Radha Mastandrea
Constraining the Higgs Potential with Neural Simulation-based Inference for Di-Higgs Production
May 24, 2024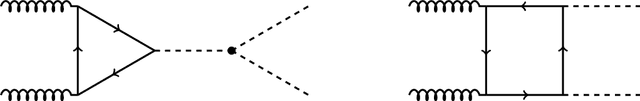

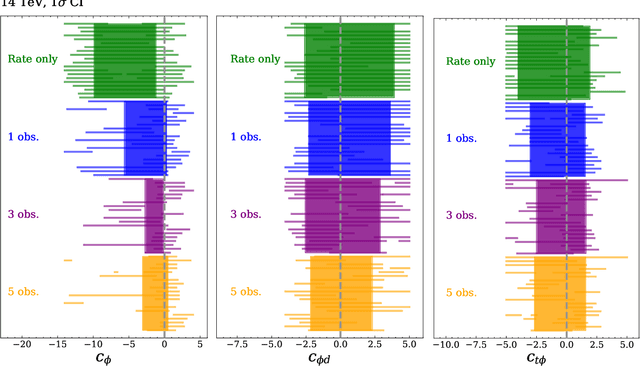
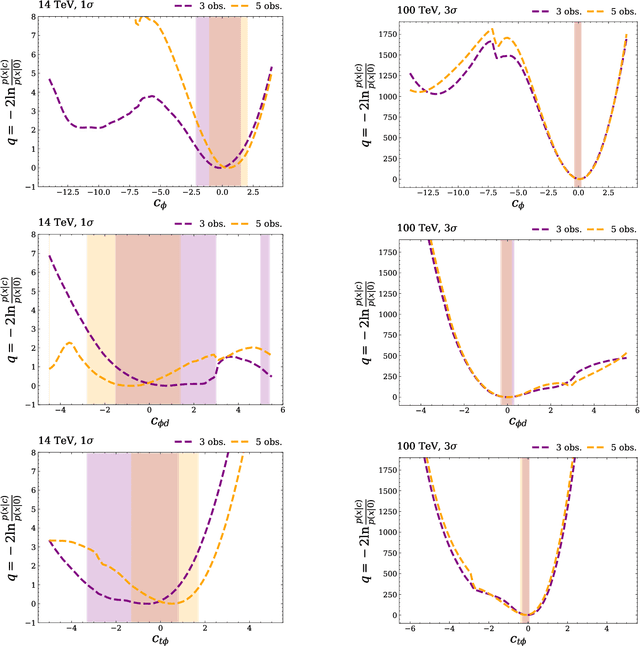
Abstract:Determining the form of the Higgs potential is one of the most exciting challenges of modern particle physics. Higgs pair production directly probes the Higgs self-coupling and should be observed in the near future at the High-Luminosity LHC. We explore how to improve the sensitivity to physics beyond the Standard Model through per-event kinematics for di-Higgs events. In particular, we employ machine learning through simulation-based inference to estimate per-event likelihood ratios and gauge potential sensitivity gains from including this kinematic information. In terms of the Standard Model Effective Field Theory, we find that adding a limited number of observables can help to remove degeneracies in Wilson coefficient likelihoods and significantly improve the experimental sensitivity.
Flows for Flows: Morphing one Dataset into another with Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Sep 12, 2023



Abstract:Many components of data analysis in high energy physics and beyond require morphing one dataset into another. This is commonly solved via reweighting, but there are many advantages of preserving weights and shifting the data points instead. Normalizing flows are machine learning models with impressive precision on a variety of particle physics tasks. Naively, normalizing flows cannot be used for morphing because they require knowledge of the probability density of the starting dataset. In most cases in particle physics, we can generate more examples, but we do not know densities explicitly. We propose a protocol called flows for flows for training normalizing flows to morph one dataset into another even if the underlying probability density of neither dataset is known explicitly. This enables a morphing strategy trained with maximum likelihood estimation, a setup that has been shown to be highly effective in related tasks. We study variations on this protocol to explore how far the data points are moved to statistically match the two datasets. Furthermore, we show how to condition the learned flows on particular features in order to create a morphing function for every value of the conditioning feature. For illustration, we demonstrate flows for flows for toy examples as well as a collider physics example involving dijet events
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge