Pinlong Zhao
Data Poisoning in Deep Learning: A Survey
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has become a cornerstone of modern artificial intelligence, enabling transformative applications across a wide range of domains. As the core element of deep learning, the quality and security of training data critically influence model performance and reliability. However, during the training process, deep learning models face the significant threat of data poisoning, where attackers introduce maliciously manipulated training data to degrade model accuracy or lead to anomalous behavior. While existing surveys provide valuable insights into data poisoning, they generally adopt a broad perspective, encompassing both attacks and defenses, but lack a dedicated, in-depth analysis of poisoning attacks specifically in deep learning. In this survey, we bridge this gap by presenting a comprehensive and targeted review of data poisoning in deep learning. First, this survey categorizes data poisoning attacks across multiple perspectives, providing an in-depth analysis of their characteristics and underlying design princinples. Second, the discussion is extended to the emerging area of data poisoning in large language models(LLMs). Finally, we explore critical open challenges in the field and propose potential research directions to advance the field further. To support further exploration, an up-to-date repository of resources on data poisoning in deep learning is available at https://github.com/Pinlong-Zhao/Data-Poisoning.
Detecting Adversarial Examples via Key-based Network
Jun 02, 2018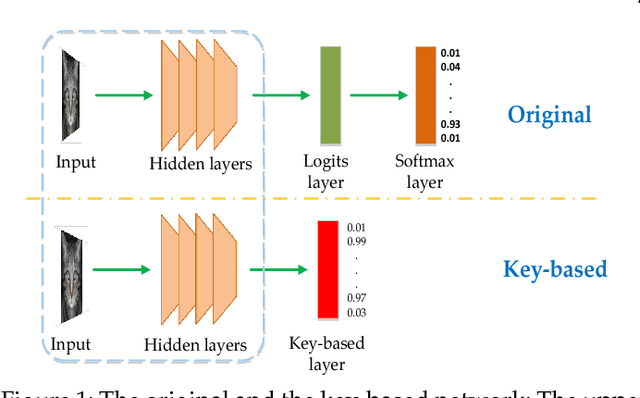
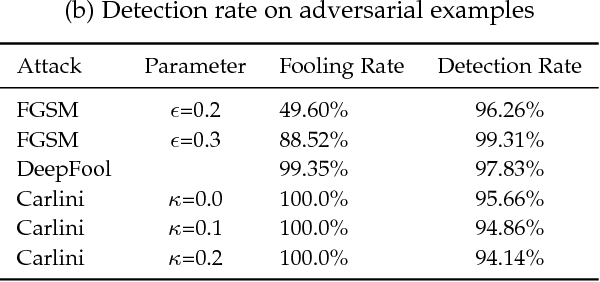
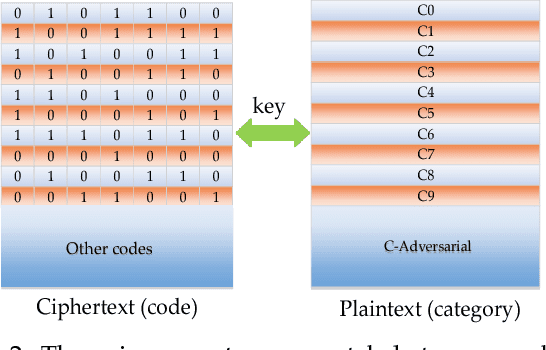
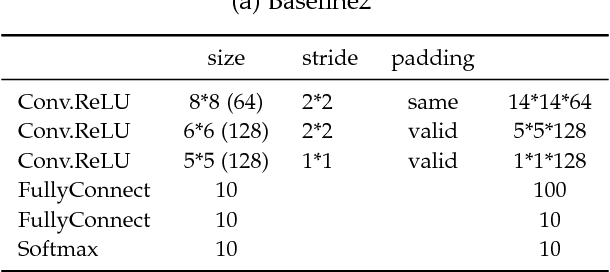
Abstract:Though deep neural networks have achieved state-of-the-art performance in visual classification, recent studies have shown that they are all vulnerable to the attack of adversarial examples. Small and often imperceptible perturbations to the input images are sufficient to fool the most powerful deep neural networks. Various defense methods have been proposed to address this issue. However, they either require knowledge on the process of generating adversarial examples, or are not robust against new attacks specifically designed to penetrate the existing defense. In this work, we introduce key-based network, a new detection-based defense mechanism to distinguish adversarial examples from normal ones based on error correcting output codes, using the binary code vectors produced by multiple binary classifiers applied to randomly chosen label-sets as signatures to match normal images and reject adversarial examples. In contrast to existing defense methods, the proposed method does not require knowledge of the process for generating adversarial examples and can be applied to defend against different types of attacks. For the practical black-box and gray-box scenarios, where the attacker does not know the encoding scheme, we show empirically that key-based network can effectively detect adversarial examples generated by several state-of-the-art attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge