Raunak P. Bhattacharyya
Safe Langevin Soft Actor Critic
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Balancing reward and safety in constrained reinforcement learning remains challenging due to poor generalization from sharp value minima and inadequate handling of heavy-tailed risk distribution. We introduce Safe Langevin Soft Actor-Critic (SL-SAC), a principled algorithm that addresses both issues through parameter-space exploration and distributional risk control. Our approach combines three key mechanisms: (1) Adaptive Stochastic Gradient Langevin Dynamics (aSGLD) for reward critics, promoting ensemble diversity and escape from poor optima; (2) distributional cost estimation via Implicit Quantile Networks (IQN) with Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR) optimization for tail-risk mitigation; and (3) a reactive Lagrangian relaxation scheme that adapts constraint enforcement based on the empirical CVaR of episodic costs. We provide theoretical guarantees on CVaR estimation error and demonstrate that CVaR-based Lagrange updates yield stronger constraint violation signals than expected-cost updates. On Safety-Gymnasium benchmarks, SL-SAC achieves the lowest cost in 7 out of 10 tasks while maintaining competitive returns, with cost reductions of 19-63% in velocity tasks compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Simulating Emergent Properties of Human Driving Behavior Using Multi-Agent Reward Augmented Imitation Learning
Mar 14, 2019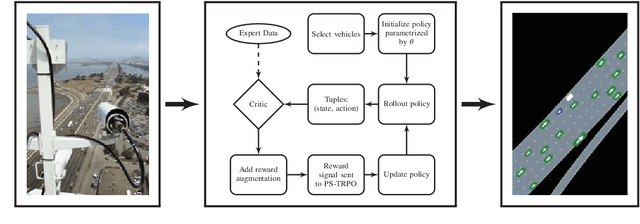
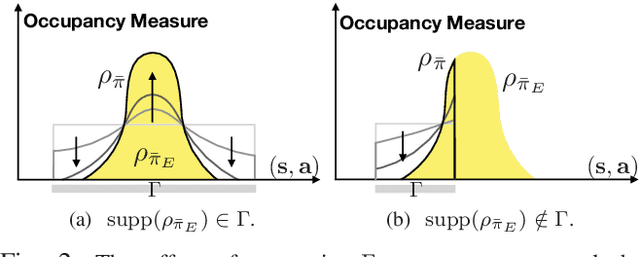
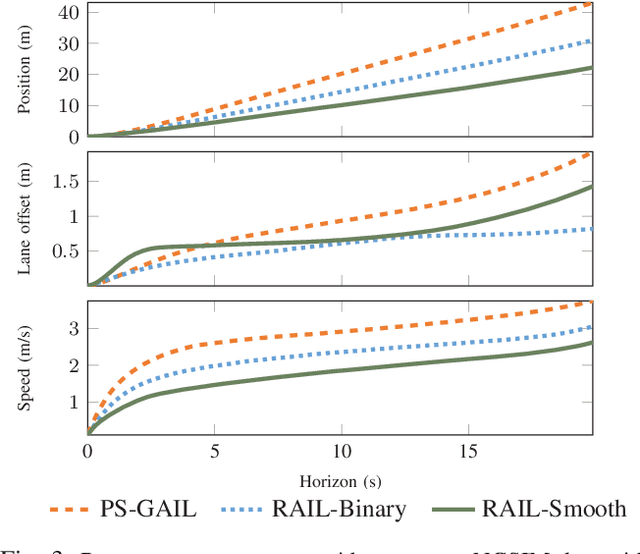
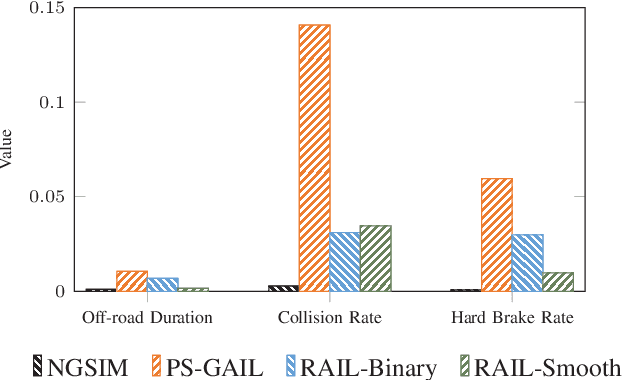
Abstract:Recent developments in multi-agent imitation learning have shown promising results for modeling the behavior of human drivers. However, it is challenging to capture emergent traffic behaviors that are observed in real-world datasets. Such behaviors arise due to the many local interactions between agents that are not commonly accounted for in imitation learning. This paper proposes Reward Augmented Imitation Learning (RAIL), which integrates reward augmentation into the multi-agent imitation learning framework and allows the designer to specify prior knowledge in a principled fashion. We prove that convergence guarantees for the imitation learning process are preserved under the application of reward augmentation. This method is validated in a driving scenario, where an entire traffic scene is controlled by driving policies learned using our proposed algorithm. Further, we demonstrate improved performance in comparison to traditional imitation learning algorithms both in terms of the local actions of a single agent and the behavior of emergent properties in complex, multi-agent settings.
Multi-Agent Imitation Learning for Driving Simulation
Mar 02, 2018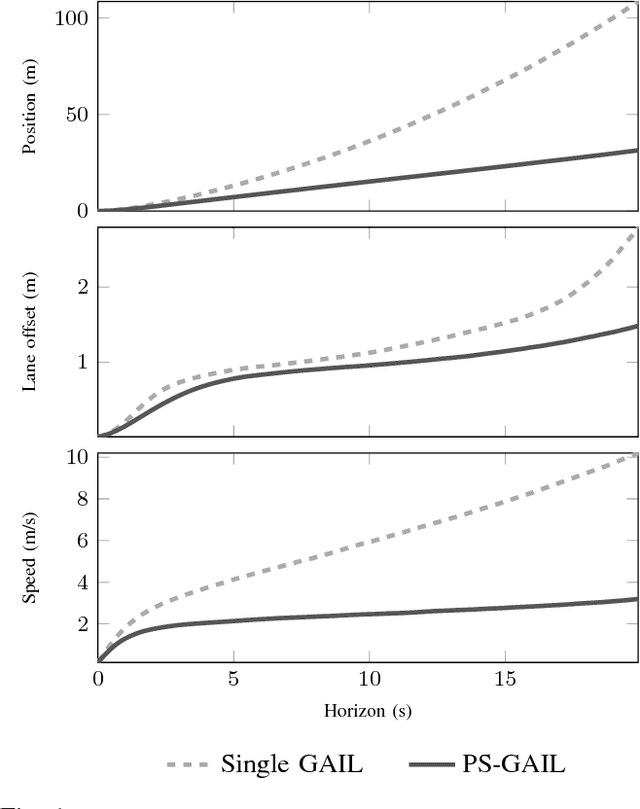
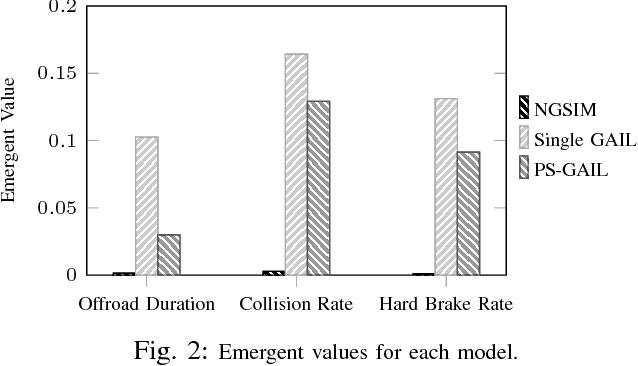
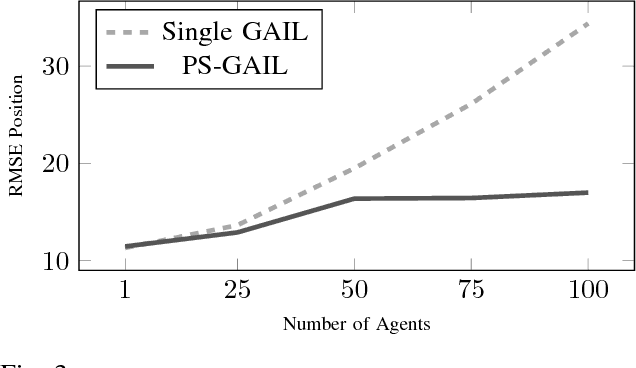
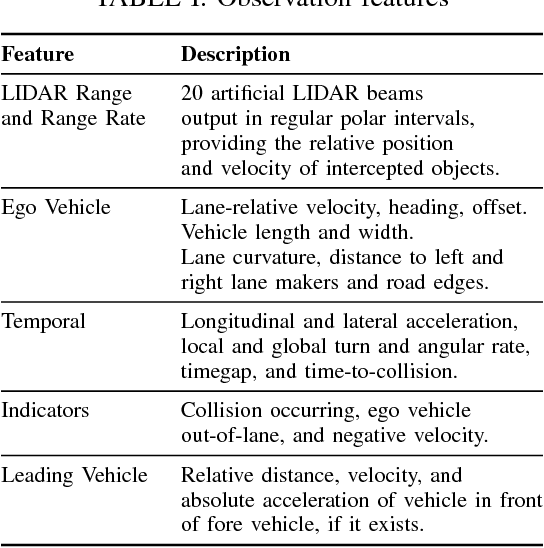
Abstract:Simulation is an appealing option for validating the safety of autonomous vehicles. Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning (GAIL) has recently been shown to learn representative human driver models. These human driver models were learned through training in single-agent environments, but they have difficulty in generalizing to multi-agent driving scenarios. We argue these difficulties arise because observations at training and test time are sampled from different distributions. This difference makes such models unsuitable for the simulation of driving scenes, where multiple agents must interact realistically over long time horizons. We extend GAIL to address these shortcomings through a parameter-sharing approach grounded in curriculum learning. Compared with single-agent GAIL policies, policies generated by our PS-GAIL method prove superior at interacting stably in a multi-agent setting and capturing the emergent behavior of human drivers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge