Quoc Truong Do
ViCocktail: Automated Multi-Modal Data Collection for Vietnamese Audio-Visual Speech Recognition
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) has gained significant attention recently due to its robustness against noise, which often challenges conventional speech recognition systems that rely solely on audio features. Despite this advantage, AVSR models remain limited by the scarcity of extensive datasets, especially for most languages beyond English. Automated data collection offers a promising solution. This work presents a practical approach to generate AVSR datasets from raw video, refining existing techniques for improved efficiency and accessibility. We demonstrate its broad applicability by developing a baseline AVSR model for Vietnamese. Experiments show the automatically collected dataset enables a strong baseline, achieving competitive performance with robust ASR in clean conditions and significantly outperforming them in noisy environments like cocktail parties. This efficient method provides a pathway to expand AVSR to more languages, particularly under-resourced ones.
Improving Vietnamese Named Entity Recognition from Speech Using Word Capitalization and Punctuation Recovery Models
Oct 01, 2020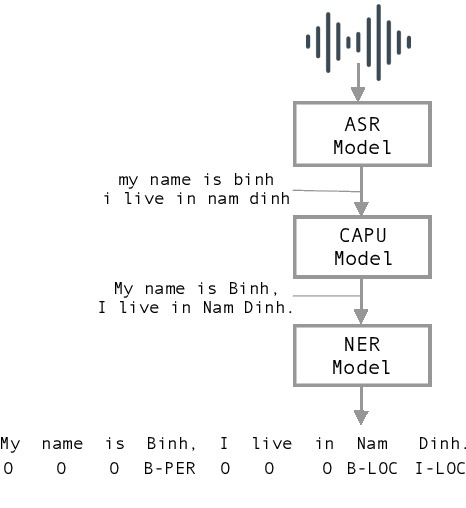

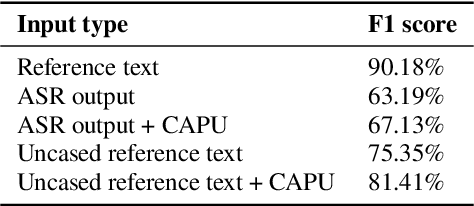
Abstract:Studies on the Named Entity Recognition (NER) task have shown outstanding results that reach human parity on input texts with correct text formattings, such as with proper punctuation and capitalization. However, such conditions are not available in applications where the input is speech, because the text is generated from a speech recognition system (ASR), and that the system does not consider the text formatting. In this paper, we (1) presented the first Vietnamese speech dataset for NER task, and (2) the first pre-trained public large-scale monolingual language model for Vietnamese that achieved the new state-of-the-art for the Vietnamese NER task by 1.3% absolute F1 score comparing to the latest study. And finally, (3) we proposed a new pipeline for NER task from speech that overcomes the text formatting problem by introducing a text capitalization and punctuation recovery model (CaPu) into the pipeline. The model takes input text from an ASR system and performs two tasks at the same time, producing proper text formatting that helps to improve NER performance. Experimental results indicated that the CaPu model helps to improve by nearly 4% of F1-score.
VAIS Hate Speech Detection System: A Deep Learning based Approach for System Combination
Oct 12, 2019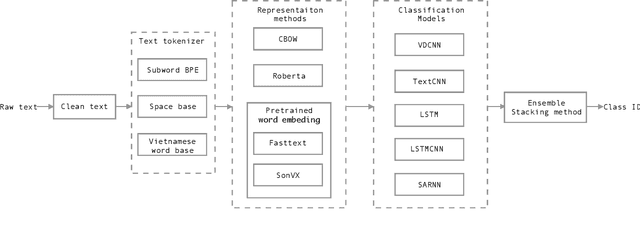
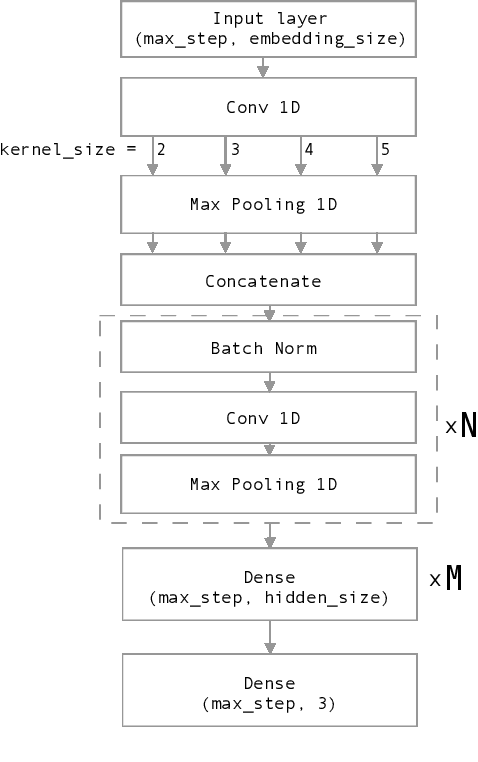
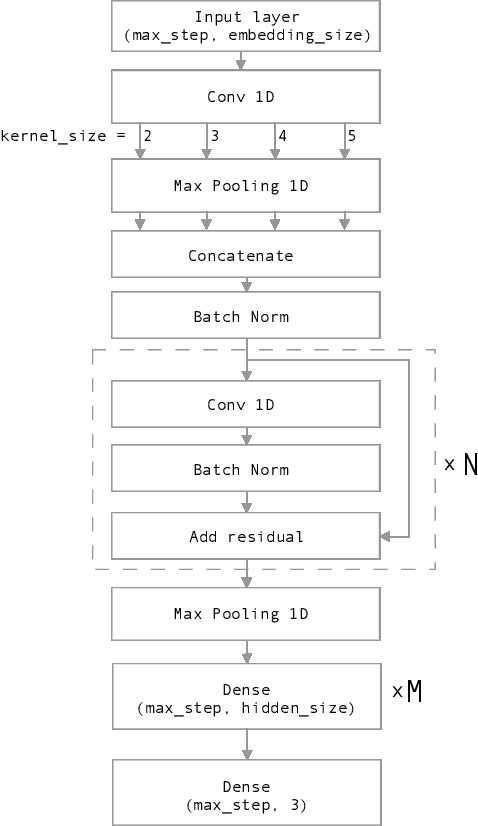
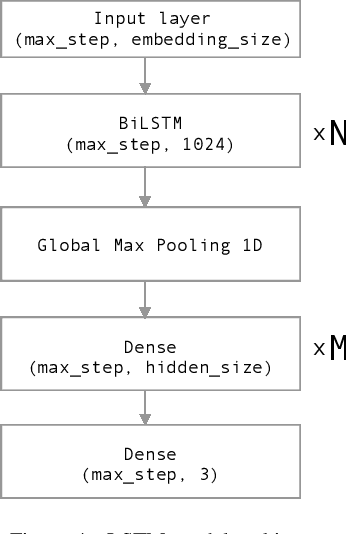
Abstract:Nowadays, Social network sites (SNSs) such as Facebook, Twitter are common places where people show their opinions, sentiments and share information with others. However, some people use SNSs to post abuse and harassment threats in order to prevent other SNSs users from expressing themselves as well as seeking different opinions. To deal with this problem, SNSs have to use a lot of resources including people to clean the aforementioned content. In this paper, we propose a supervised learning model based on the ensemble method to solve the problem of detecting hate content on SNSs in order to make conversations on SNSs more effective. Our proposed model got the first place for public dashboard with 0.730 F1 macro-score and the third place with 0.584 F1 macro-score for private dashboard at the sixth international workshop on Vietnamese Language and Speech Processing 2019.
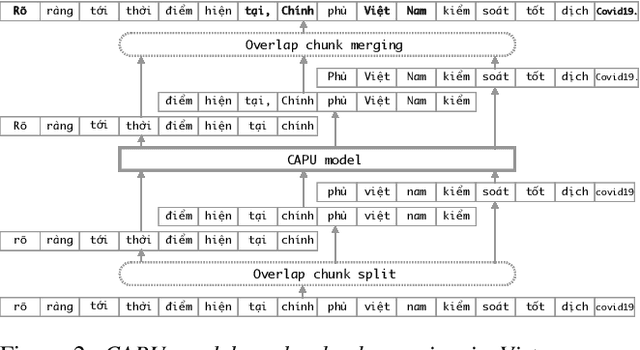
Fast and Accurate Capitalization and Punctuation for Automatic Speech Recognition Using Transformer and Chunk Merging
Aug 07, 2019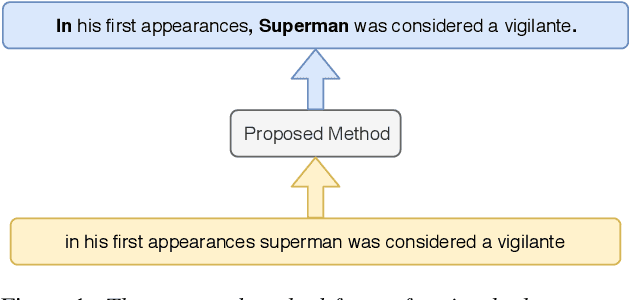
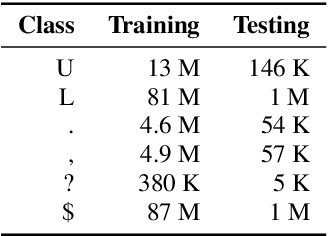
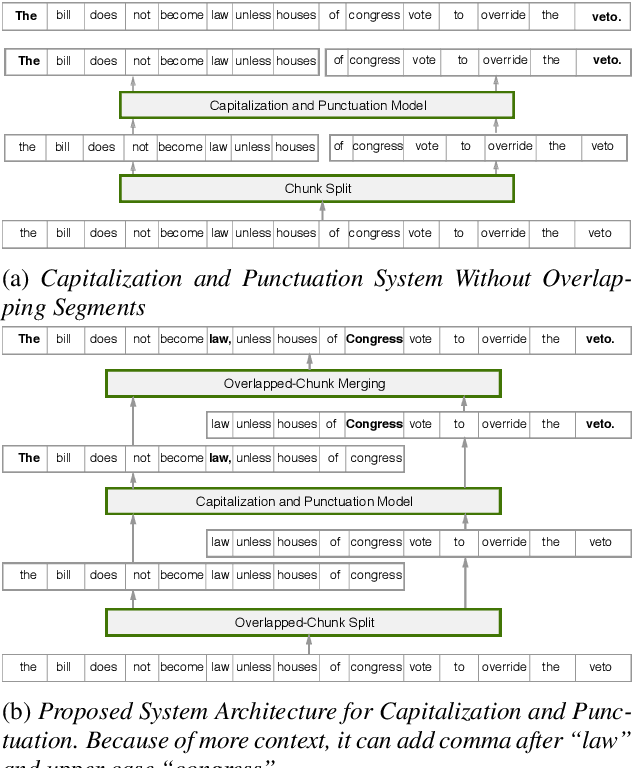
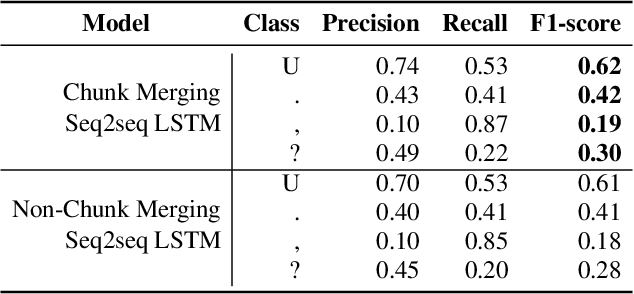
Abstract:In recent years, studies on automatic speech recognition (ASR) have shown outstanding results that reach human parity on short speech segments. However, there are still difficulties in standardizing the output of ASR such as capitalization and punctuation restoration for long-speech transcription. The problems obstruct readers to understand the ASR output semantically and also cause difficulties for natural language processing models such as NER, POS and semantic parsing. In this paper, we propose a method to restore the punctuation and capitalization for long-speech ASR transcription. The method is based on Transformer models and chunk merging that allows us to (1), build a single model that performs punctuation and capitalization in one go, and (2), perform decoding in parallel while improving the prediction accuracy. Experiments on British National Corpus showed that the proposed approach outperforms existing methods in both accuracy and decoding speed.
A high quality and phonetic balanced speech corpus for Vietnamese
Apr 11, 2019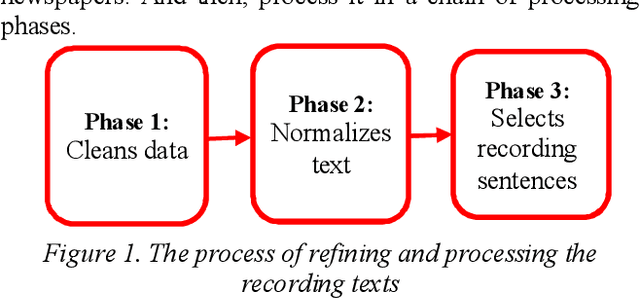
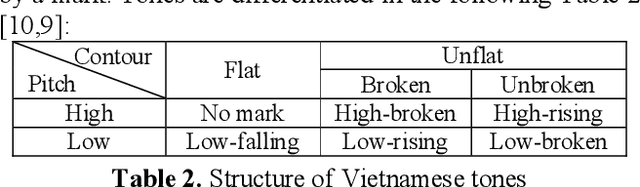

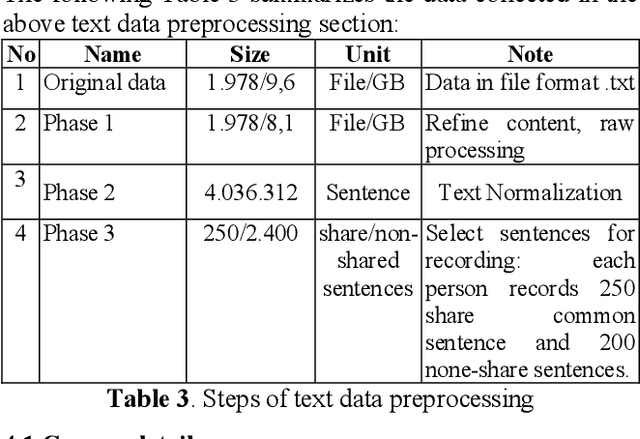
Abstract:This paper presents a high quality Vietnamese speech corpus that can be used for analyzing Vietnamese speech characteristic as well as building speech synthesis models. The corpus consists of 5400 clean-speech utterances spoken by 12 speakers including 6 males and 6 females. The corpus is designed with phonetic balanced in mind so that it can be used for speech synthesis, especially, speech adaptation approaches. Specifically, all speakers utter a common dataset contains 250 phonetic balanced sentences. To increase the variety of speech context, each speaker also utters another 200 non-shared, phonetic-balanced sentences. The speakers are selected to cover a wide range of age and come from different regions of the North of Vietnam. The audios are recorded in a soundproof studio room, they are sampling at 48 kHz, 16 bits PCM, mono channel.
* 5 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge