Pingyue Yue
Multiple Satellites Collaboration for Joint Code-aided CFOs and CPOs Estimation
Sep 25, 2023

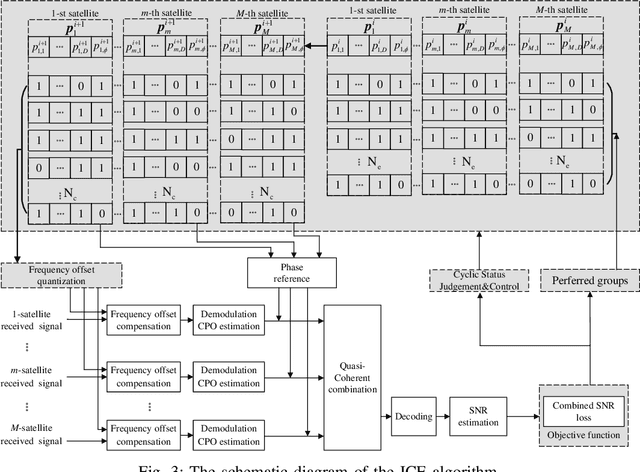

Abstract:Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are being extensively researched in the development of secure Internet of Remote Things (IoRT). In scenarios with miniaturized terminals, the limited transmission power and long transmission distance often lead to low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) at the satellite receiver, which degrades communication performance. A solution to address this issue is the utilization of cooperative satellites, which can combine signals received from multiple satellites, thereby significantly improve SNR. However, in order to maximize the combination gain, the signal coherent combining is necessary, which requires the carrier frequency and phase of each receiving signal to be aligned. Under low SNR circumstances, carrier parameter estimation can be a significant challenge, especially for short burst transmission with no training sequence. In order to tackle it, we propose an iterative code-aided estimation algorithm for joint Carrier Frequency Offset (CFO) and Carrier Phase Offset (CPO). The Cram\'er-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) is suggested as the limit on the parameter estimation performance. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can approach Bit Error Rate (BER) performance bound within 0.4 dB with regards to four-satellite collaboration.
On the Security of LEO Satellite Communication Systems: Vulnerabilities, Countermeasures, and Future Trends
Jan 09, 2022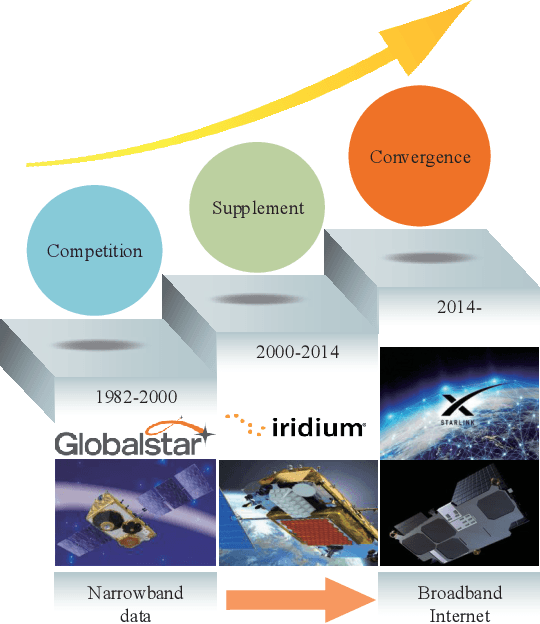
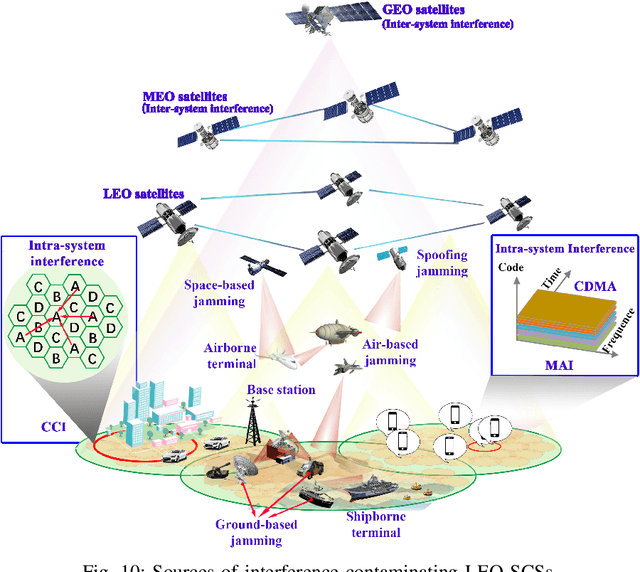
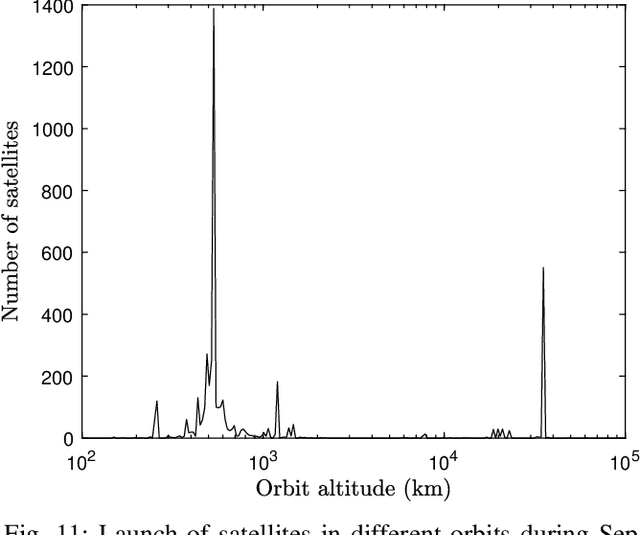
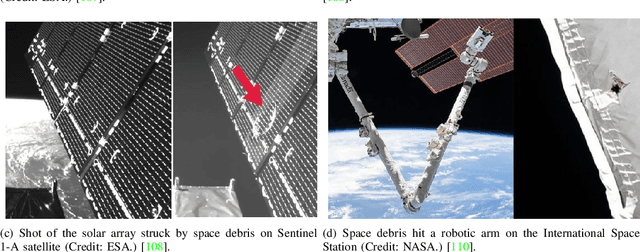
Abstract:Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite systems undergo a period of rapid development driven by the ever-increasing user demands, reduced costs, and technological progress. Since there is a paucity of literature on the security issues of LEO Satellite Communication Systems (SCSs), we aim for filling this knowledge gap. Specifically, we critically appraise the inherent characteristics of LEO SCSs and summarize their unique security vulnerabilities. In light of this, we further discuss their security vulnerabilities, including the issues of passive and active eavesdropping attacks, interference scenarios, single event upsets, and space debris. Subsequently, we discuss the corresponding active and passive security countermeasures, followed by unveiling a range of trade-offs, security vulnerabilities and their countermeasures. Furthermore, we shed light on several promising future research directions for enhancing the security of LEO SCSs, such as secure quantum communications, three-dimensional virtual arrays, artificial intelligence-based security measures, space-based blockchain, and intelligent reflecting surface enabled secure transmission. Finally, the take-away messages of this paper are crystallized in our concluding design guidelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge