Pengfei Fan
Toward Dependency Dynamics in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Traffic Signal Control
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) emerges as a promising data-driven approach for adaptive traffic signal control (ATSC) in complex urban traffic networks, with deep neural networks substantially augmenting its learning capabilities. However, centralized RL becomes impractical for ATSC involving multiple agents due to the exceedingly high dimensionality of the joint action space. Multi-agent RL (MARL) mitigates this scalability issue by decentralizing control to local RL agents. Nevertheless, this decentralized method introduces new challenges: the environment becomes partially observable from the perspective of each local agent due to constrained inter-agent communication. Both centralized RL and MARL exhibit distinct strengths and weaknesses, particularly under heavy intersectional traffic conditions. In this paper, we justify that MARL can achieve the optimal global Q-value by separating into multiple IRL (Independent Reinforcement Learning) processes when no spill-back congestion occurs (no agent dependency) among agents (intersections). In the presence of spill-back congestion (with agent dependency), the maximum global Q-value can be achieved by using centralized RL. Building upon the conclusions, we propose a novel Dynamic Parameter Update Strategy for Deep Q-Network (DQN-DPUS), which updates the weights and bias based on the dependency dynamics among agents, i.e. updating only the diagonal sub-matrices for the scenario without spill-back congestion. We validate the DQN-DPUS in a simple network with two intersections under varying traffic, and show that the proposed strategy can speed up the convergence rate without sacrificing optimal exploration. The results corroborate our theoretical findings, demonstrating the efficacy of DQN-DPUS in optimizing traffic signal control.
High speed free-space optical communication using standard fiber communication component without optical amplification
Feb 27, 2023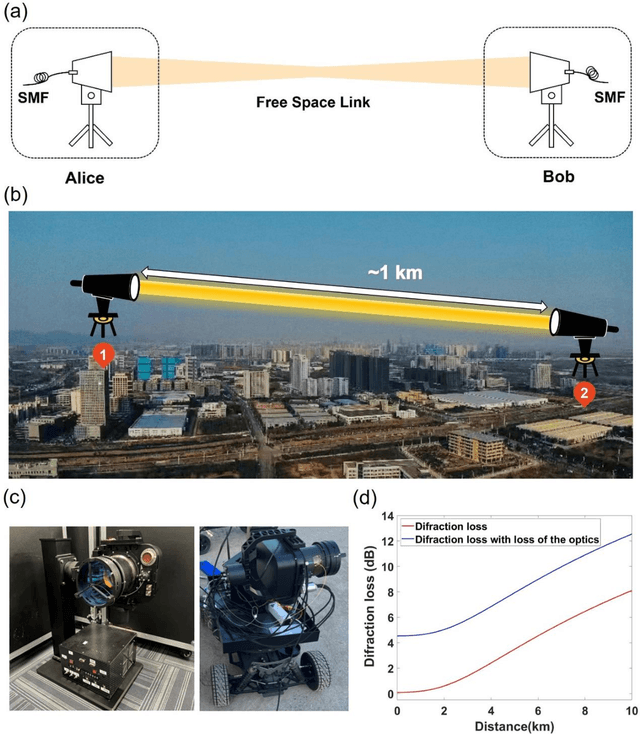
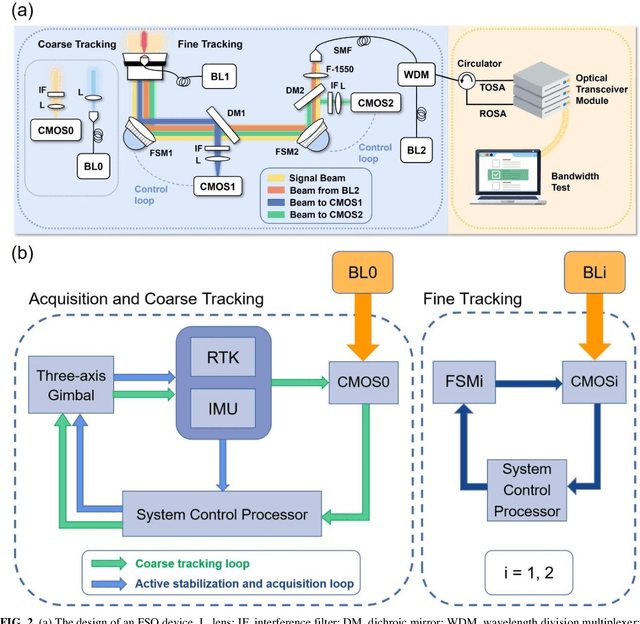
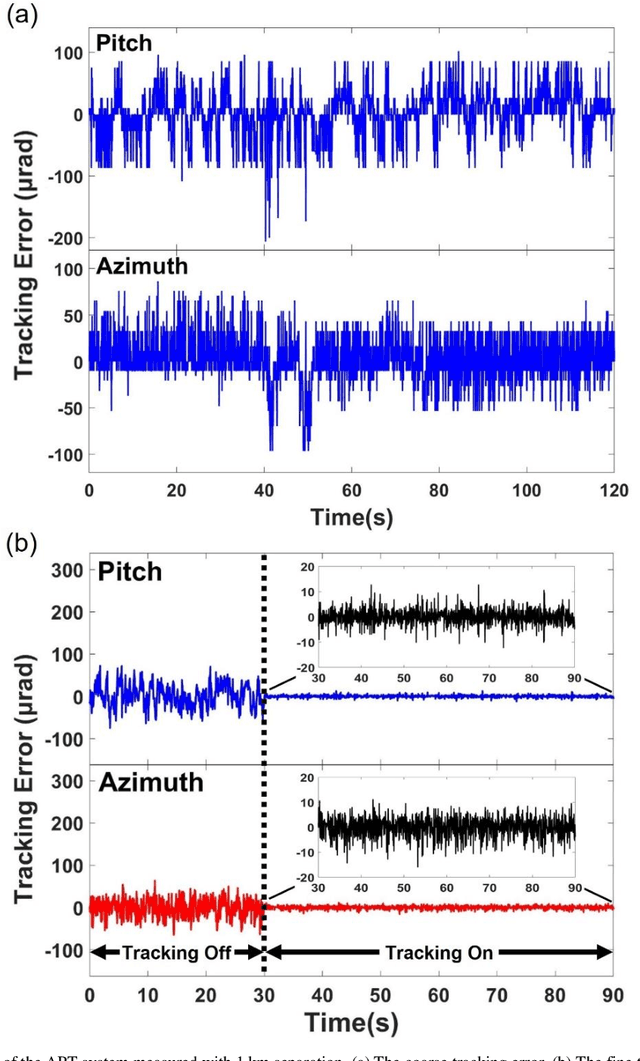
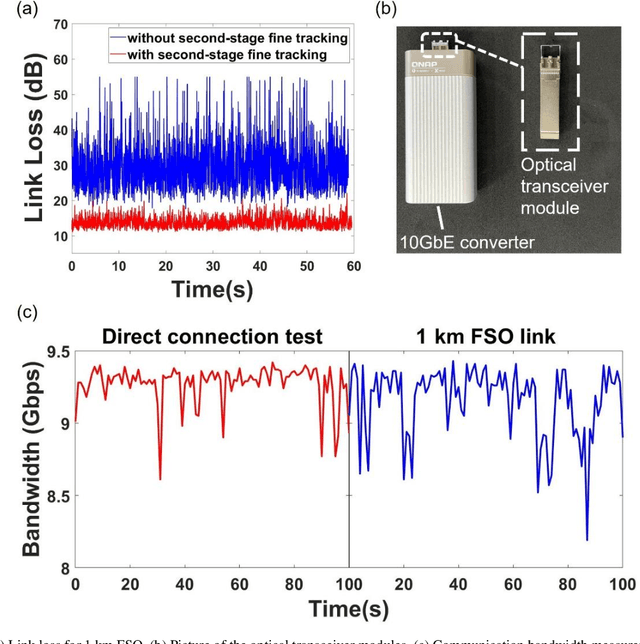
Abstract:Free-space optical communication (FSO) can achieve fast, secure and license-free communication without need for physical cables, making it a cost-effective, energy-efficient and flexible solution when the fiber connection is absent. To establish FSO connection on-demand, it is essential to build portable FSO devices with compact structure and light weight. Here, we develop a miniaturized FSO system and realize 9.16 Gbps FSO between two nodes that is 1 km apart, using a commercial fiber-coupled optical transceiver module with no optical amplification. Basing on the home-made compact 90 mm-diameter acquisition, pointing and tracking (APT) system with four-stage close-loop feedback, the link tracking error is controlled at 3 {\mu}rad and results an average coupling loss of 13.7 dB. Such loss is within the tolerance of the commercial optical communication modules, and without the need of optical amplifiers, which contributes to the low system weight and power consumption. As a result, a single FSO device weighs only about 12 kg, making it compact and portable for potential application in high-speed wireless communication. Our FSO link has been tested up to 4 km, with link loss of 18 dB in the foggy weather in Nanjing, that shows longer distances can be covered with optical amplification.
Light Propagation Prediction through Multimode Optical Fibers with a Deep Neural Network
Dec 06, 2018

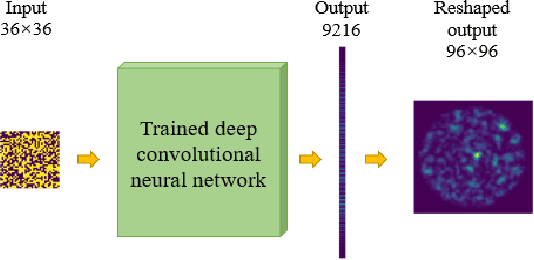
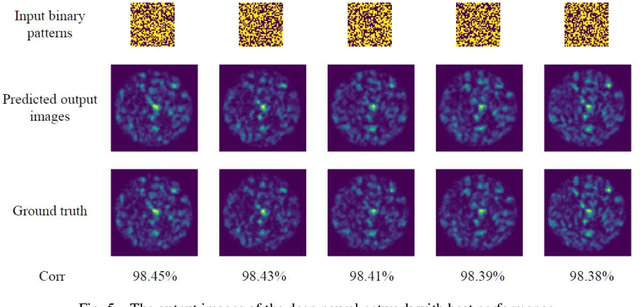
Abstract:This work demonstrates a computational method for predicting the light propagation through a single multimode fiber using a deep neural network. The experiment for gathering training and testing data is performed with a digital micro-mirror device that enables the spatial light modulation. The modulated patterns on the device and the captured intensity-only images by the camera form the aligned data pairs. This sufficiently-trained deep neural network frame has very excellent performance for directly inferring the intensity-only output delivered though a multimode fiber. The model is validated by three standards: the mean squared error (MSE), the correlation coefficient (corr) and the structural similarity index (SSIM).
Deep learning the high variability and randomness inside multimode fibres
Jul 18, 2018


Abstract:Multimode fibres (MMF) are remarkable high-capacity information channels owing to the large number of transmitting fibre modes, and have recently attracted significant renewed interest in applications such as optical communication, imaging, and optical trapping. At the same time, the optical transmitting modes inside MMFs are highly sensitive to external perturbations and environmental changes, resulting in MMF transmission channels being highly variable and random. This largely limits the practical application of MMFs and hinders the full exploitation of their information capacity. Despite great research efforts made to overcome the high variability and randomness inside MMFs, any geometric change to the MMF leads to completely different transmission matrices, which unavoidably fails at the information recovery. Here, we show the successful binary image transmission using deep learning through a single MMF, which is stationary or subject to dynamic shape variations. We found that a single convolutional neural network has excellent generalisation capability with various MMF transmission states. This deep neural network can be trained by multiple MMF transmission states to accurately predict unknown information at the other end of the MMF at any of these states, without knowing which state is present. Our results demonstrate that deep learning is a promising solution to address the variability and randomness challenge of MMF based information channels. This deep-learning approach is the starting point of developing future high-capacity MMF optical systems and devices, and is applicable to optical systems concerning other diffusing media.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge