Peipei Zhu
Prompt-based Learning for Unpaired Image Captioning
May 26, 2022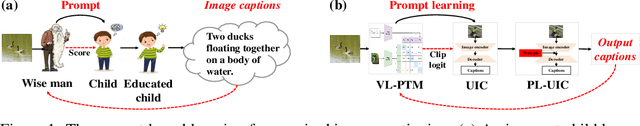
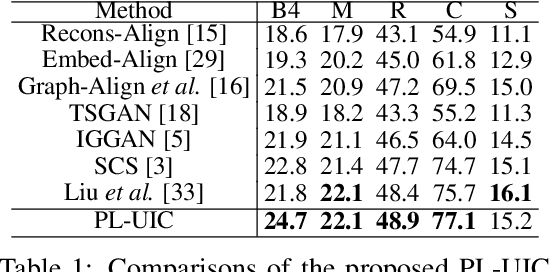
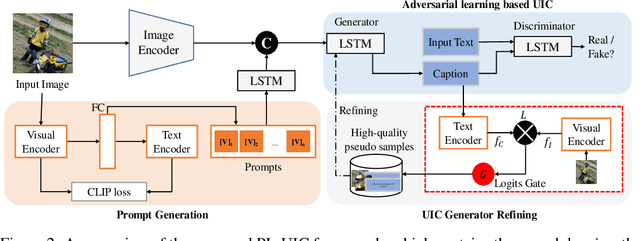
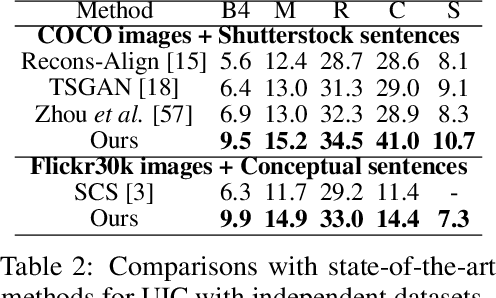
Abstract:Unpaired Image Captioning (UIC) has been developed to learn image descriptions from unaligned vision-language sample pairs. Existing schemes usually adopt the visual concept reward of reinforcement learning to obtain the alignment between visual concepts and images. However, the cross-domain alignment is usually weak that severely constrains the overall performance of these existing schemes. Recent successes of Vision-Language Pre-Trained Models (VL-PTMs) have triggered the development of prompt-based learning from VL-PTMs. We present in this paper a novel scheme based on prompt to train the UIC model, making best use of the powerful generalization ability and abundant vision-language prior knowledge learned under VL-PTMs. We adopt the CLIP model for this research in unpaired image captioning. Specifically, the visual images are taken as input to the prompt generation module, which contains the pre-trained model as well as one feed-forward layer for prompt extraction. Then, the input images and generated prompts are aggregated for unpaired adversarial captioning learning. To further enhance the potential performance of the captioning, we designed a high-quality pseudo caption filter guided by the CLIP logits to measure correlations between predicted captions and the corresponding images. This allows us to improve the captioning model in a supervised learning manner. Extensive experiments on the COCO and Flickr30K datasets have been carried out to validate the superiority of the proposed model. We have achieved the state-of-the-art performance on the COCO dataset, which outperforms the best UIC model by 1.9% on the BLEU-4 metric. We expect that the proposed prompt-based UIC model will inspire a new line of research for the VL-PTMs based captioning.
Unpaired Image Captioning by Image-level Weakly-Supervised Visual Concept Recognition
Mar 07, 2022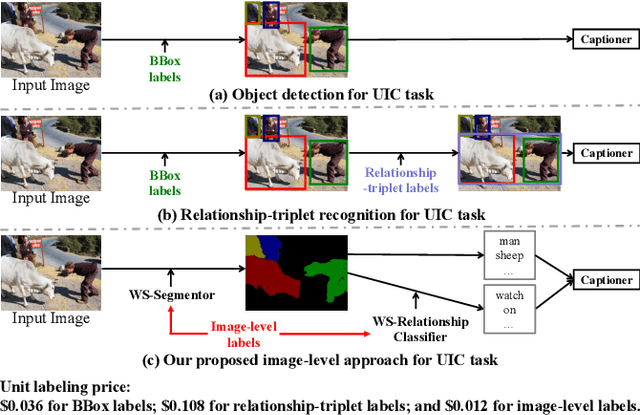
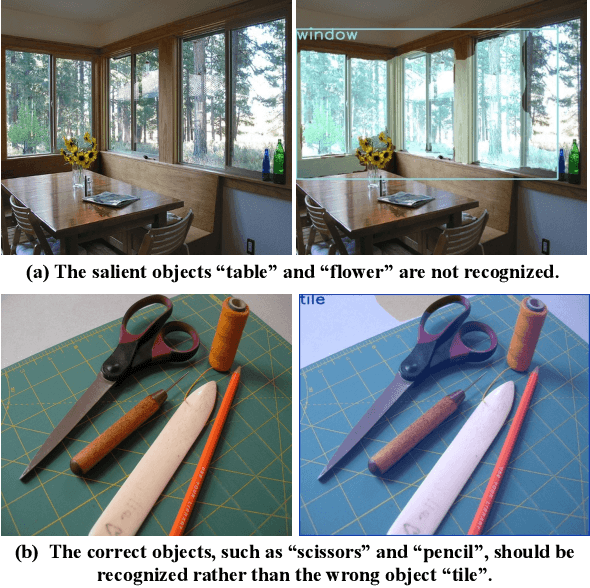

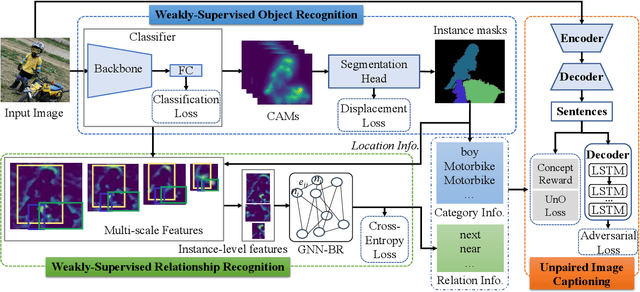
Abstract:The goal of unpaired image captioning (UIC) is to describe images without using image-caption pairs in the training phase. Although challenging, we except the task can be accomplished by leveraging a training set of images aligned with visual concepts. Most existing studies use off-the-shelf algorithms to obtain the visual concepts because the Bounding Box (BBox) labels or relationship-triplet labels used for the training are expensive to acquire. In order to resolve the problem in expensive annotations, we propose a novel approach to achieve cost-effective UIC. Specifically, we adopt image-level labels for the optimization of the UIC model in a weakly-supervised manner. For each image, we assume that only the image-level labels are available without specific locations and numbers. The image-level labels are utilized to train a weakly-supervised object recognition model to extract object information (e.g., instance) in an image, and the extracted instances are adopted to infer the relationships among different objects based on an enhanced graph neural network (GNN). The proposed approach achieves comparable or even better performance compared with previous methods without the expensive cost of annotations. Furthermore, we design an unrecognized object (UnO) loss combined with a visual concept reward to improve the alignment of the inferred object and relationship information with the images. It can effectively alleviate the issue encountered by existing UIC models about generating sentences with nonexistent objects. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to solve the problem of Weakly-Supervised visual concept recognition for UIC (WS-UIC) based only on image-level labels. Extensive experiments have been carried out to demonstrate that the proposed WS-UIC model achieves inspiring results on the COCO dataset while significantly reducing the cost of labeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge