Patrick Aichroth
Environment Classification via Blind Roomprints Estimation
Sep 15, 2022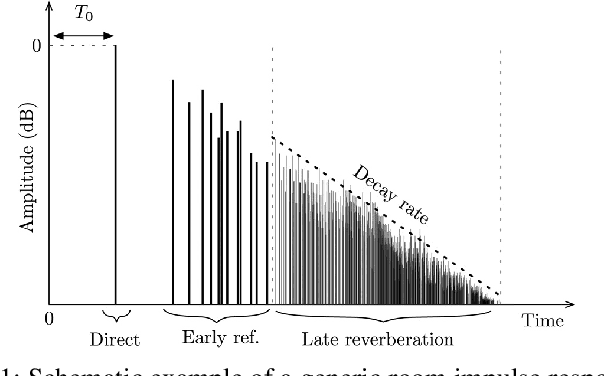
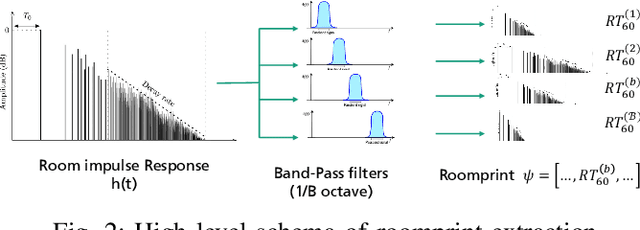


Abstract:In this paper we present a novel approach for environment classification for speech recordings, which does not require the selection of decaying reverberation tails. It is based on a multi-band RT60 analysis of blind channel estimates and achieves an accuracy of up to 93.6% on test recordings derived from the ACE corpus.
Open Challenges in Synthetic Speech Detection
Sep 15, 2022
Abstract:In this paper the current status and open challenges of synthetic speech detection are addressed. The work comprises an initial analysis of available open datasets and of existing detection methods, a description of the requirements for new research datasets compliant with regulations and better representing real-case scenarios, and a discussion of the desired characteristics of future trustworthy detection methods in terms of both functional and non-functional requirements. Compared to other works, based on specific detection solutions or presenting single dataset of synthetic speeches, our paper is meant to orient future state-of-the-art research in the domain, to quickly lessen the current gap between synthesis and detection approaches.
Speaker-Independent Microphone Identification in Noisy Conditions
Jun 23, 2022


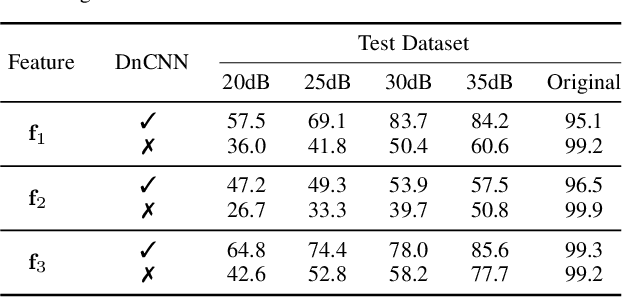
Abstract:This work proposes a method for source device identification from speech recordings that applies neural-network-based denoising, to mitigate the impact of counter-forensics attacks using noise injection. The method is evaluated by comparing the impact of denoising on three state-of-the-art features for microphone classification, determining their discriminating power with and without denoising being applied. The proposed framework achieves a significant performance increase for noisy material, and more generally, validates the usefulness of applying denoising prior to device identification for noisy recordings.
Text Classification Components for Detecting Descriptions and Names of CAD models
Apr 04, 2019

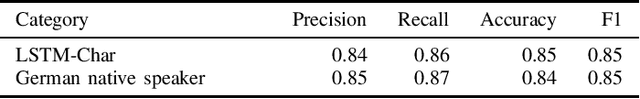

Abstract:We apply text analysis approaches for a specialized search engine for 3D CAD models and associated products. The main goals are to distinguish between actual product descriptions and other text on a website, as well as to decide whether a given text is or contains a product name. For this we use paragraph vectors for text classification, a character-level long short-term memory network (LSTM) for a single word classification and an LSTM tagger based on word embeddings for detecting product names within sentences. Despite the need to collect bigger datasets in our specific problem domain, the first results are promising and partially fit for production use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge