Pavan Kandru
GrapeQA: GRaph Augmentation and Pruning to Enhance Question-Answering
Mar 22, 2023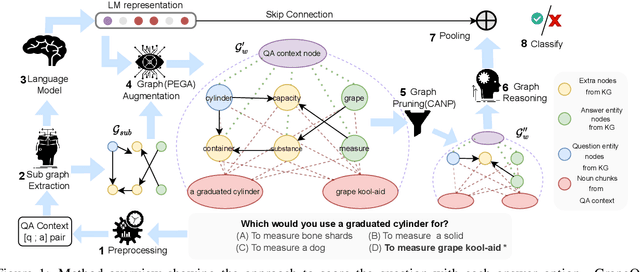
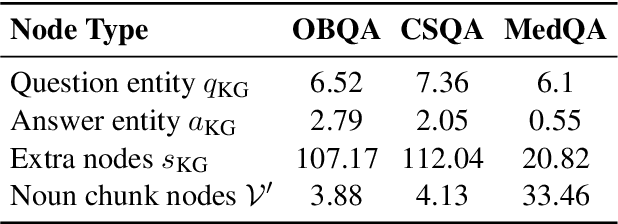
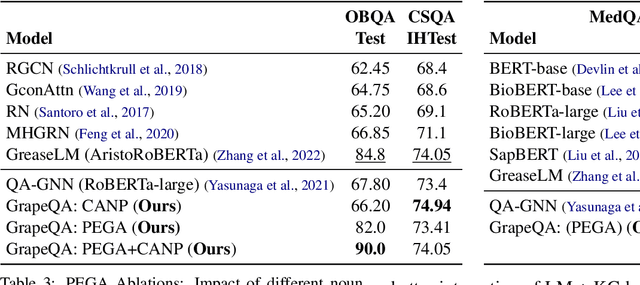

Abstract:Commonsense question-answering (QA) methods combine the power of pre-trained Language Models (LM) with the reasoning provided by Knowledge Graphs (KG). A typical approach collects nodes relevant to the QA pair from a KG to form a Working Graph (WG) followed by reasoning using Graph Neural Networks(GNNs). This faces two major challenges: (i) it is difficult to capture all the information from the QA in the WG, and (ii) the WG contains some irrelevant nodes from the KG. To address these, we propose GrapeQA with two simple improvements on the WG: (i) Prominent Entities for Graph Augmentation identifies relevant text chunks from the QA pair and augments the WG with corresponding latent representations from the LM, and (ii) Context-Aware Node Pruning removes nodes that are less relevant to the QA pair. We evaluate our results on OpenBookQA, CommonsenseQA and MedQA-USMLE and see that GrapeQA shows consistent improvements over its LM + KG predecessor (QA-GNN in particular) and large improvements on OpenBookQA.
Massively Multilingual Language Models for Cross Lingual Fact Extraction from Low Resource Indian Languages
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:Massive knowledge graphs like Wikidata attempt to capture world knowledge about multiple entities. Recent approaches concentrate on automatically enriching these KGs from text. However a lot of information present in the form of natural text in low resource languages is often missed out. Cross Lingual Information Extraction aims at extracting factual information in the form of English triples from low resource Indian Language text. Despite its massive potential, progress made on this task is lagging when compared to Monolingual Information Extraction. In this paper, we propose the task of Cross Lingual Fact Extraction(CLFE) from text and devise an end-to-end generative approach for the same which achieves an overall F1 score of 77.46.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge