Panagiotis Galopoulos
The MeVer DeepFake Detection Service: Lessons Learnt from Developing and Deploying in the Wild
Apr 27, 2022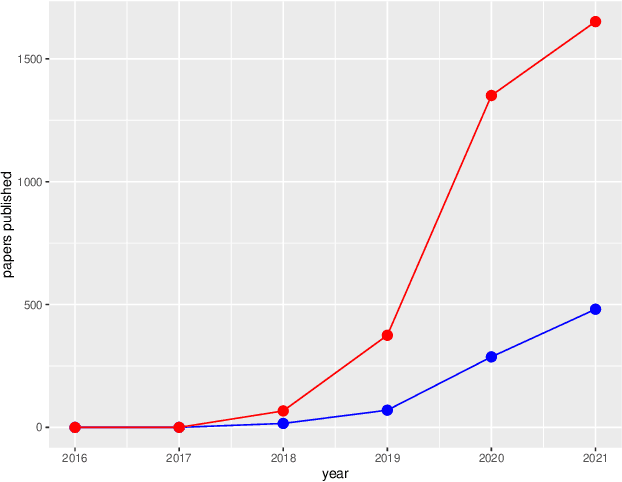
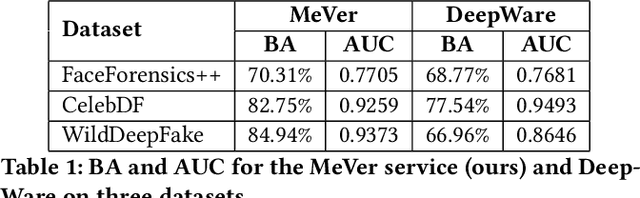
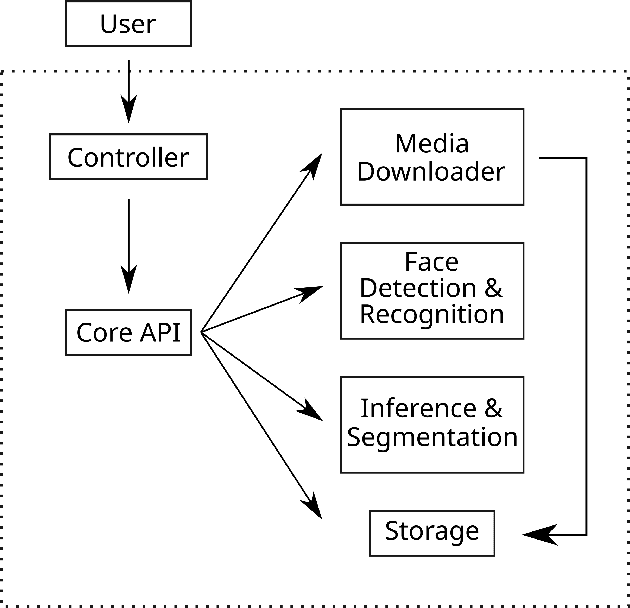
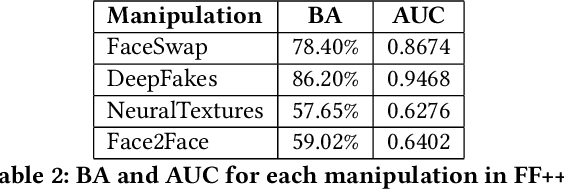
Abstract:Enabled by recent improvements in generation methodologies, DeepFakes have become mainstream due to their increasingly better visual quality, the increase in easy-to-use generation tools and the rapid dissemination through social media. This fact poses a severe threat to our societies with the potential to erode social cohesion and influence our democracies. To mitigate the threat, numerous DeepFake detection schemes have been introduced in the literature but very few provide a web service that can be used in the wild. In this paper, we introduce the MeVer DeepFake detection service, a web service detecting deep learning manipulations in images and video. We present the design and implementation of the proposed processing pipeline that involves a model ensemble scheme, and we endow the service with a model card for transparency. Experimental results show that our service performs robustly on the three benchmark datasets while being vulnerable to Adversarial Attacks. Finally, we outline our experience and lessons learned when deploying a research system into production in the hopes that it will be useful to other academic and industry teams.
Leveraging EfficientNet and Contrastive Learning for Accurate Global-scale Location Estimation
May 17, 2021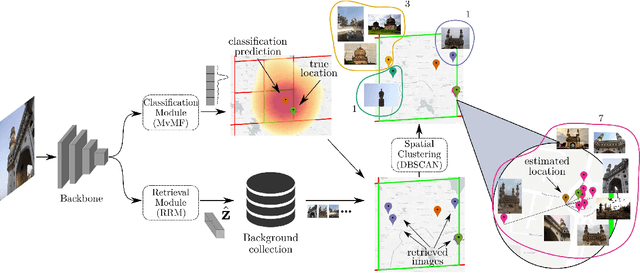
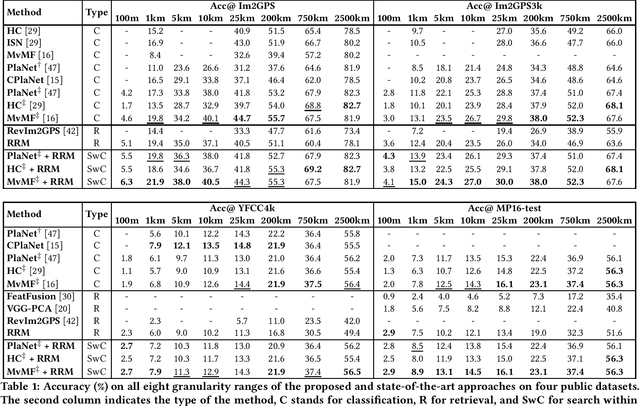
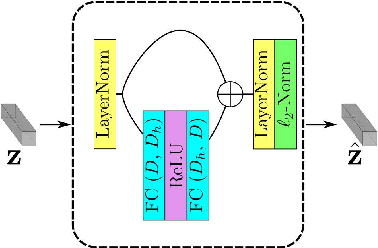
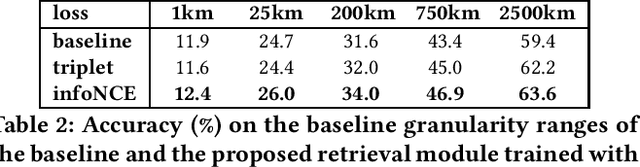
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of global-scale image geolocation, proposing a mixed classification-retrieval scheme. Unlike other methods that strictly tackle the problem as a classification or retrieval task, we combine the two practices in a unified solution leveraging the advantages of each approach with two different modules. The first leverages the EfficientNet architecture to assign images to a specific geographic cell in a robust way. The second introduces a new residual architecture that is trained with contrastive learning to map input images to an embedding space that minimizes the pairwise geodesic distance of same-location images. For the final location estimation, the two modules are combined with a search-within-cell scheme, where the locations of most similar images from the predicted geographic cell are aggregated based on a spatial clustering scheme. Our approach demonstrates very competitive performance on four public datasets, achieving new state-of-the-art performance in fine granularity scales, i.e., 15.0% at 1km range on Im2GPS3k.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge