Rachel
Lei
Dancing with a Robot: An Experimental Study of Child-Robot Interaction in a Performative Art Setting
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an evaluation of 18 children's in-the-wild experiences with the autonomous robot arm performer NED (Never-Ending Dancer) within the Thingamabobas installation, showcased across the UK. We detail NED's design, including costume, behaviour, and human interactions, all integral to the installation. Our observational analysis revealed three key challenges in child-robot interactions: 1) Initiating and maintaining engagement, 2) Lack of robot expressivity and reciprocity, and 3) Unmet expectations. Our findings show that children are naturally curious, and adept at interacting with a robotic art performer. However, our observations emphasise the critical need to optimise human-robot interaction (HRI) systems through careful consideration of audience's capabilities, perceptions, and expectations, within the performative arts context, to enable engaging and meaningful experiences, especially for young audiences.
* published by Springer
3D object quality prediction for Metal Jet Printer with Multimodal thermal encoder
Apr 17, 2024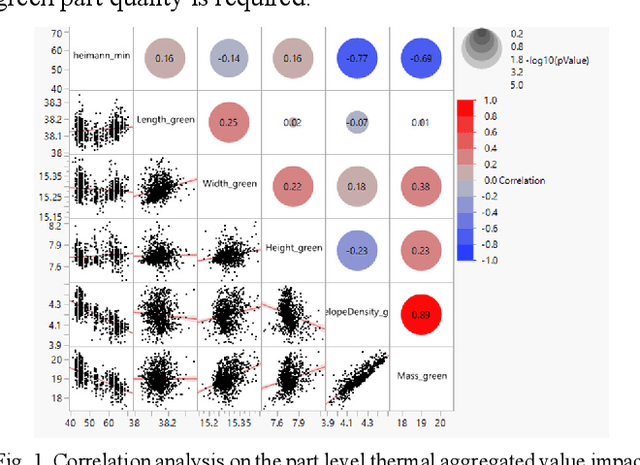
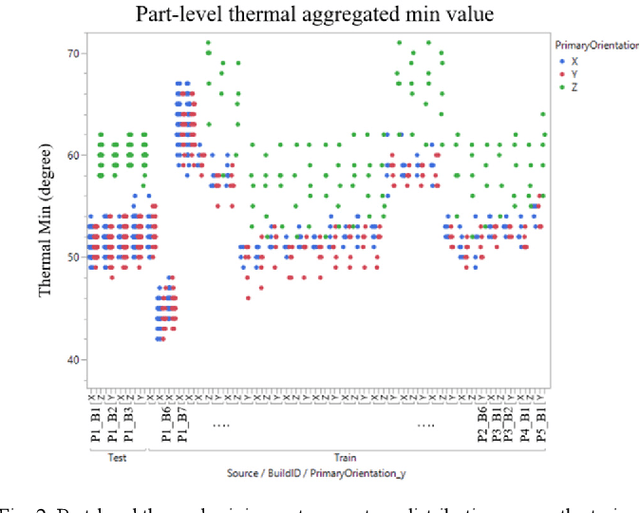
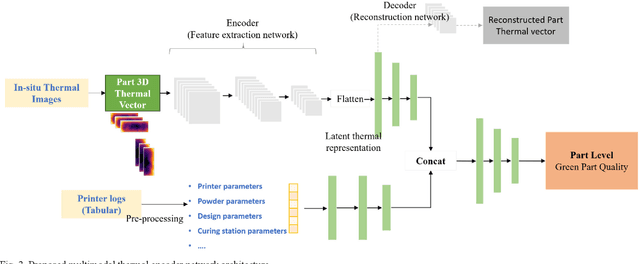
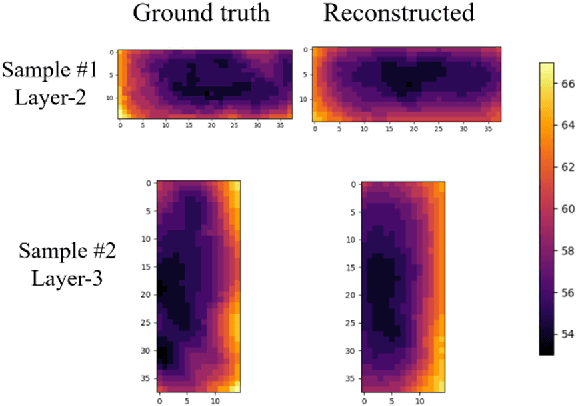
Abstract:With the advancements in 3D printing technologies, it is extremely important that the quality of 3D printed objects, and dimensional accuracies should meet the customer's specifications. Various factors during metal printing affect the printed parts' quality, including the power quality, the printing stage parameters, the print part's location inside the print bed, the curing stage parameters, and the metal sintering process. With the large data gathered from HP's MetJet printing process, AI techniques can be used to analyze, learn, and effectively infer the printed part quality metrics, as well as assist in improving the print yield. In-situ thermal sensing data captured by printer-installed thermal sensors contains the part thermal signature of fusing layers. Such part thermal signature contains a convoluted impact from various factors. In this paper, we use a multimodal thermal encoder network to fuse data of a different nature including the video data vectorized printer control data, and exact part thermal signatures with a trained encoder-decoder module. We explored the data fusing techniques and stages for data fusing, the optimized end-to-end model architecture indicates an improved part quality prediction accuracy.
Virtual Foundry Graphnet for Metal Sintering Deformation Prediction
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Metal Sintering is a necessary step for Metal Injection Molded parts and binder jet such as HP's metal 3D printer. The metal sintering process introduces large deformation varying from 25 to 50% depending on the green part porosity. In this paper, we use a graph-based deep learning approach to predict the part deformation, which can speed up the deformation simulation substantially at the voxel level. Running a well-trained Metal Sintering inferencing engine only takes a range of seconds to obtain the final sintering deformation value. The tested accuracy on example complex geometry achieves 0.7um mean deviation for a 63mm testing part.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge