Rafael Hostettler
Ravestate: Distributed Composition of a Causal-Specificity-Guided Interaction Policy
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:In human-robot interaction policy design, a rule-based method is efficient, explainable, expressive and intuitive. In this paper, we present the Signal-Rule-Slot framework, which refines prior work on rule-based symbol system design and introduces a new, Bayesian notion of interaction rule utility called Causal Pathway Self-information. We offer a rigorous theoretical foundation as well as a rich open-source reference implementation Ravestate, with which we conduct user studies in text-, speech-, and vision-based scenarios. The experiments show robust contextual behaviour of our probabilistically informed rule-based system, paving the way for more effective human-machine interaction.
Ball-and-socket joint pose estimation using magnetic field
Oct 08, 2022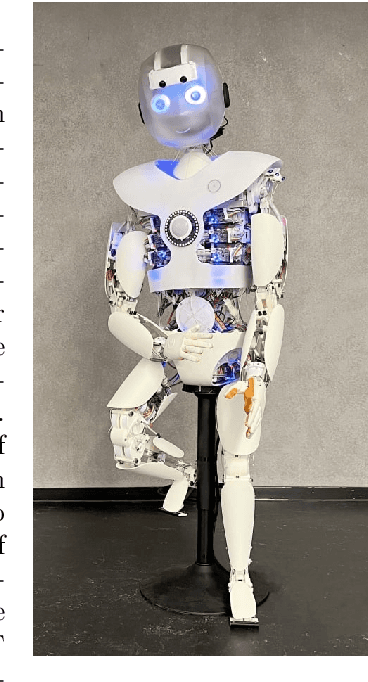
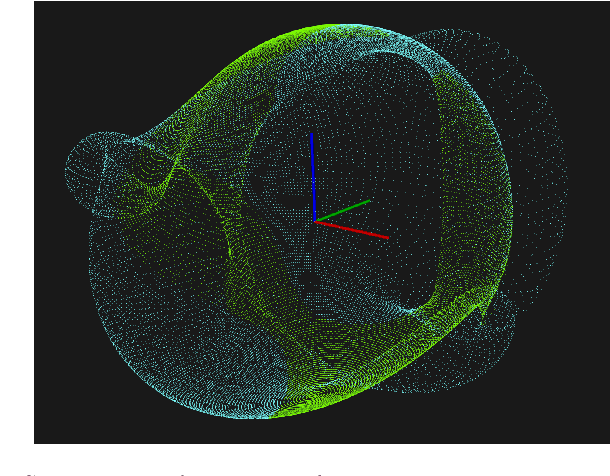
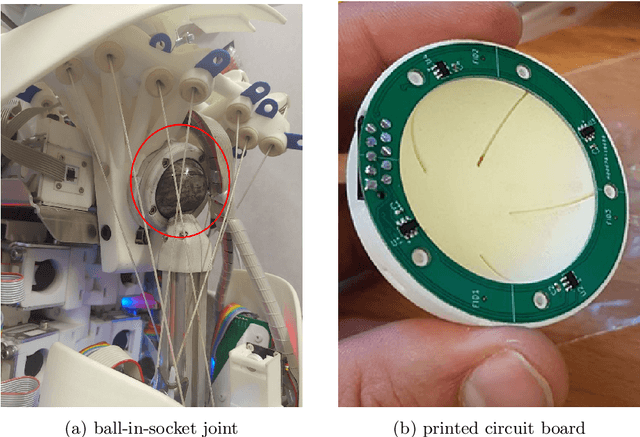
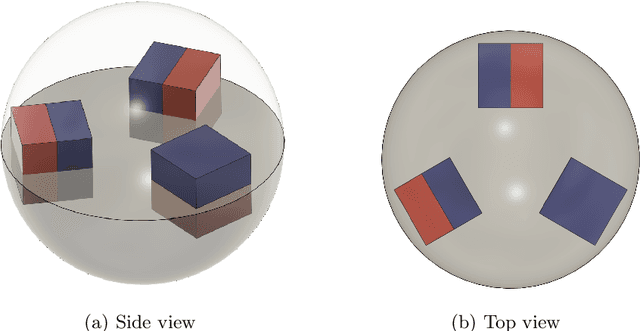

Abstract:Roboy 3.0 is an open-source tendon-driven humanoid robot that mimics the musculoskeletal system of the human body. Roboy 3.0 is being developed as a remote robotic body - or a robotic avatar - for humans to achieve remote physical presence. Artificial muscles and tendons allow it to closely resemble human morphology with 3-DoF neck, shoulders and wrists. Roboy 3.0 3-DoF joints are implemented as ball-and-socket joints. While industry provides a clear solution for 1-DoF joint pose sensing, it is not the case for the ball-and-socket joint type. In this paper we present a custom solution to estimate the pose of a ball-and-socket joint. We embed an array of magnets into the ball and an array of 3D magnetic sensors into the socket. We then, based on the changes in the magnetic field as the joint rotates, are able to estimate the orientation of the joint. We evaluate the performance of two neural network approaches using the LSTM and Bayesian-filter like DVBF. Results show that in order to achieve the same mean square error (MSE) DVBFs require significantly more time training and hyperparameter tuning compared to LSTMs, while DVBF cope with sensor noise better. Both methods are capable of real-time joint pose estimation at 37 Hz with MSE of around 0.03 rad for all three degrees of freedom combined. The LSTM model is deployed and used for joint pose estimation of Roboy 3.0's shoulder and neck joints. The software implementation and PCB designs are open-sourced under https://github.com/Roboy/ball_and_socket_estimator
Scalability in Neural Control of Musculoskeletal Robots
Jan 19, 2016
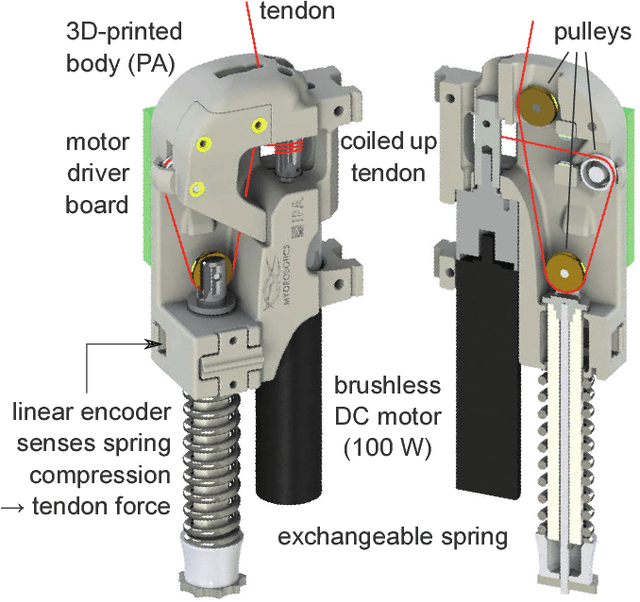

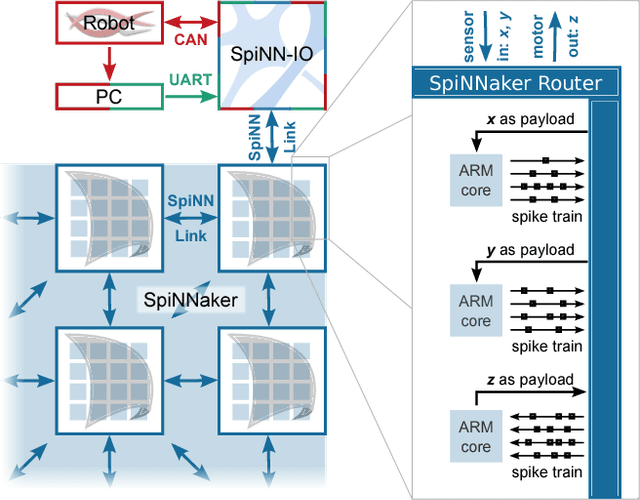
Abstract:Anthropomimetic robots are robots that sense, behave, interact and feel like humans. By this definition, anthropomimetic robots require human-like physical hardware and actuation, but also brain-like control and sensing. The most self-evident realization to meet those requirements would be a human-like musculoskeletal robot with a brain-like neural controller. While both musculoskeletal robotic hardware and neural control software have existed for decades, a scalable approach that could be used to build and control an anthropomimetic human-scale robot has not been demonstrated yet. Combining Myorobotics, a framework for musculoskeletal robot development, with SpiNNaker, a neuromorphic computing platform, we present the proof-of-principle of a system that can scale to dozens of neurally-controlled, physically compliant joints. At its core, it implements a closed-loop cerebellar model which provides real-time low-level neural control at minimal power consumption and maximal extensibility: higher-order (e.g., cortical) neural networks and neuromorphic sensors like silicon-retinae or -cochleae can naturally be incorporated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge