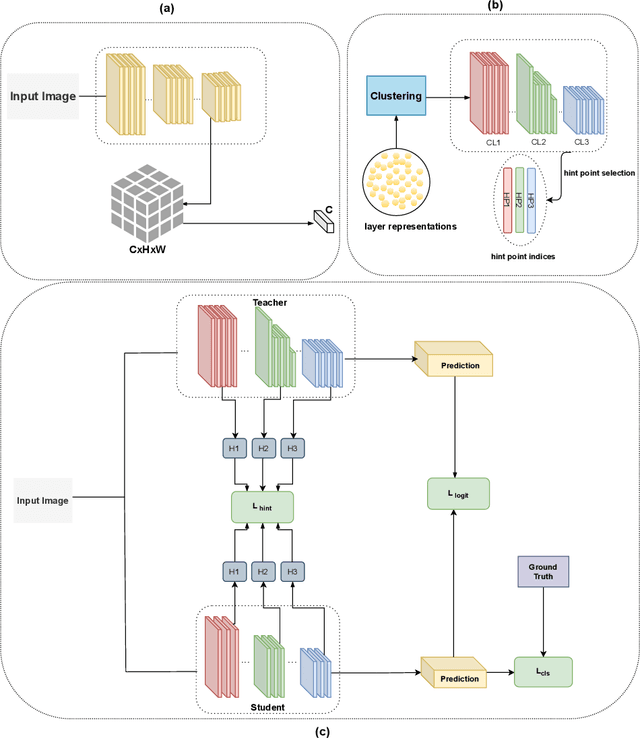
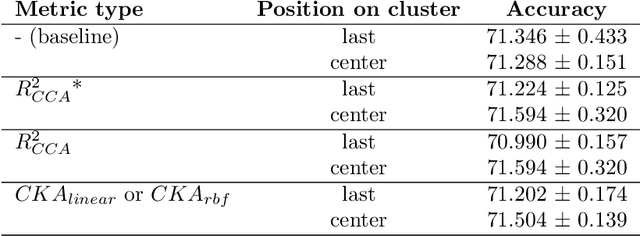
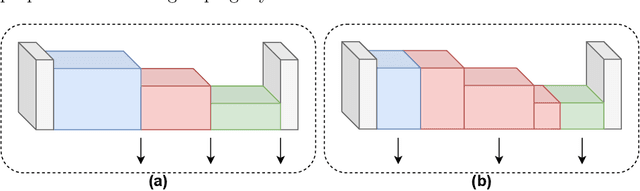
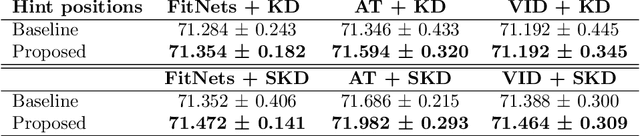
Abstract:We propose a novel knowledge distillation methodology for compressing deep neural networks. One of the most efficient methods for knowledge distillation is hint distillation, where the student model is injected with information (hints) from several different layers of the teacher model. Although the selection of hint points can drastically alter the compression performance, there is no systematic approach for selecting them, other than brute-force hyper-parameter search. We propose a clustering based hint selection methodology, where the layers of teacher model are clustered with respect to several metrics and the cluster centers are used as the hint points. The proposed approach is validated in CIFAR-100 dataset, where ResNet-110 network was used as the teacher model. Our results show that hint points selected by our algorithm results in superior compression performance with respect to state-of-the-art knowledge distillation algorithms on the same student models and datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge