Ranajit Saha
Spatio-Temporal Video Representation Learning for AI Based Video Playback Style Prediction
Oct 03, 2021
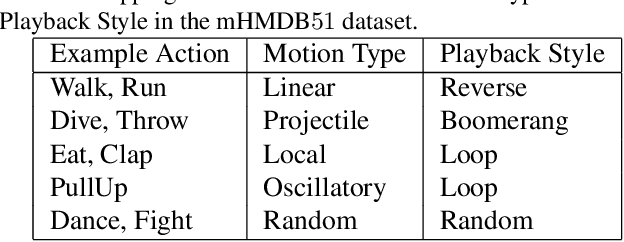
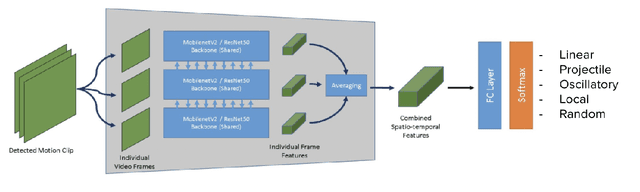
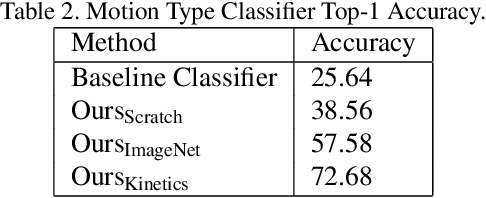
Abstract:Ever-increasing smartphone-generated video content demands intelligent techniques to edit and enhance videos on power-constrained devices. Most of the best performing algorithms for video understanding tasks like action recognition, localization, etc., rely heavily on rich spatio-temporal representations to make accurate predictions. For effective learning of the spatio-temporal representation, it is crucial to understand the underlying object motion patterns present in the video. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for understanding object motions via motion type classification. The proposed motion type classifier predicts a motion type for the video based on the trajectories of the objects present. Our classifier assigns a motion type for the given video from the following five primitive motion classes: linear, projectile, oscillatory, local and random. We demonstrate that the representations learned from the motion type classification generalizes well for the challenging downstream task of video retrieval. Further, we proposed a recommendation system for video playback style based on the motion type classifier predictions.
Graphical Object Detection in Document Images
Aug 25, 2020
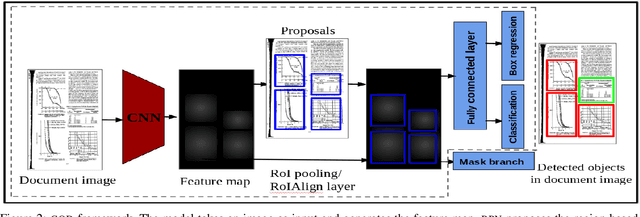


Abstract:Graphical elements: particularly tables and figures contain a visual summary of the most valuable information contained in a document. Therefore, localization of such graphical objects in the document images is the initial step to understand the content of such graphical objects or document images. In this paper, we present a novel end-to-end trainable deep learning based framework to localize graphical objects in the document images called as Graphical Object Detection (GOD). Our framework is data-driven and does not require any heuristics or meta-data to locate graphical objects in the document images. The GOD explores the concept of transfer learning and domain adaptation to handle scarcity of labeled training images for graphical object detection task in the document images. Performance analysis carried out on the various public benchmark data sets: ICDAR-2013, ICDAR-POD2017,and UNLV shows that our model yields promising results as compared to state-of-the-art techniques.
* 8
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge