Raluca Scona
CodeMapping: Real-Time Dense Mapping for Sparse SLAM using Compact Scene Representations
Jul 19, 2021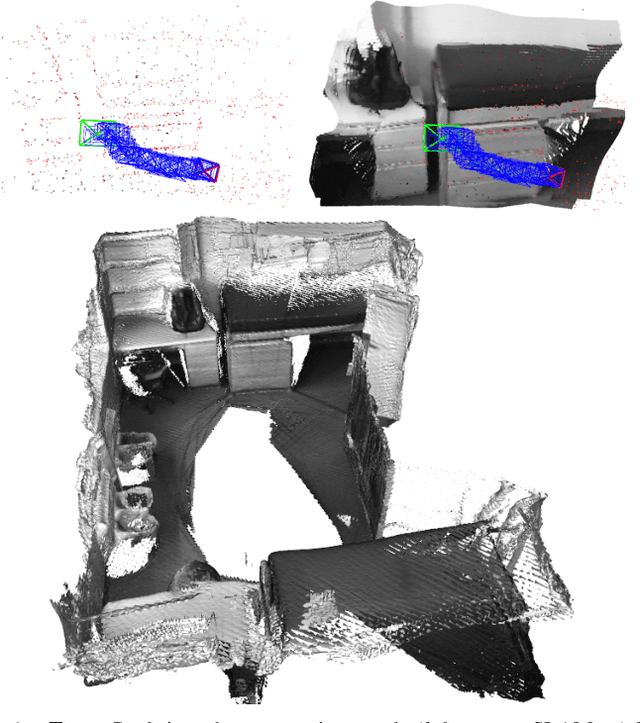
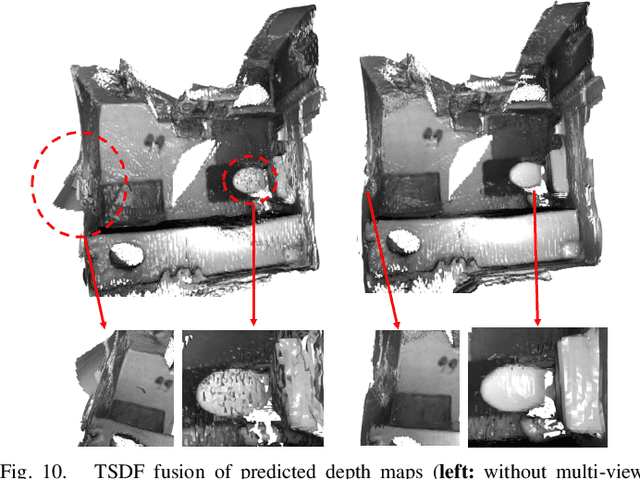
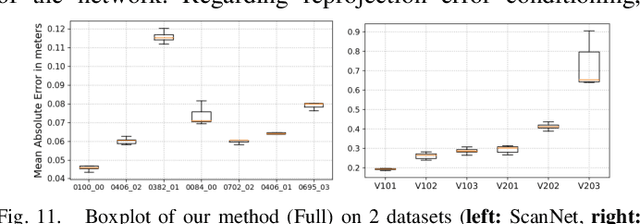
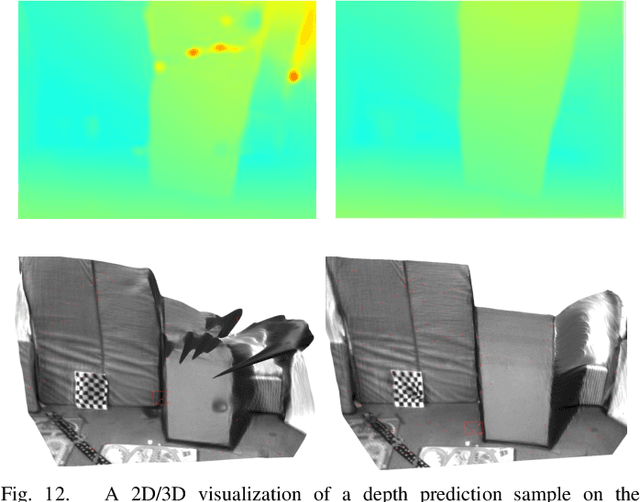
Abstract:We propose a novel dense mapping framework for sparse visual SLAM systems which leverages a compact scene representation. State-of-the-art sparse visual SLAM systems provide accurate and reliable estimates of the camera trajectory and locations of landmarks. While these sparse maps are useful for localization, they cannot be used for other tasks such as obstacle avoidance or scene understanding. In this paper we propose a dense mapping framework to complement sparse visual SLAM systems which takes as input the camera poses, keyframes and sparse points produced by the SLAM system and predicts a dense depth image for every keyframe. We build on CodeSLAM and use a variational autoencoder (VAE) which is conditioned on intensity, sparse depth and reprojection error images from sparse SLAM to predict an uncertainty-aware dense depth map. The use of a VAE then enables us to refine the dense depth images through multi-view optimization which improves the consistency of overlapping frames. Our mapper runs in a separate thread in parallel to the SLAM system in a loosely coupled manner. This flexible design allows for integration with arbitrary metric sparse SLAM systems without delaying the main SLAM process. Our dense mapper can be used not only for local mapping but also globally consistent dense 3D reconstruction through TSDF fusion. We demonstrate our system running with ORB-SLAM3 and show accurate dense depth estimation which could enable applications such as robotics and augmented reality.
SIMstack: A Generative Shape and Instance Model for Unordered Object Stacks
Mar 30, 2021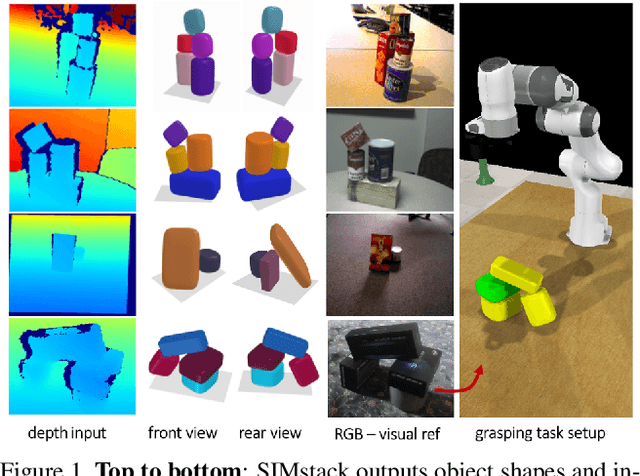
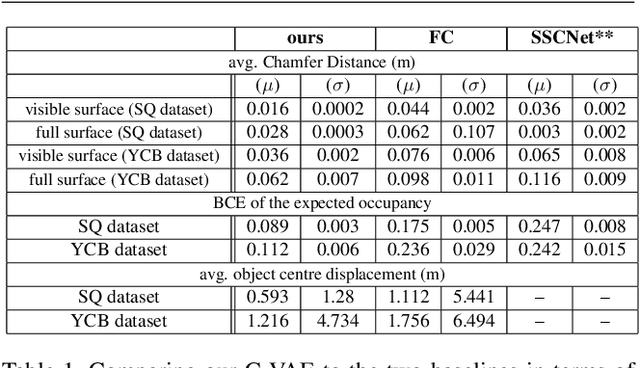
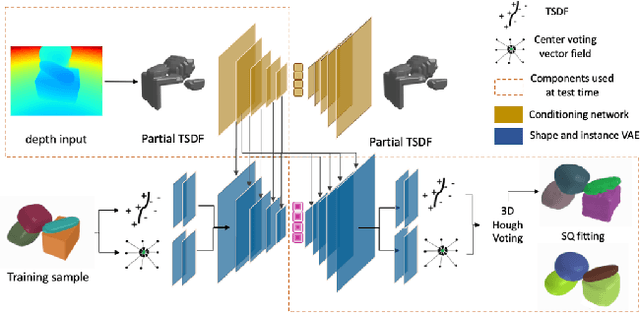

Abstract:By estimating 3D shape and instances from a single view, we can capture information about an environment quickly, without the need for comprehensive scanning and multi-view fusion. Solving this task for composite scenes (such as object stacks) is challenging: occluded areas are not only ambiguous in shape but also in instance segmentation; multiple decompositions could be valid. We observe that physics constrains decomposition as well as shape in occluded regions and hypothesise that a latent space learned from scenes built under physics simulation can serve as a prior to better predict shape and instances in occluded regions. To this end we propose SIMstack, a depth-conditioned Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE), trained on a dataset of objects stacked under physics simulation. We formulate instance segmentation as a centre voting task which allows for class-agnostic detection and doesn't require setting the maximum number of objects in the scene. At test time, our model can generate 3D shape and instance segmentation from a single depth view, probabilistically sampling proposals for the occluded region from the learned latent space. Our method has practical applications in providing robots some of the ability humans have to make rapid intuitive inferences of partially observed scenes. We demonstrate an application for precise (non-disruptive) object grasping of unknown objects from a single depth view.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge