Paras Chopra
Building Interpretable Models for Moral Decision-Making
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We build a custom transformer model to study how neural networks make moral decisions on trolley-style dilemmas. The model processes structured scenarios using embeddings that encode who is affected, how many people, and which outcome they belong to. Our 2-layer architecture achieves 77% accuracy on Moral Machine data while remaining small enough for detailed analysis. We use different interpretability techniques to uncover how moral reasoning distributes across the network, demonstrating that biases localize to distinct computational stages among other findings.
Language Models Entangle Language and Culture
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Users should not be systemically disadvantaged by the language they use for interacting with LLMs; i.e. users across languages should get responses of similar quality irrespective of language used. In this work, we create a set of real-world open-ended questions based on our analysis of the WildChat dataset and use it to evaluate whether responses vary by language, specifically, whether answer quality depends on the language used to query the model. We also investigate how language and culture are entangled in LLMs such that choice of language changes the cultural information and context used in the response by using LLM-as-a-Judge to identify the cultural context present in responses. To further investigate this, we evaluate LLMs on a translated subset of the CulturalBench benchmark across multiple languages. Our evaluations reveal that LLMs consistently provide lower quality answers to open-ended questions in low resource languages. We find that language significantly impacts the cultural context used by the model. This difference in context impacts the quality of the downstream answer.
METIS: Mentoring Engine for Thoughtful Inquiry & Solutions
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Many students lack access to expert research mentorship. We ask whether an AI mentor can move undergraduates from an idea to a paper. We build METIS, a tool-augmented, stage-aware assistant with literature search, curated guidelines, methodology checks, and memory. We evaluate METIS against GPT-5 and Claude Sonnet 4.5 across six writing stages using LLM-as-a-judge pairwise preferences, student-persona rubrics, short multi-turn tutoring, and evidence/compliance checks. On 90 single-turn prompts, LLM judges preferred METIS to Claude Sonnet 4.5 in 71% and to GPT-5 in 54%. Student scores (clarity/actionability/constraint-fit; 90 prompts x 3 judges) are higher across stages. In multi-turn sessions (five scenarios/agent), METIS yields slightly higher final quality than GPT-5. Gains concentrate in document-grounded stages (D-F), consistent with stage-aware routing and groundings failure modes include premature tool routing, shallow grounding, and occasional stage misclassification.
Why LLMs Aren't Scientists Yet: Lessons from Four Autonomous Research Attempts
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:We report a case study of four end-to-end attempts to autonomously generate ML research papers using a pipeline of six LLM agents mapped to stages of the scientific workflow. Of these four, three attempts failed during implementation or evaluation. One completed the pipeline and was accepted to Agents4Science 2025, an experimental inaugural venue that required AI systems as first authors, passing both human and multi-AI review. From these attempts, we document six recurring failure modes: bias toward training data defaults, implementation drift under execution pressure, memory and context degradation across long-horizon tasks, overexcitement that declares success despite obvious failures, insufficient domain intelligence, and weak scientific taste in experimental design. We conclude by discussing four design principles for more robust AI-scientist systems, implications for autonomous scientific discovery, and we release all prompts, artifacts, and outputs at https://github.com/Lossfunk/ai-scientist-artefacts-v1
Do GFlowNets Transfer? Case Study on the Game of 24/42
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Generating diverse solutions is key to human-like reasoning, yet autoregressive language models focus on single accurate responses, limiting creativity. GFlowNets optimize solution generation as a flow network, promising greater diversity. Our case study shows their limited zero-shot transferability by fine-tuning small and medium-sized large language models on the Game of 24 and testing them on the Game of 42 datasets. Results revealed that GFlowNets struggle to maintain solution diversity and accuracy, highlighting key limitations in their cross-task generalization and the need for future research in improved transfer learning capabilities.
IPO: Your Language Model is Secretly a Preference Classifier
Feb 22, 2025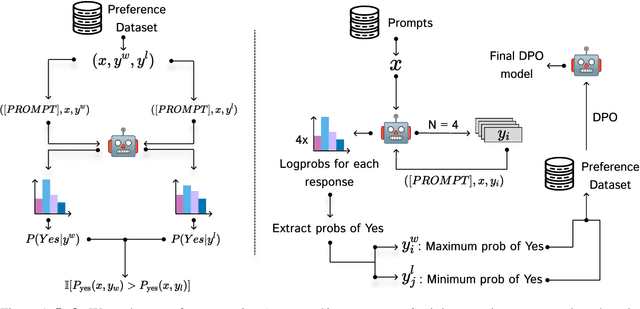
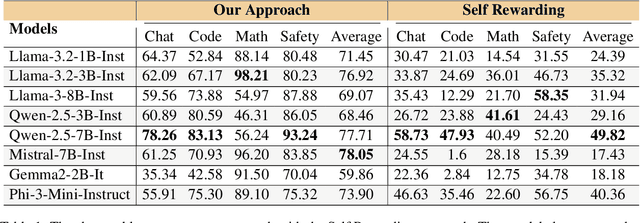

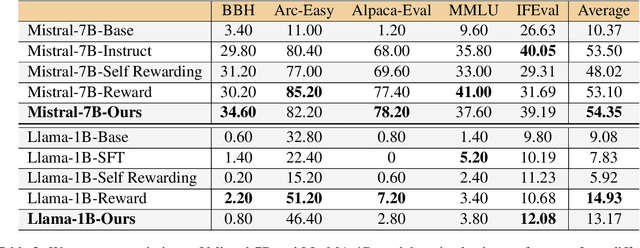
Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) has emerged as the primary method for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. While it enables LLMs to achieve human-level alignment, it often incurs significant computational and financial costs due to its reliance on training external reward models or human-labeled preferences. In this work, we propose \textbf{Implicit Preference Optimization (IPO)}, an alternative approach that leverages generative LLMs as preference classifiers, thereby reducing the dependence on external human feedback or reward models to obtain preferences. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on the preference classification ability of LLMs using RewardBench, assessing models across different sizes, architectures, and training levels to validate our hypothesis. Furthermore, we investigate the self-improvement capabilities of LLMs by generating multiple responses for a given instruction and employing the model itself as a preference classifier for Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)-based training. Our findings demonstrate that models trained through IPO achieve performance comparable to those utilizing state-of-the-art reward models for obtaining preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge