Qiusheng Zhou
Deep Spatial Gradient and Temporal Depth Learning for Face Anti-spoofing
Mar 18, 2020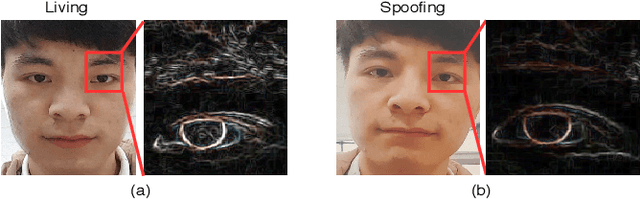
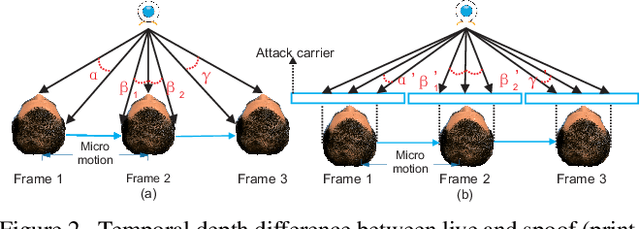

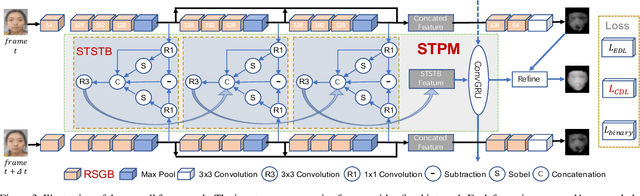
Abstract:Face anti-spoofing is critical to the security of face recognition systems. Depth supervised learning has been proven as one of the most effective methods for face anti-spoofing. Despite the great success, most previous works still formulate the problem as a single-frame multi-task one by simply augmenting the loss with depth, while neglecting the detailed fine-grained information and the interplay between facial depths and moving patterns. In contrast, we design a new approach to detect presentation attacks from multiple frames based on two insights: 1) detailed discriminative clues (e.g., spatial gradient magnitude) between living and spoofing face may be discarded through stacked vanilla convolutions, and 2) the dynamics of 3D moving faces provide important clues in detecting the spoofing faces. The proposed method is able to capture discriminative details via Residual Spatial Gradient Block (RSGB) and encode spatio-temporal information from Spatio-Temporal Propagation Module (STPM) efficiently. Moreover, a novel Contrastive Depth Loss is presented for more accurate depth supervision. To assess the efficacy of our method, we also collect a Double-modal Anti-spoofing Dataset (DMAD) which provides actual depth for each sample. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art results on five benchmark datasets including OULU-NPU, SiW, CASIA-MFSD, Replay-Attack, and the new DMAD. Codes will be available at https://github.com/clks-wzz/FAS-SGTD.
Exploiting temporal and depth information for multi-frame face anti-spoofing
Nov 26, 2018



Abstract:Face anti-spoofing is significant to the security of face recognition systems. Previous works on depth supervised learning have proved the effectiveness for face anti-spoofing. Nevertheless, they only considered the depth as an auxiliary supervision in the single frame. Different from these methods, we develop a new method to estimate depth information from multiple RGB frames and propose a depth-supervised architecture which can efficiently encodes spatiotemporal information for presentation attack detection. It includes two novel modules: optical flow guided feature block (OFFB) and convolution gated recurrent units (ConvGRU) module, which are designed to extract short-term and long-term motion to discriminate living and spoofing faces. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art results on four benchmark datasets, namely OULU-NPU, SiW, CASIA-MFSD, and Replay-Attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge