Pai-Shun Ting
FEAST: An Automated Feature Selection Framework for Compilation Tasks
Oct 29, 2016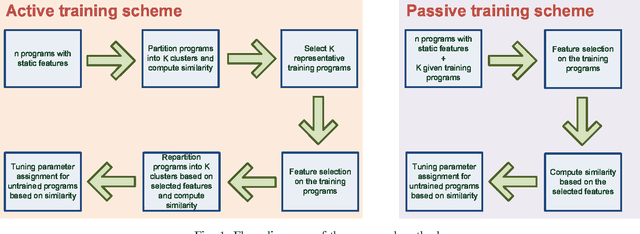
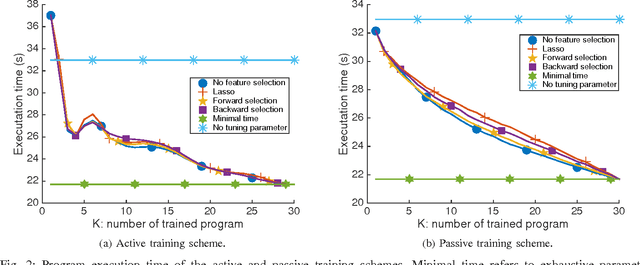

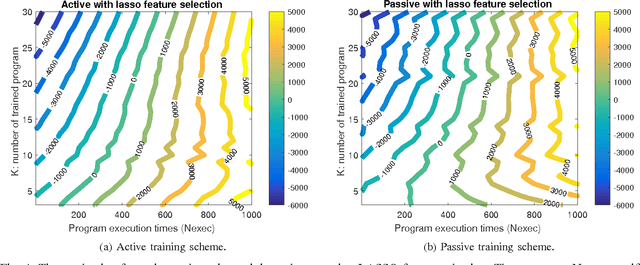
Abstract:The success of the application of machine-learning techniques to compilation tasks can be largely attributed to the recent development and advancement of program characterization, a process that numerically or structurally quantifies a target program. While great achievements have been made in identifying key features to characterize programs, choosing a correct set of features for a specific compiler task remains an ad hoc procedure. In order to guarantee a comprehensive coverage of features, compiler engineers usually need to select excessive number of features. This, unfortunately, would potentially lead to a selection of multiple similar features, which in turn could create a new problem of bias that emphasizes certain aspects of a program's characteristics, hence reducing the accuracy and performance of the target compiler task. In this paper, we propose FEAture Selection for compilation Tasks (FEAST), an efficient and automated framework for determining the most relevant and representative features from a feature pool. Specifically, FEAST utilizes widely used statistics and machine-learning tools, including LASSO, sequential forward and backward selection, for automatic feature selection, and can in general be applied to any numerical feature set. This paper further proposes an automated approach to compiler parameter assignment for assessing the performance of FEAST. Intensive experimental results demonstrate that, under the compiler parameter assignment task, FEAST can achieve comparable results with about 18% of features that are automatically selected from the entire feature pool. We also inspect these selected features and discuss their roles in program execution.
Supervised Collective Classification for Crowdsourcing
Sep 08, 2015

Abstract:Crowdsourcing utilizes the wisdom of crowds for collective classification via information (e.g., labels of an item) provided by labelers. Current crowdsourcing algorithms are mainly unsupervised methods that are unaware of the quality of crowdsourced data. In this paper, we propose a supervised collective classification algorithm that aims to identify reliable labelers from the training data (e.g., items with known labels). The reliability (i.e., weighting factor) of each labeler is determined via a saddle point algorithm. The results on several crowdsourced data show that supervised methods can achieve better classification accuracy than unsupervised methods, and our proposed method outperforms other algorithms.
When Crowdsourcing Meets Mobile Sensing: A Social Network Perspective
Aug 03, 2015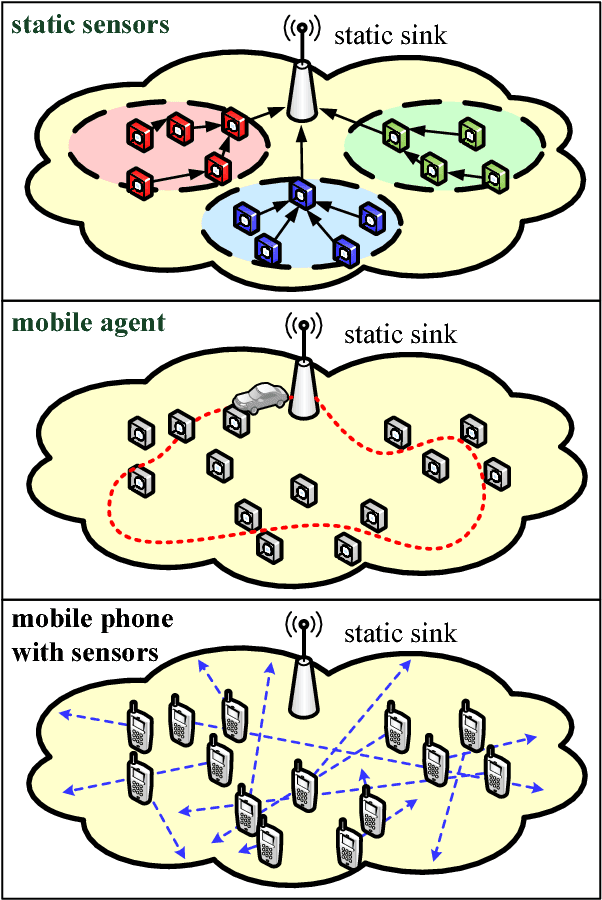


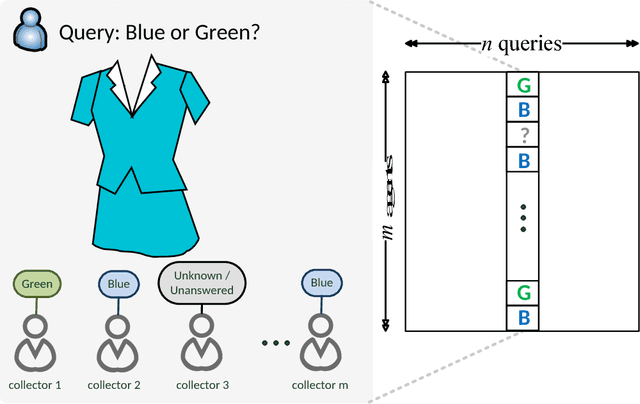
Abstract:Mobile sensing is an emerging technology that utilizes agent-participatory data for decision making or state estimation, including multimedia applications. This article investigates the structure of mobile sensing schemes and introduces crowdsourcing methods for mobile sensing. Inspired by social network, one can establish trust among participatory agents to leverage the wisdom of crowds for mobile sensing. A prototype of social network inspired mobile multimedia and sensing application is presented for illustrative purpose. Numerical experiments on real-world datasets show improved performance of mobile sensing via crowdsourcing. Challenges for mobile sensing with respect to Internet layers are discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge