Raffaella Fiamma Cabini
Cell Behavior Video Classification Challenge, a benchmark for computer vision methods in time-lapse microscopy
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:The classification of microscopy videos capturing complex cellular behaviors is crucial for understanding and quantifying the dynamics of biological processes over time. However, it remains a frontier in computer vision, requiring approaches that effectively model the shape and motion of objects without rigid boundaries, extract hierarchical spatiotemporal features from entire image sequences rather than static frames, and account for multiple objects within the field of view. To this end, we organized the Cell Behavior Video Classification Challenge (CBVCC), benchmarking 35 methods based on three approaches: classification of tracking-derived features, end-to-end deep learning architectures to directly learn spatiotemporal features from the entire video sequence without explicit cell tracking, or ensembling tracking-derived with image-derived features. We discuss the results achieved by the participants and compare the potential and limitations of each approach, serving as a basis to foster the development of computer vision methods for studying cellular dynamics.
Understanding the Impact of Evaluation Metrics in Kinetic Models for Consensus-based Segmentation
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:In this article we extend a recently introduced kinetic model for consensus-based segmentation of images. In particular, we will interpret the set of pixels of a 2D image as an interacting particle system which evolves in time in view of a consensus-type process obtained by interactions between pixels and external noise. Thanks to a kinetic formulation of the introduced model we derive the large time solution of the model. We will show that the choice of parameters defining the segmentation task can be chosen from a plurality of loss functions characterising the evaluation metrics.
Classification and regression of trajectories rendered as images via 2D Convolutional Neural Networks
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Trajectories can be regarded as time-series of coordinates, typically arising from motile objects. Methods for trajectory classification are particularly important to detect different movement patterns, while methods for regression to compute motility metrics and forecasting. Recent advances in computer vision have facilitated the processing of trajectories rendered as images via artificial neural networks with 2d convolutional layers (CNNs). This approach leverages the capability of CNNs to learn spatial hierarchies of features from images, necessary to recognize complex shapes. Moreover, it overcomes the limitation of other machine learning methods that require input trajectories with a fixed number of points. However, rendering trajectories as images can introduce poorly investigated artifacts such as information loss due to the plotting of coordinates on a discrete grid, and spectral changes due to line thickness and aliasing. In this study, we investigate the effectiveness of CNNs for solving classification and regression problems from synthetic trajectories that have been rendered as images using different modalities. The parameters considered in this study include line thickness, image resolution, usage of motion history (color-coding of the temporal component) and anti-aliasing. Results highlight the importance of choosing an appropriate image resolution according to model depth and motion history in applications where movement direction is critical.
A kinetic approach to consensus-based segmentation of biomedical images
Nov 08, 2022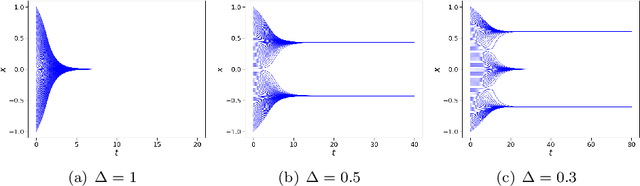
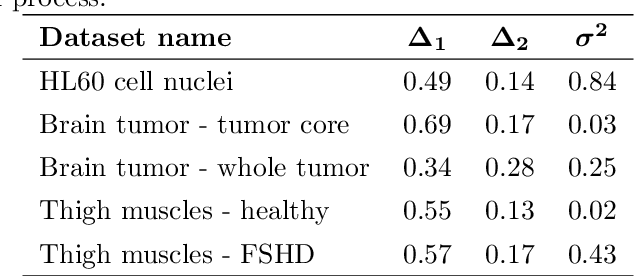
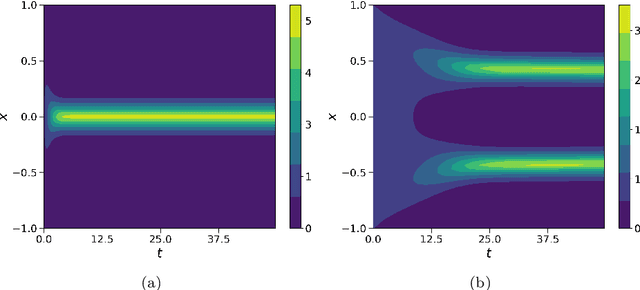
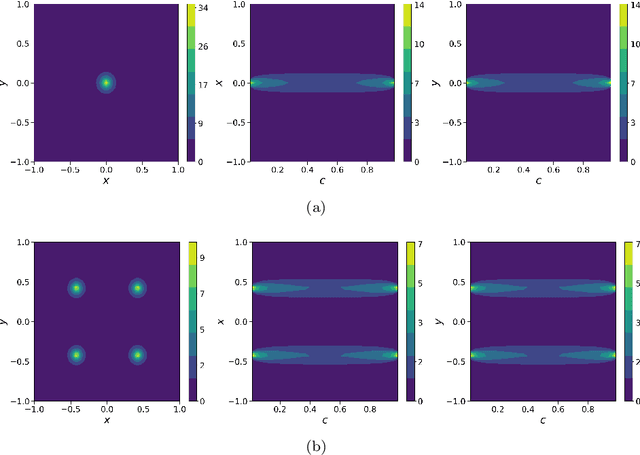
Abstract:In this work, we apply a kinetic version of a bounded confidence consensus model to biomedical segmentation problems. In the presented approach, time-dependent information on the microscopic state of each particle/pixel includes its space position and a feature representing a static characteristic of the system, i.e. the gray level of each pixel. From the introduced microscopic model we derive a kinetic formulation of the model. The large time behavior of the system is then computed with the aid of a surrogate Fokker-Planck approach that can be obtained in the quasi-invariant scaling. We exploit the computational efficiency of direct simulation Monte Carlo methods for the obtained Boltzmann-type description of the problem for parameter identification tasks. Based on a suitable loss function measuring the distance between the ground truth segmentation mask and the evaluated mask, we minimize the introduced segmentation metric for a relevant set of 2D gray-scale images. Applications to biomedical segmentation concentrate on different imaging research contexts.
Quantification of pulmonary involvement in COVID-19 pneumonia by means of a cascade oftwo U-nets: training and assessment on multipledatasets using different annotation criteria
May 06, 2021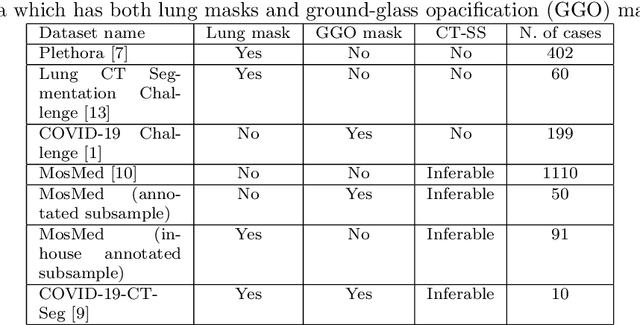
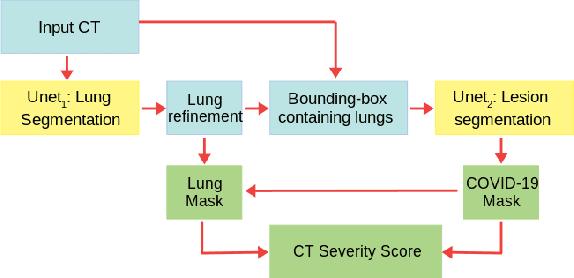
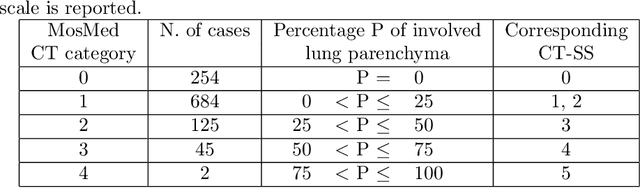
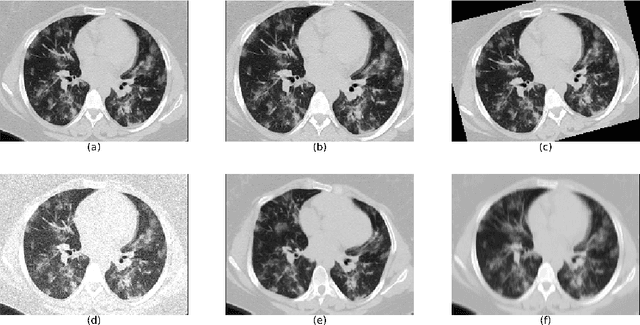
Abstract:The automatic assignment of a severity score to the CT scans of patients affected by COVID-19 pneumonia could reduce the workload in radiology departments. This study aims at exploiting Artificial intelligence (AI) for the identification, segmentation and quantification of COVID-19 pulmonary lesions. We investigated the effects of using multiple datasets, heterogeneously populated and annotated according to different criteria. We developed an automated analysis pipeline, the LungQuant system, based on a cascade of two U-nets. The first one (U-net_1) is devoted to the identification of the lung parenchyma, the second one (U-net_2) acts on a bounding box enclosing the segmented lungs to identify the areas affected by COVID-19 lesions. Different public datasets were used to train the U-nets and to evaluate their segmentation performances, which have been quantified in terms of the Dice index. The accuracy in predicting the CT-Severity Score (CT-SS) of the LungQuant system has been also evaluated. Both Dice and accuracy showed a dependency on the quality of annotations of the available data samples. On an independent and publicly available benchmark dataset, the Dice values measured between the masks predicted by LungQuant system and the reference ones were 0.95$\pm$0.01 and 0.66$\pm$0.13 for the segmentation of lungs and COVID-19 lesions, respectively. The accuracy of 90% in the identification of the CT-SS on this benchmark dataset was achieved. We analysed the impact of using data samples with different annotation criteria in training an AI-based quantification system for pulmonary involvement in COVID-19 pneumonia. In terms of the Dice index, the U-net segmentation quality strongly depends on the quality of the lesion annotations. Nevertheless, the CT-SS can be accurately predicted on independent validation sets, demonstrating the satisfactory generalization ability of the LungQuant.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge