Qiwei Han
Harmonizing the Deep: A Unified Information Pipeline for Robust Marine Biodiversity Assessment Across Heterogeneous Domains
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Marine biodiversity monitoring requires scalability and reliability across complex underwater environments to support conservation and invasive-species management. Yet existing detection solutions often exhibit a pronounced deployment gap, with performance degrading sharply when transferred to new sites. This work establishes the foundational detection layer for a multi-year invasive species monitoring initiative targeting Arctic and Atlantic marine ecosystems. We address this challenge by developing a Unified Information Pipeline that standardises heterogeneous datasets into a comparable information flow and evaluates a fixed, deployment-relevant detector under controlled cross-domain protocols. Across multiple domains, we find that structural factors, such as scene composition, object density, and contextual redundancy, explain cross-domain performance loss more strongly than visual degradation such as turbidity, with sparse scenes inducing a characteristic "Context Collapse" failure mode. We further validate operational feasibility by benchmarking inference on low-cost edge hardware, showing that runtime optimisation enables practical sampling rates for remote monitoring. The results shift emphasis from image enhancement toward structure-aware reliability, providing a democratised tool for consistent marine ecosystem assessment.
MMCTOP: A Multimodal Textualization and Mixture-of-Experts Framework for Clinical Trial Outcome Prediction
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Addressing the challenge of multimodal data fusion in high-dimensional biomedical informatics, we propose MMCTOP, a MultiModal Clinical-Trial Outcome Prediction framework that integrates heterogeneous biomedical signals spanning (i) molecular structure representations, (ii) protocol metadata and long-form eligibility narratives, and (iii) disease ontologies. MMCTOP couples schema-guided textualization and input-fidelity validation with modality-aware representation learning, in which domain-specific encoders generate aligned embeddings that are fused by a transformer backbone augmented with a drug-disease-conditioned sparse Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE). This design explicitly supports specialization across therapeutic and design subspaces while maintaining scalable computation through top-k routing. MMCTOP achieves consistent improvements in precision, F1, and AUC over unimodal and multimodal baselines on benchmark datasets, and ablations show that schema-guided textualization and selective expert routing contribute materially to performance and stability. We additionally apply temperature scaling to obtain calibrated probabilities, ensuring reliable risk estimation for downstream decision support. Overall, MMCTOP advances multimodal trial modeling by combining controlled narrative normalization, context-conditioned expert fusion, and operational safeguards aimed at auditability and reproducibility in biomedical informatics.
Cross-Platform E-Commerce Product Categorization and Recategorization: A Multimodal Hierarchical Classification Approach
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:This study addresses critical industrial challenges in e-commerce product categorization, namely platform heterogeneity and the structural limitations of existing taxonomies, by developing and deploying a multimodal hierarchical classification framework. Using a dataset of 271,700 products from 40 international fashion e-commerce platforms, we integrate textual features (RoBERTa), visual features (ViT), and joint vision--language representations (CLIP). We investigate fusion strategies, including early, late, and attention-based fusion within a hierarchical architecture enhanced by dynamic masking to ensure taxonomic consistency. Results show that CLIP embeddings combined via an MLP-based late-fusion strategy achieve the highest hierarchical F1 (98.59\%), outperforming unimodal baselines. To address shallow or inconsistent categories, we further introduce a self-supervised ``product recategorization'' pipeline using SimCLR, UMAP, and cascade clustering, which discovered new, fine-grained categories (e.g., subtypes of ``Shoes'') with cluster purities above 86\%. Cross-platform experiments reveal a deployment-relevant trade-off: complex late-fusion methods maximize accuracy with diverse training data, while simpler early-fusion methods generalize more effectively to unseen platforms. Finally, we demonstrate the framework's industrial scalability through deployment in EURWEB's commercial transaction intelligence platform via a two-stage inference pipeline, combining a lightweight RoBERTa stage with a GPU--accelerated multimodal stage to balance cost and accuracy.
C-PATH: Conversational Patient Assistance and Triage in Healthcare System
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Navigating healthcare systems can be complex and overwhelming, creating barriers for patients seeking timely and appropriate medical attention. In this paper, we introduce C-PATH (Conversational Patient Assistance and Triage in Healthcare), a novel conversational AI system powered by large language models (LLMs) designed to assist patients in recognizing symptoms and recommending appropriate medical departments through natural, multi-turn dialogues. C-PATH is fine-tuned on medical knowledge, dialogue data, and clinical summaries using a multi-stage pipeline built on the LLaMA3 architecture. A core contribution of this work is a GPT-based data augmentation framework that transforms structured clinical knowledge from DDXPlus into lay-person-friendly conversations, allowing alignment with patient communication norms. We also implement a scalable conversation history management strategy to ensure long-range coherence. Evaluation with GPTScore demonstrates strong performance across dimensions such as clarity, informativeness, and recommendation accuracy. Quantitative benchmarks show that C-PATH achieves superior performance in GPT-rewritten conversational datasets, significantly outperforming domain-specific baselines. C-PATH represents a step forward in the development of user-centric, accessible, and accurate AI tools for digital health assistance and triage.
Optimizing Luxury Vehicle Dealership Networks: A Graph Neural Network Approach to Site Selection
Aug 25, 2024Abstract:This study presents a novel application of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to optimize dealership network planning for a luxury car manufacturer in the U.S. By conducting a comprehensive literature review on dealership location determinants, the study identifies 65 county-level explanatory variables, augmented by two additional measures of regional interconnectedness derived from social and mobility data. An ablation study involving 34 variable combinations and ten state-of-the-art GNN operators reveals key insights into the predictive power of various variables, particularly highlighting the significance of competition, demographic factors, and mobility patterns in influencing dealership location decisions. The analysis pinpoints seven specific counties as promising targets for network expansion. This research not only illustrates the effectiveness of GNNs in solving complex geospatial decision-making problems but also provides actionable recommendations and valuable methodological insights for industry practitioners.
AiGen-FoodReview: A Multimodal Dataset of Machine-Generated Restaurant Reviews and Images on Social Media
Jan 16, 2024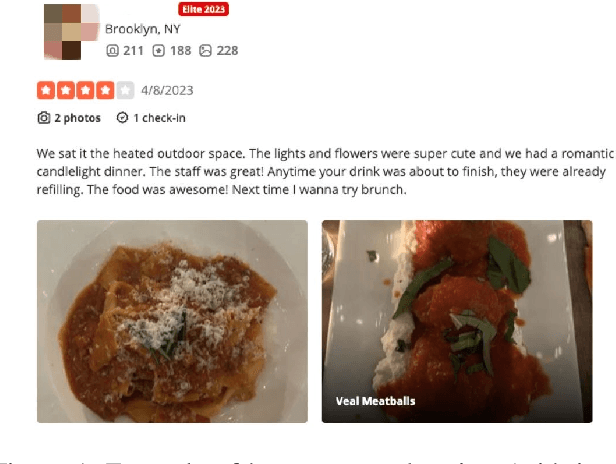

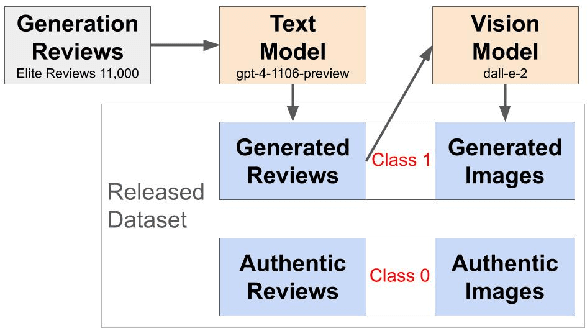
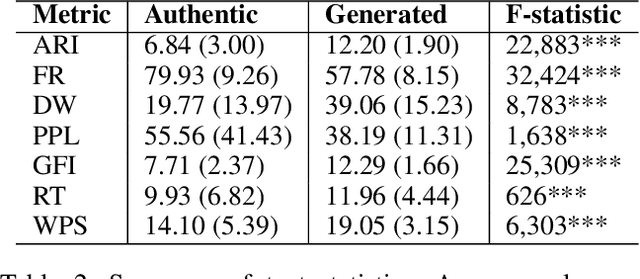
Abstract:Online reviews in the form of user-generated content (UGC) significantly impact consumer decision-making. However, the pervasive issue of not only human fake content but also machine-generated content challenges UGC's reliability. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) may pave the way to fabricate indistinguishable fake generated content at a much lower cost. Leveraging OpenAI's GPT-4-Turbo and DALL-E-2 models, we craft AiGen-FoodReview, a multi-modal dataset of 20,144 restaurant review-image pairs divided into authentic and machine-generated. We explore unimodal and multimodal detection models, achieving 99.80% multimodal accuracy with FLAVA. We use attributes from readability and photographic theories to score reviews and images, respectively, demonstrating their utility as hand-crafted features in scalable and interpretable detection models, with comparable performance. The paper contributes by open-sourcing the dataset and releasing fake review detectors, recommending its use in unimodal and multimodal fake review detection tasks, and evaluating linguistic and visual features in synthetic versus authentic data.
Dissecting Medical Referral Mechanisms in Health Services: Role of Physician Professional Networks
Dec 04, 2023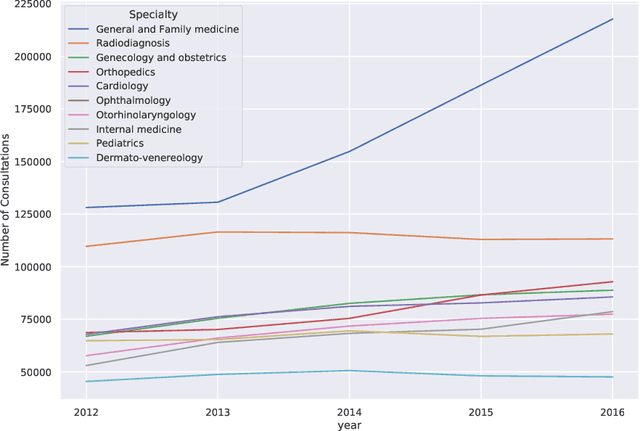
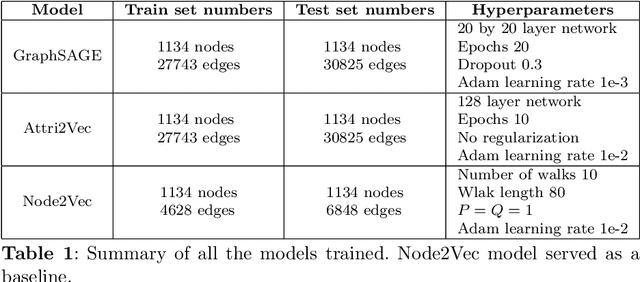
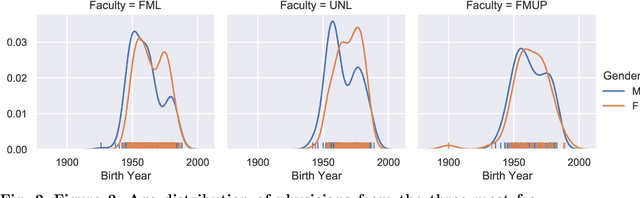
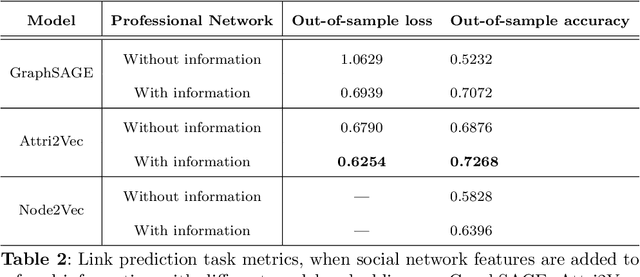
Abstract:Medical referrals between primary care physicians (PC) and specialist care (SC) physicians profoundly impact patient care regarding quality, satisfaction, and cost. This paper investigates the influence of professional networks among medical doctors on referring patients from PC to SC. Using five-year consultation data from a Portuguese private health provider, we conducted exploratory data analysis and constructed both professional and referral networks among physicians. We then apply Graph Neural Network (GNN) models to learn latent representations of the referral network. Our analysis supports the hypothesis that doctors' professional social connections can predict medical referrals, potentially enhancing collaboration within organizations and improving healthcare services. This research contributes to dissecting the underlying mechanisms in primary-specialty referrals, thereby providing valuable insights for enhancing patient care and effective healthcare management.
Extreme Multilabel Classification for Specialist Doctor Recommendation with Implicit Feedback and Limited Patient Metadata
Aug 21, 2023Abstract:Recommendation Systems (RS) are often used to address the issue of medical doctor referrals. However, these systems require access to patient feedback and medical records, which may not always be available in real-world scenarios. Our research focuses on medical referrals and aims to predict recommendations in different specialties of physicians for both new patients and those with a consultation history. We use Extreme Multilabel Classification (XML), commonly employed in text-based classification tasks, to encode available features and explore different scenarios. While its potential for recommendation tasks has often been suggested, this has not been thoroughly explored in the literature. Motivated by the doctor referral case, we show how to recast a traditional recommender setting into a multilabel classification problem that current XML methods can solve. Further, we propose a unified model leveraging patient history across different specialties. Compared to state-of-the-art RS using the same features, our approach consistently improves standard recommendation metrics up to approximately $10\%$ for patients with a previous consultation history. For new patients, XML proves better at exploiting available features, outperforming the benchmark in favorable scenarios, with particular emphasis on recall metrics. Thus, our approach brings us one step closer to creating more effective and personalized doctor referral systems. Additionally, it highlights XML as a promising alternative to current hybrid or content-based RS, while identifying key aspects to take into account when using XML for recommendation tasks.
Beyond Rankings: Exploring the Impact of SERP Features on Organic Click-through Rates
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) serve as the digital gateways to the vast expanse of the internet. Past decades have witnessed a surge in research primarily centered on the influence of website ranking on these pages, to determine the click-through rate (CTR). However, during this period, the landscape of SERPs has undergone a dramatic evolution: SERP features, encompassing elements such as knowledge panels, media galleries, FAQs, and more, have emerged as an increasingly prominent facet of these result pages. Our study examines the crucial role of these features, revealing them to be not merely aesthetic components, but strongly influence CTR and the associated behavior of internet users. We demonstrate how these features can significantly modulate web traffic, either amplifying or attenuating it. We dissect these intricate interaction effects leveraging a unique dataset of 67,000 keywords and their respective Google SERPs, spanning over 40 distinct US-based e-commerce domains, generating over 6 million clicks from 24 million views. This cross-website dataset, unprecedented in its scope, enables us to assess the impact of 24 different SERP features on organic CTR. Through an ablation study modeling CTR, we illustrate the incremental predictive power these features hold.
Interpretable Deep Learning for Forecasting Online Advertising Costs: Insights from the Competitive Bidding Landscape
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:As advertisers increasingly shift their budgets toward digital advertising, forecasting advertising costs is essential for making budget plans to optimize marketing campaign returns. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive study using a variety of time-series forecasting methods to predict daily average cost-per-click (CPC) in the online advertising market. We show that forecasting advertising costs would benefit from multivariate models using covariates from competitors' CPC development identified through time-series clustering. We further interpret the results by analyzing feature importance and temporal attention. Finally, we show that our approach has several advantages over models that individual advertisers might build based solely on their collected data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge