Rajiv Bajpai
The Truth and Nothing but the Truth: Multimodal Analysis for Deception Detection
Mar 11, 2019
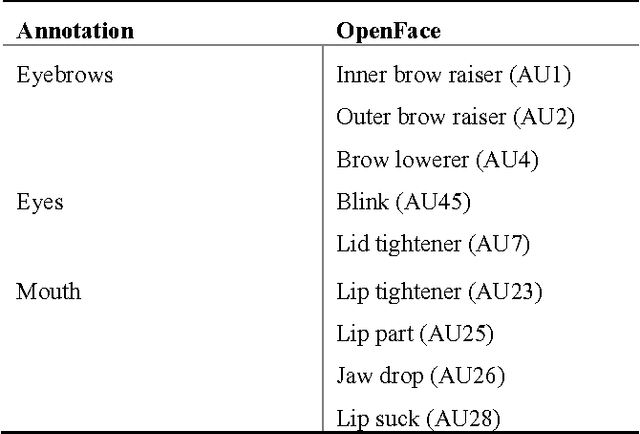
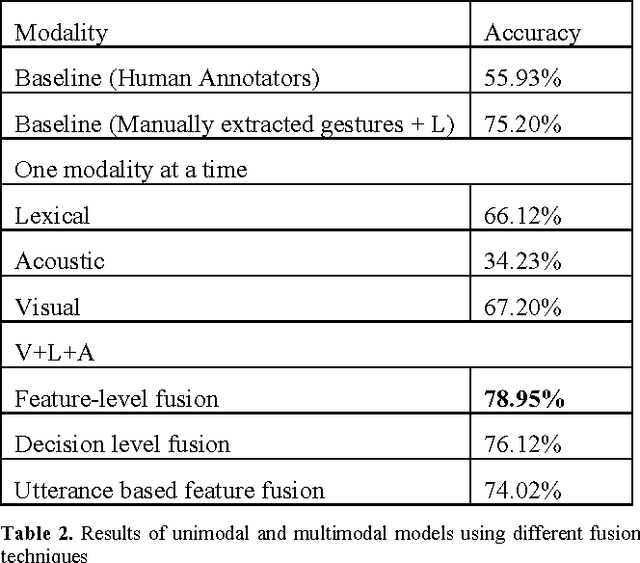
Abstract:We propose a data-driven method for automatic deception detection in real-life trial data using visual and verbal cues. Using OpenFace with facial action unit recognition, we analyze the movement of facial features of the witness when posed with questions and the acoustic patterns using OpenSmile. We then perform a lexical analysis on the spoken words, emphasizing the use of pauses and utterance breaks, feeding that to a Support Vector Machine to test deceit or truth prediction. We then try out a method to incorporate utterance-based fusion of visual and lexical analysis, using string based matching.
Aspect-Sentiment Embeddings for Company Profiling and Employee Opinion Mining
Feb 22, 2019

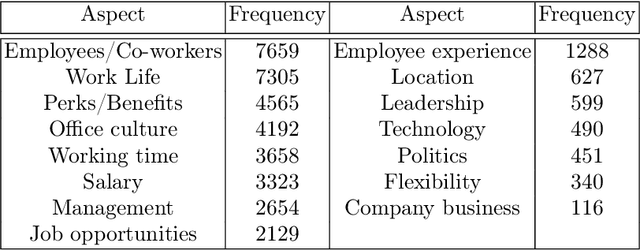
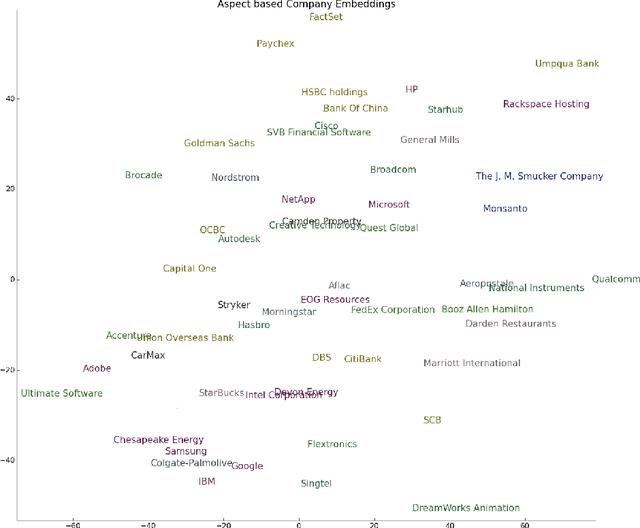
Abstract:With the multitude of companies and organizations abound today, ranking them and choosing one out of the many is a difficult and cumbersome task. Although there are many available metrics that rank companies, there is an inherent need for a generalized metric that takes into account the different aspects that constitute employee opinions of the companies. In this work, we aim to overcome the aforementioned problem by generating aspect-sentiment based embedding for the companies by looking into reliable employee reviews of them. We created a comprehensive dataset of company reviews from the famous website Glassdoor.com and employed a novel ensemble approach to perform aspect-level sentiment analysis. Although a relevant amount of work has been done on reviews centered on subjects like movies, music, etc., this work is the first of its kind. We also provide several insights from the collated embeddings, thus helping users gain a better understanding of their options as well as select companies using customized preferences.
Developing a concept-level knowledge base for sentiment analysis in Singlish
Jul 14, 2017



Abstract:In this paper, we present Singlish sentiment lexicon, a concept-level knowledge base for sentiment analysis that associates multiword expressions to a set of emotion labels and a polarity value. Unlike many other sentiment analysis resources, this lexicon is not built by manually labeling pieces of knowledge coming from general NLP resources such as WordNet or DBPedia. Instead, it is automatically constructed by applying graph-mining and multi-dimensional scaling techniques on the affective common-sense knowledge collected from three different sources. This knowledge is represented redundantly at three levels: semantic network, matrix, and vector space. Subsequently, the concepts are labeled by emotions and polarity through the ensemble application of spreading activation, neural networks and an emotion categorization model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge