Qiong Gu
CountFormer: Multi-View Crowd Counting Transformer
Jul 02, 2024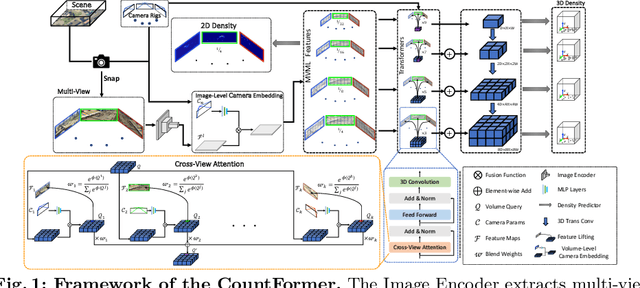
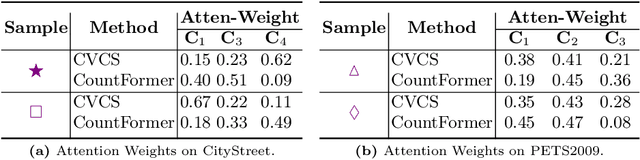

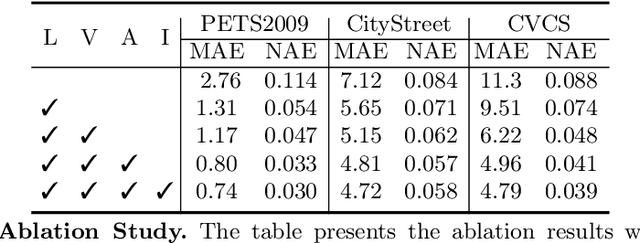
Abstract:Multi-view counting (MVC) methods have shown their superiority over single-view counterparts, particularly in situations characterized by heavy occlusion and severe perspective distortions. However, hand-crafted heuristic features and identical camera layout requirements in conventional MVC methods limit their applicability and scalability in real-world scenarios.In this work, we propose a concise 3D MVC framework called \textbf{CountFormer}to elevate multi-view image-level features to a scene-level volume representation and estimate the 3D density map based on the volume features. By incorporating a camera encoding strategy, CountFormer successfully embeds camera parameters into the volume query and image-level features, enabling it to handle various camera layouts with significant differences.Furthermore, we introduce a feature lifting module capitalized on the attention mechanism to transform image-level features into a 3D volume representation for each camera view. Subsequently, the multi-view volume aggregation module attentively aggregates various multi-view volumes to create a comprehensive scene-level volume representation, allowing CountFormer to handle images captured by arbitrary dynamic camera layouts. The proposed method performs favorably against the state-of-the-art approaches across various widely used datasets, demonstrating its greater suitability for real-world deployment compared to conventional MVC frameworks.
MToP: A MATLAB Optimization Platform for Evolutionary Multitasking
Dec 13, 2023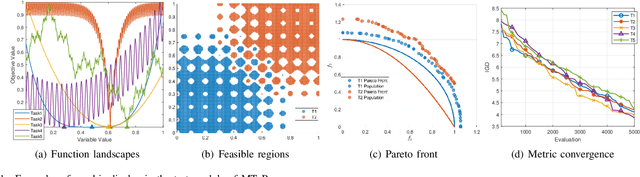
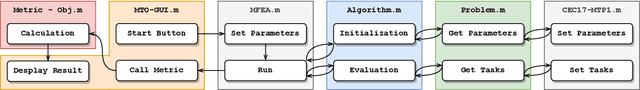
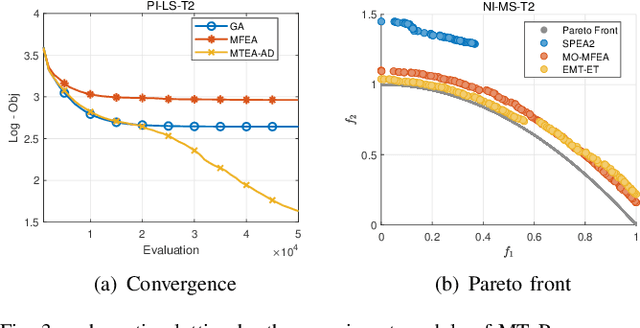
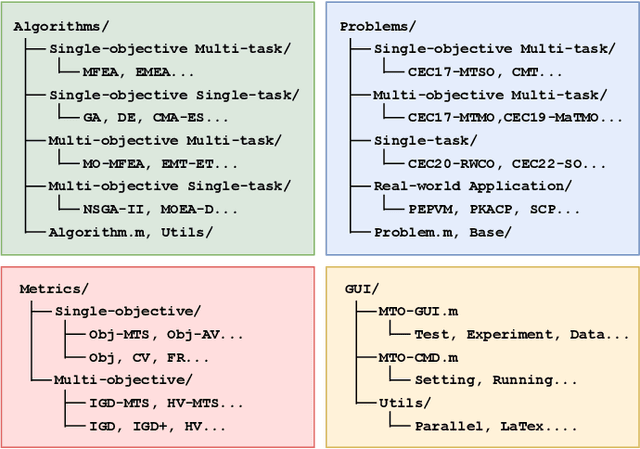
Abstract:Evolutionary multitasking (EMT) has been attracting much attention over the past years. It aims to handle multiple optimization tasks simultaneously within limited computing resources assisted by inter-task knowledge transfer techniques. Numerous multitask evolutionary algorithms (MTEAs) for solving multitask optimization (MTO) problems have been proposed in the EMT field, but there lacks a comprehensive software platform to help researchers evaluate MTEA performance on benchmark MTO problems as well as explore real-world applications. To address this issue, we introduce the first open-source optimization platform, named MTO-Platform (MToP), for EMT. It incorporates more than 30 MTEAs, more than 150 MTO problem cases with real-world applications, and more than 10 performance metrics. Moreover, for comparing MTEAs with traditional evolutionary algorithms, we modified more than 30 popular single-task evolutionary algorithms to be able to solve MTO problems in MToP. MToP is a user-friendly tool with a graphical user interface that makes it easy to analyze results, export data, and plot schematics. More importantly, MToP is extensible, allowing users to develop new algorithms and define new problems. The source code of MToP is available at https://github.com/intLyc/MTO-Platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge