Alessandro Gambetti
Cross-Platform E-Commerce Product Categorization and Recategorization: A Multimodal Hierarchical Classification Approach
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:This study addresses critical industrial challenges in e-commerce product categorization, namely platform heterogeneity and the structural limitations of existing taxonomies, by developing and deploying a multimodal hierarchical classification framework. Using a dataset of 271,700 products from 40 international fashion e-commerce platforms, we integrate textual features (RoBERTa), visual features (ViT), and joint vision--language representations (CLIP). We investigate fusion strategies, including early, late, and attention-based fusion within a hierarchical architecture enhanced by dynamic masking to ensure taxonomic consistency. Results show that CLIP embeddings combined via an MLP-based late-fusion strategy achieve the highest hierarchical F1 (98.59\%), outperforming unimodal baselines. To address shallow or inconsistent categories, we further introduce a self-supervised ``product recategorization'' pipeline using SimCLR, UMAP, and cascade clustering, which discovered new, fine-grained categories (e.g., subtypes of ``Shoes'') with cluster purities above 86\%. Cross-platform experiments reveal a deployment-relevant trade-off: complex late-fusion methods maximize accuracy with diverse training data, while simpler early-fusion methods generalize more effectively to unseen platforms. Finally, we demonstrate the framework's industrial scalability through deployment in EURWEB's commercial transaction intelligence platform via a two-stage inference pipeline, combining a lightweight RoBERTa stage with a GPU--accelerated multimodal stage to balance cost and accuracy.
AiGen-FoodReview: A Multimodal Dataset of Machine-Generated Restaurant Reviews and Images on Social Media
Jan 16, 2024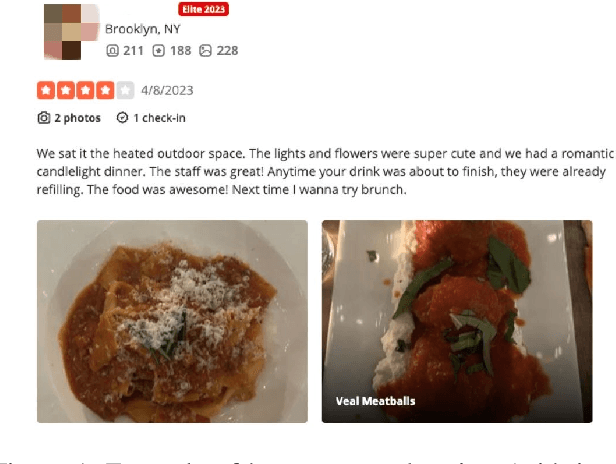

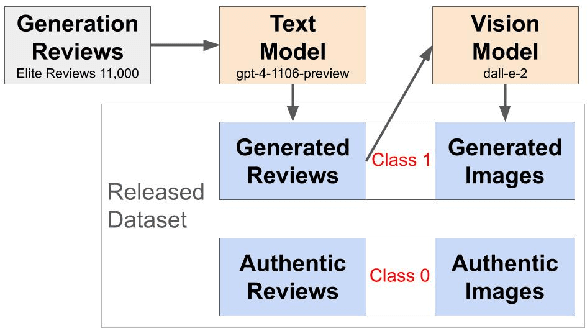
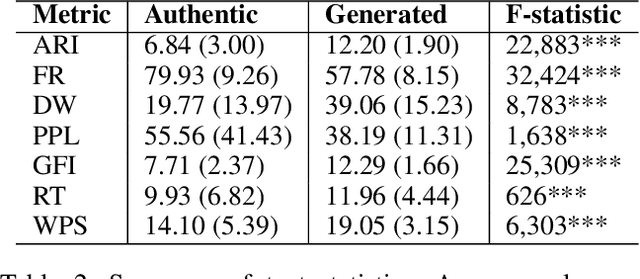
Abstract:Online reviews in the form of user-generated content (UGC) significantly impact consumer decision-making. However, the pervasive issue of not only human fake content but also machine-generated content challenges UGC's reliability. Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) may pave the way to fabricate indistinguishable fake generated content at a much lower cost. Leveraging OpenAI's GPT-4-Turbo and DALL-E-2 models, we craft AiGen-FoodReview, a multi-modal dataset of 20,144 restaurant review-image pairs divided into authentic and machine-generated. We explore unimodal and multimodal detection models, achieving 99.80% multimodal accuracy with FLAVA. We use attributes from readability and photographic theories to score reviews and images, respectively, demonstrating their utility as hand-crafted features in scalable and interpretable detection models, with comparable performance. The paper contributes by open-sourcing the dataset and releasing fake review detectors, recommending its use in unimodal and multimodal fake review detection tasks, and evaluating linguistic and visual features in synthetic versus authentic data.
Combat AI With AI: Counteract Machine-Generated Fake Restaurant Reviews on Social Media
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in generative models such as GPT may be used to fabricate indistinguishable fake customer reviews at a much lower cost, thus posing challenges for social media platforms to detect these machine-generated fake reviews. We propose to leverage the high-quality elite restaurant reviews verified by Yelp to generate fake reviews from the OpenAI GPT review creator and ultimately fine-tune a GPT output detector to predict fake reviews that significantly outperforms existing solutions. We further apply the model to predict non-elite reviews and identify the patterns across several dimensions, such as review, user and restaurant characteristics, and writing style. We show that social media platforms are continuously challenged by machine-generated fake reviews, although they may implement detection systems to filter out suspicious reviews.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge