Paul Schneider
The Wisdom of Deliberating AI Crowds: Does Deliberation Improve LLM-Based Forecasting?
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Structured deliberation has been found to improve the performance of human forecasters. This study investigates whether a similar intervention, i.e. allowing LLMs to review each other's forecasts before updating, can improve accuracy in large language models (GPT-5, Claude Sonnet 4.5, Gemini Pro 2.5). Using 202 resolved binary questions from the Metaculus Q2 2025 AI Forecasting Tournament, accuracy was assessed across four scenarios: (1) diverse models with distributed information, (2) diverse models with shared information, (3) homogeneous models with distributed information, and (4) homogeneous models with shared information. Results show that the intervention significantly improves accuracy in scenario (2), reducing Log Loss by 0.020 or about 4 percent in relative terms (p = 0.017). However, when homogeneous groups (three instances of the same model) engaged in the same process, no benefit was observed. Unexpectedly, providing LLMs with additional contextual information did not improve forecast accuracy, limiting our ability to study information pooling as a mechanism. Our findings suggest that deliberation may be a viable strategy for improving LLM forecasting.
Kernel Density Machines
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce kernel density machines (KDM), a novel density ratio estimator in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space setting. KDM applies to general probability measures on countably generated measurable spaces without restrictive assumptions on continuity, or the existence of a Lebesgue density. For computational efficiency, we incorporate a low-rank approximation with precisely controlled error that grants scalability to large-sample settings. We provide rigorous theoretical guarantees, including asymptotic consistency, a functional central limit theorem, and finite-sample error bounds, establishing a strong foundation for practical use. Empirical results based on simulated and real data demonstrate the efficacy and precision of KDM.
Joint Estimation of Conditional Mean and Covariance for Unbalanced Panels
Oct 29, 2024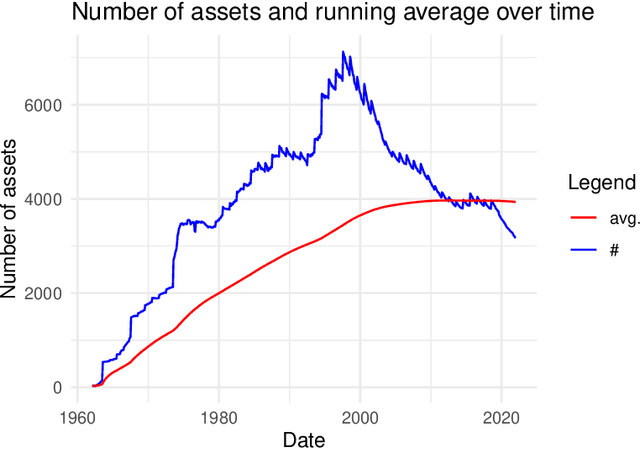
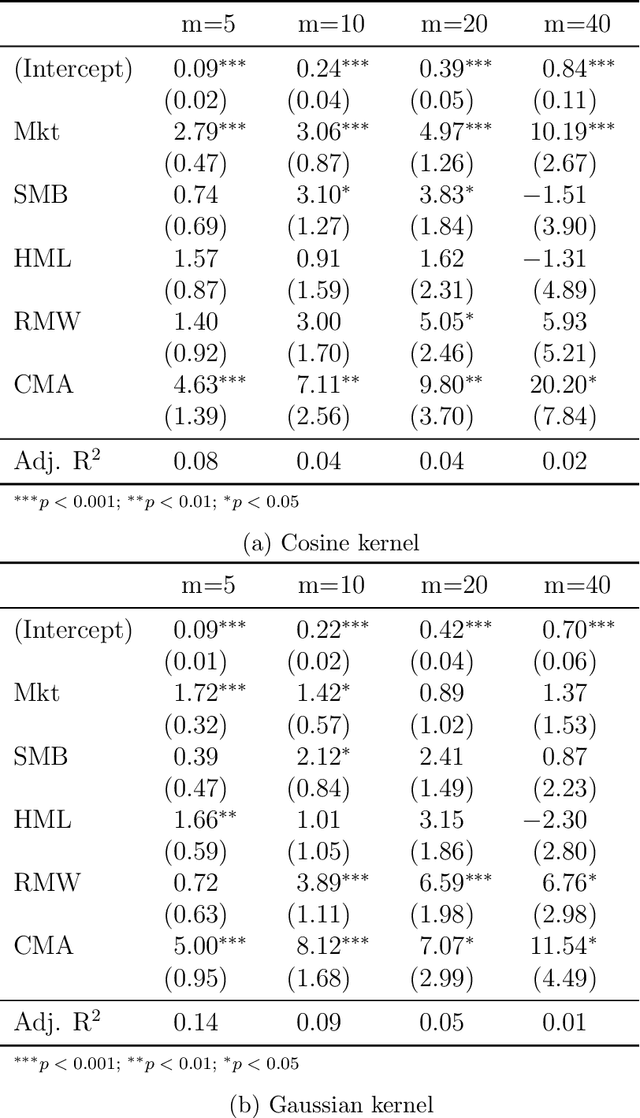
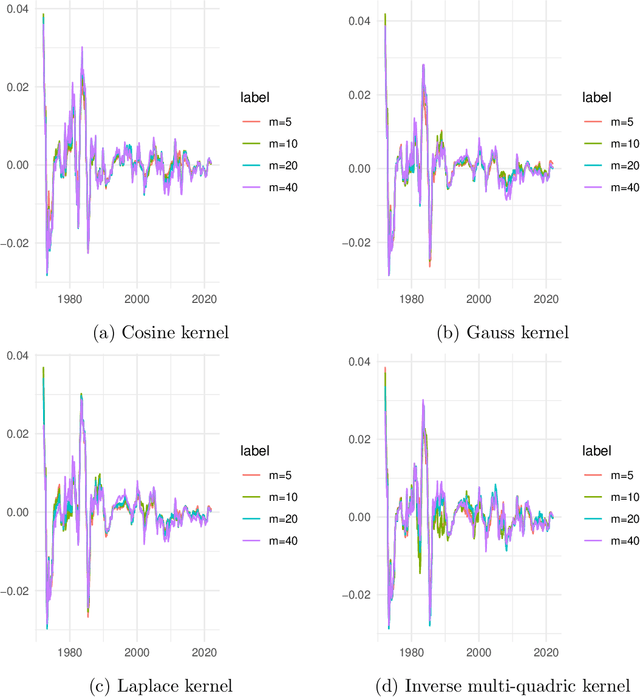
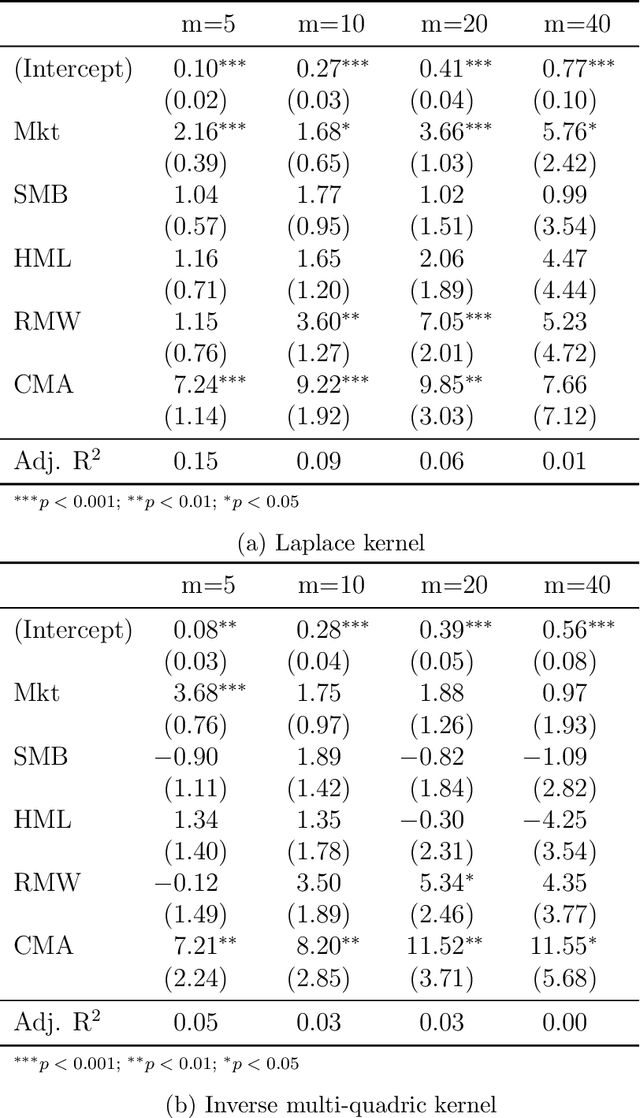
Abstract:We propose a novel nonparametric kernel-based estimator of cross-sectional conditional mean and covariance matrices for large unbalanced panels. We show its consistency and provide finite-sample guarantees. In an empirical application, we estimate conditional mean and covariance matrices for a large unbalanced panel of monthly stock excess returns given macroeconomic and firm-specific covariates from 1962 to 2021.The estimator performs well with respect to statistical measures. It is informative for empirical asset pricing, generating conditional mean-variance efficient portfolios with substantial out-of-sample Sharpe ratios far beyond equal-weighted benchmarks.
Fast Empirical Scenarios
Jul 08, 2023Abstract:We seek to extract a small number of representative scenarios from large and high-dimensional panel data that are consistent with sample moments. Among two novel algorithms, the first identifies scenarios that have not been observed before, and comes with a scenario-based representation of covariance matrices. The second proposal picks important data points from states of the world that have already realized, and are consistent with higher-order sample moment information. Both algorithms are efficient to compute, and lend themselves to consistent scenario-based modeling and high-dimensional numerical integration. Extensive numerical benchmarking studies and an application in portfolio optimization favor the proposed algorithms.
Adaptive joint distribution learning
Oct 10, 2021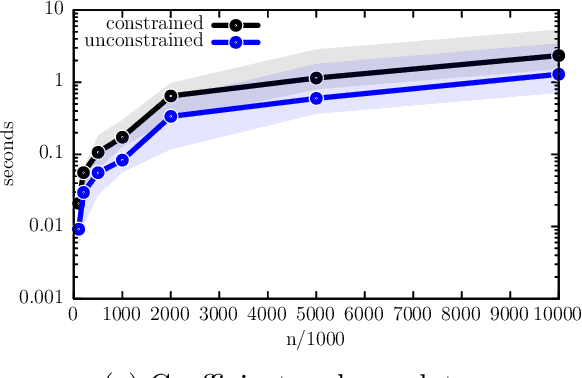
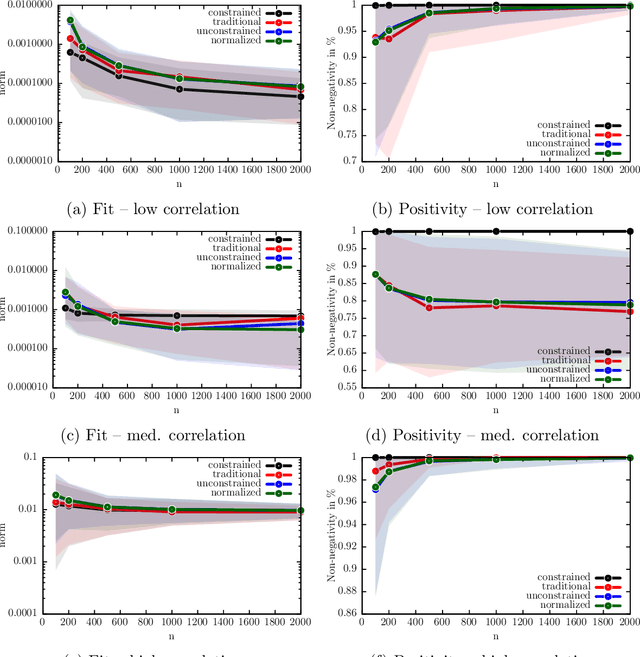
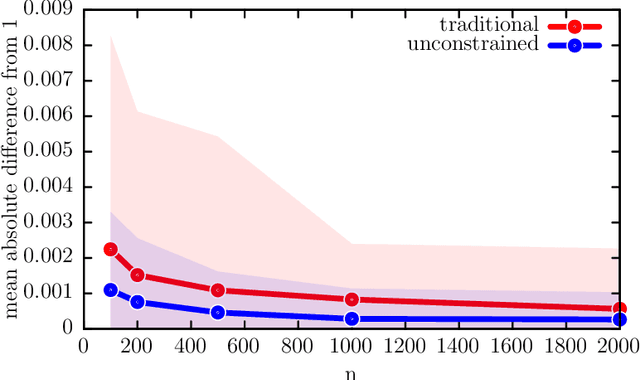
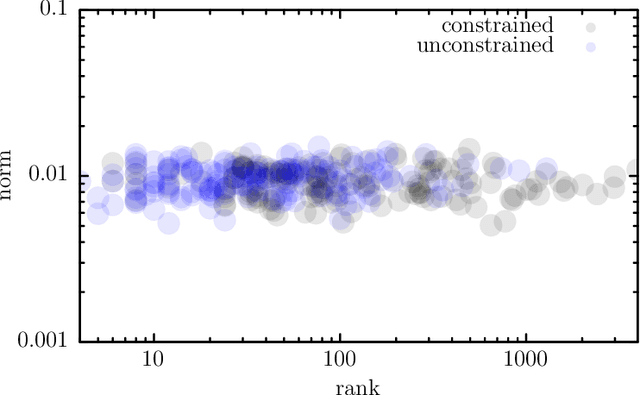
Abstract:We develop a new framework for embedding (joint) probability distributions in tensor product reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces (RKHS). This framework accommodates a low-dimensional, positive, and normalized model of a Radon-Nikodym derivative, estimated from sample sizes of up to several million data points, alleviating the inherent limitations of RKHS modeling. Well-defined normalized and positive conditional distributions are natural by-products to our approach. The embedding is fast to compute and naturally accommodates learning problems ranging from prediction to classification. The theoretical findings are supplemented by favorable numerical results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge