Pranav Ganti
Visual SLAM with Network Uncertainty Informed Feature Selection
Nov 29, 2018



Abstract:In order to facilitate long-term localization using a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm, careful feature selection is required such that reference points persist over long durations and the runtime and storage complexity of the algorithm remain consistent. We present SIVO (Semantically Informed Visual Odometry and Mapping), a novel information-theoretic feature selection method for visual SLAM which incorporates machine learning and neural network uncertainty into the feature selection pipeline. Our algorithm selects points which provide the highest reduction in Shannon entropy between the entropy of the current state, and the joint entropy of the state given the addition of the new feature with the classification entropy of the feature from a Bayesian neural network. This feature selection strategy generates a sparse map suitable for long-term localization, as each selected feature significantly reduces the uncertainty of the vehicle state and has been detected to be a static object (building, traffic sign, etc.) repeatedly with a high confidence. The KITTI odometry dataset is used to evaluate our method, and we also compare our results against ORB_SLAM2. Overall, SIVO performs comparably to ORB_SLAM2 (average of 0.17% translation error difference, 6.2 x 10^(-5) deg/m rotation error difference) while reducing the map size by 69%.
Encoderless Gimbal Calibration of Dynamic Multi-Camera Clusters
Jul 24, 2018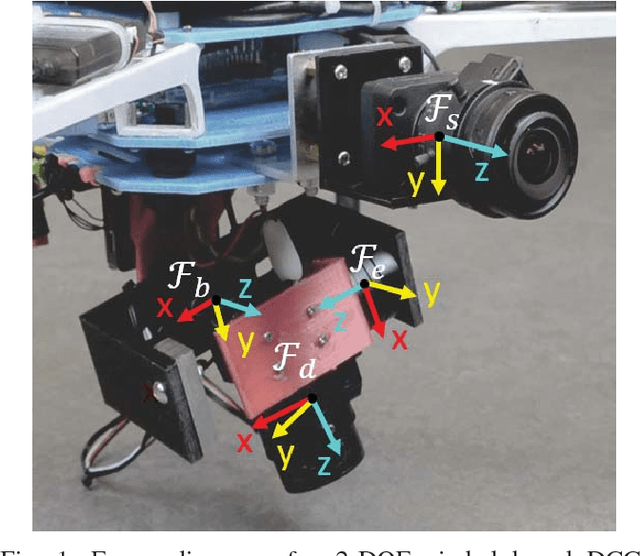
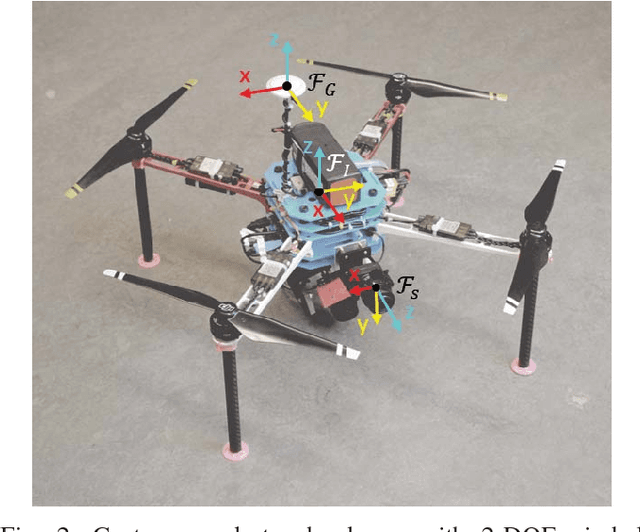
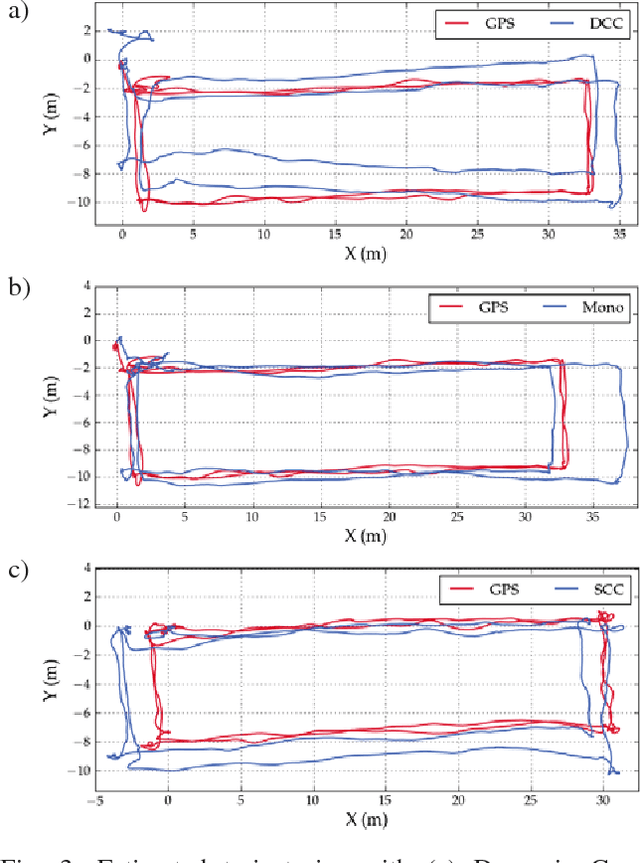

Abstract:Dynamic Camera Clusters (DCCs) are multi-camera systems where one or more cameras are mounted on actuated mechanisms such as a gimbal. Existing methods for DCC calibration rely on joint angle measurements to resolve the time-varying transformation between the dynamic and static camera. This information is usually provided by motor encoders, however, joint angle measurements are not always readily available on off-the-shelf mechanisms. In this paper, we present an encoderless approach for DCC calibration which simultaneously estimates the kinematic parameters of the transformation chain as well as the unknown joint angles. We also demonstrate the integration of an encoderless gimbal mechanism with a state-of-the art VIO algorithm, and show the extensions required in order to perform simultaneous online estimation of the joint angles and vehicle localization state. The proposed calibration approach is validated both in simulation and on a physical DCC composed of a 2-DOF gimbal mounted on a UAV. Finally, we show the experimental results of the calibrated mechanism integrated into the OKVIS VIO package, and demonstrate successful online joint angle estimation while maintaining localization accuracy that is comparable to a standard static multi-camera configuration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge