Pooja Maknikar
Embracing Structure in Data for Billion-Scale Semantic Product Search
Oct 12, 2021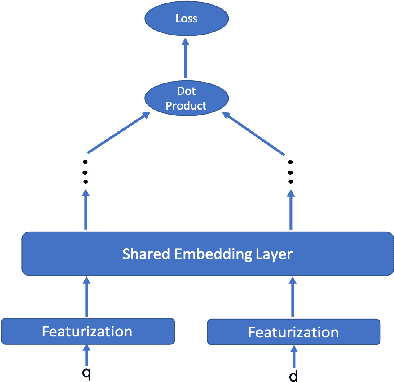
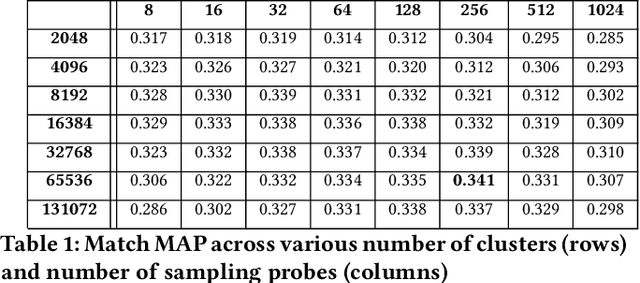
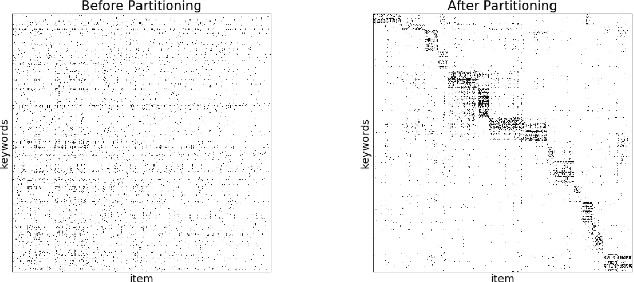
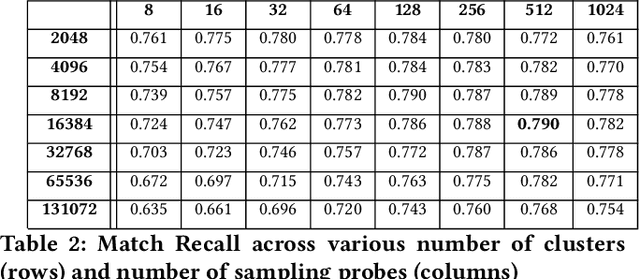
Abstract:We present principled approaches to train and deploy dyadic neural embedding models at the billion scale, focusing our investigation on the application of semantic product search. When training a dyadic model, one seeks to embed two different types of entities (e.g., queries and documents or users and movies) in a common vector space such that pairs with high relevance are positioned nearby. During inference, given an embedding of one type (e.g., a query or a user), one seeks to retrieve the entities of the other type (e.g., documents or movies, respectively) that are highly relevant. In this work, we show that exploiting the natural structure of real-world datasets helps address both challenges efficiently. Specifically, we model dyadic data as a bipartite graph with edges between pairs with positive associations. We then propose to partition this network into semantically coherent clusters and thus reduce our search space by focusing on a small subset of these partitions for a given input. During training, this technique enables us to efficiently mine hard negative examples while, at inference, we can quickly find the nearest neighbors for a given embedding. We provide offline experimental results that demonstrate the efficacy of our techniques for both training and inference on a billion-scale Amazon.com product search dataset.
Performance Evaluation of Different Techniques for texture Classification
Oct 29, 2012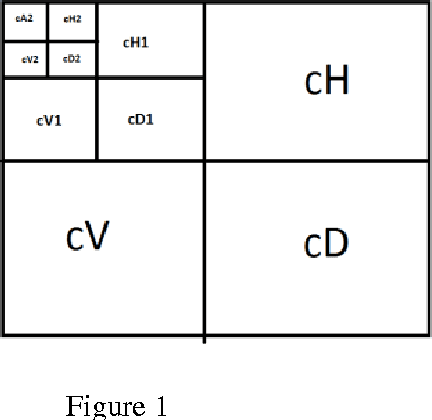
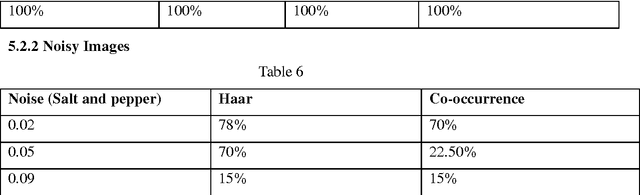
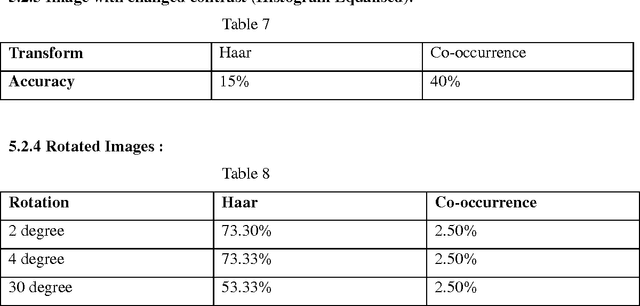
Abstract:Texture is the term used to characterize the surface of a given object or phenomenon and is an important feature used in image processing and pattern recognition. Our aim is to compare various Texture analyzing methods and compare the results based on time complexity and accuracy of classification. The project describes texture classification using Wavelet Transform and Co occurrence Matrix. Comparison of features of a sample texture with database of different textures is performed. In wavelet transform we use the Haar, Symlets and Daubechies wavelets. We find that, thee Haar wavelet proves to be the most efficient method in terms of performance assessment parameters mentioned above. Comparison of Haar wavelet and Co-occurrence matrix method of classification also goes in the favor of Haar. Though the time requirement is high in the later method, it gives excellent results for classification accuracy except if the image is rotated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge