Raymond Wong
High-dimensional Regret Minimization
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Multi-criteria decision making in large databases is very important in real world applications. Recently, an interactive query has been studied extensively in the database literature with the advantage of both the top-k query (with limited output size) and the skyline query (which does not require users to explicitly specify their preference function). This approach iteratively asks the user to select the one preferred within a set of options. Based on rounds of feedback, the query learns the implicit preference and returns the most favorable as a recommendation. However, many modern applications in areas like housing or financial product markets feature datasets with hundreds of attributes. Existing interactive algorithms either fail to scale or require excessive user interactions (often exceeding 1000 rounds). Motivated by this, we propose FHDR (Fast High-Dimensional Reduction), a novel framework that takes less than 0.01s with fewer than 30 rounds of interaction. It is considered a breakthrough in the field of interactive queries since most, if not all, existing studies are not scalable to high-dimensional datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FHDR outperforms the best-known algorithms by at least an order of magnitude in execution time and up to several orders of magnitude in terms of the number of interactions required, establishing a new state of the art for scalable interactive regret minimization.
From Surface to Semantics: Semantic Structure Parsing for Table-Centric Document Analysis
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Documents are core carriers of information and knowl-edge, with broad applications in finance, healthcare, and scientific research. Tables, as the main medium for structured data, encapsulate key information and are among the most critical document components. Existing studies largely focus on surface-level tasks such as layout analysis, table detection, and data extraction, lacking deep semantic parsing of tables and their contextual associations. This limits advanced tasks like cross-paragraph data interpretation and context-consistent analysis. To address this, we propose DOTABLER, a table-centric semantic document parsing framework designed to uncover deep semantic links between tables and their context. DOTABLER leverages a custom dataset and domain-specific fine-tuning of pre-trained models, integrating a complete parsing pipeline to identify context segments semantically tied to tables. Built on this semantic understanding, DOTABLER implements two core functionalities: table-centric document structure parsing and domain-specific table retrieval, delivering comprehensive table-anchored semantic analysis and precise extraction of semantically relevant tables. Evaluated on nearly 4,000 pages with over 1,000 tables from real-world PDFs, DOTABLER achieves over 90% Precision and F1 scores, demonstrating superior performance in table-context semantic analysis and deep document parsing compared to advanced models such as GPT-4o.
A Semantically Motivated Approach to Compute ROUGE Scores
Oct 20, 2017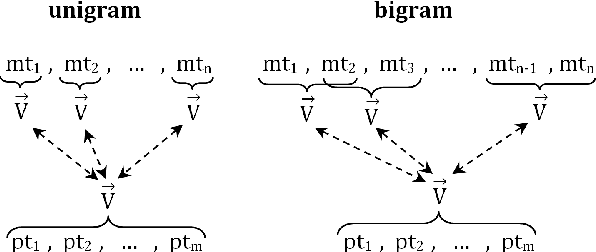
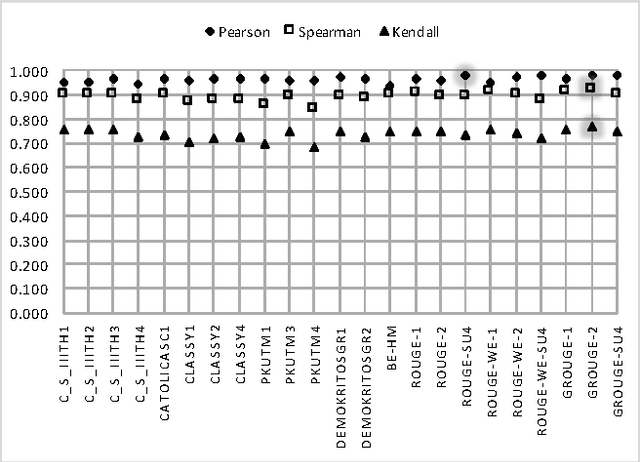
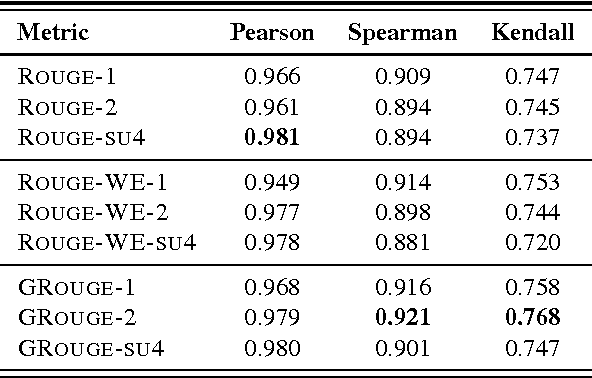
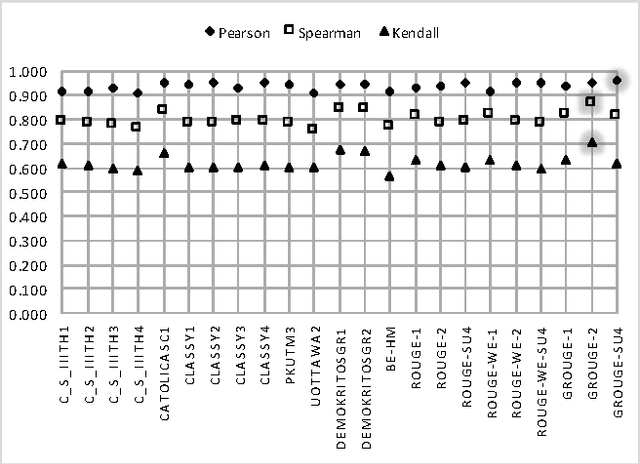
Abstract:ROUGE is one of the first and most widely used evaluation metrics for text summarization. However, its assessment merely relies on surface similarities between peer and model summaries. Consequently, ROUGE is unable to fairly evaluate abstractive summaries including lexical variations and paraphrasing. Exploring the effectiveness of lexical resource-based models to address this issue, we adopt a graph-based algorithm into ROUGE to capture the semantic similarities between peer and model summaries. Our semantically motivated approach computes ROUGE scores based on both lexical and semantic similarities. Experiment results over TAC AESOP datasets indicate that exploiting the lexico-semantic similarity of the words used in summaries would significantly help ROUGE correlate better with human judgments.
On Improving Informativity and Grammaticality for Multi-Sentence Compression
May 07, 2016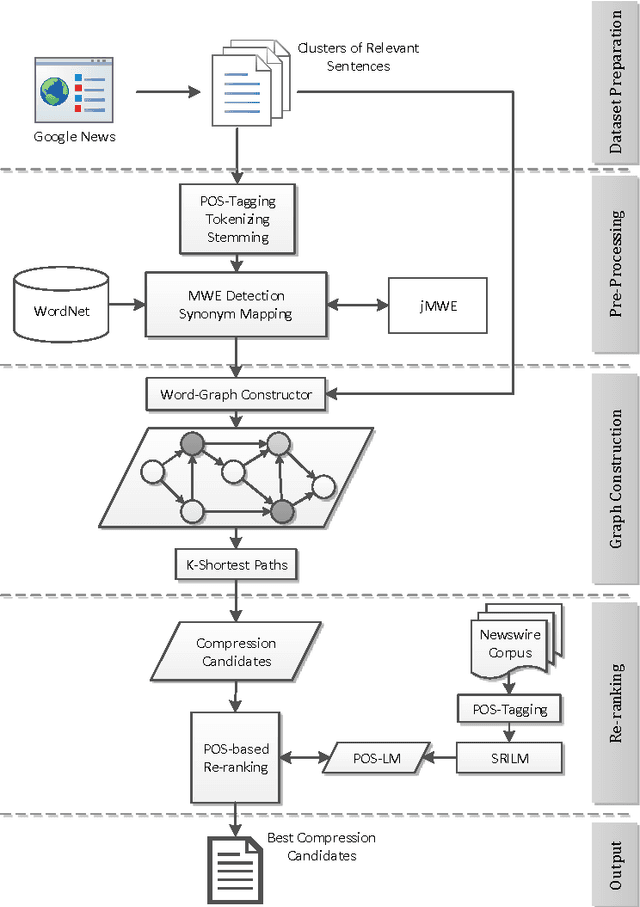
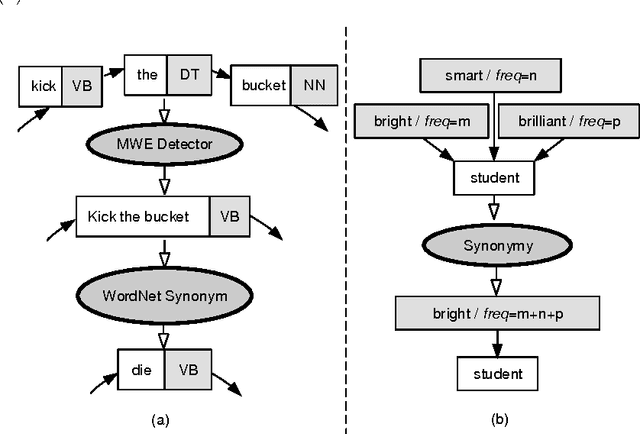
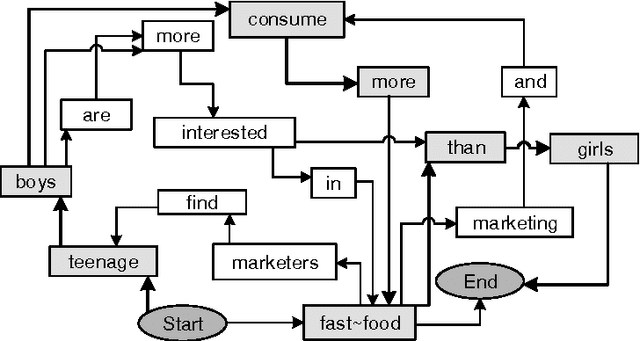
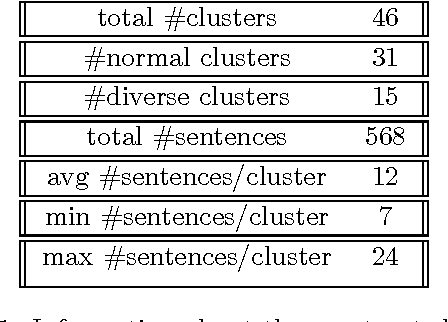
Abstract:Multi Sentence Compression (MSC) is of great value to many real world applications, such as guided microblog summarization, opinion summarization and newswire summarization. Recently, word graph-based approaches have been proposed and become popular in MSC. Their key assumption is that redundancy among a set of related sentences provides a reliable way to generate informative and grammatical sentences. In this paper, we propose an effective approach to enhance the word graph-based MSC and tackle the issue that most of the state-of-the-art MSC approaches are confronted with: i.e., improving both informativity and grammaticality at the same time. Our approach consists of three main components: (1) a merging method based on Multiword Expressions (MWE); (2) a mapping strategy based on synonymy between words; (3) a re-ranking step to identify the best compression candidates generated using a POS-based language model (POS-LM). We demonstrate the effectiveness of this novel approach using a dataset made of clusters of English newswire sentences. The observed improvements on informativity and grammaticality of the generated compressions show that our approach is superior to state-of-the-art MSC methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge