Ozlem Ozmen
Importance of Preprocessing in Histopathology Image Classification Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Jan 24, 2022


Abstract:The aim of this study is to propose an alternative and hybrid solution method for diagnosing the disease from histopathology images taken from animals with paratuberculosis and intact intestine. In detail, the hybrid method is based on using both image processing and deep learning for better results. Reliable disease detection from histo-pathology images is known as an open problem in medical image processing and alternative solutions need to be developed. In this context, 520 histopathology images were collected in a joint study with Burdur Mehmet Akif Ersoy University, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, and Department of Pathology. Manually detecting and interpreting these images requires expertise and a lot of processing time. For this reason, veterinarians, especially newly recruited physicians, have a great need for imaging and computer vision systems in the development of detection and treatment methods for this disease. The proposed solution method in this study is to use the CLAHE method and image processing together. After this preprocessing, the diagnosis is made by classifying a convolutional neural network sup-ported by the VGG-16 architecture. This method uses completely original dataset images. Two types of systems were applied for the evaluation parameters. While the F1 Score was 93% in the method classified without data preprocessing, it was 98% in the method that was preprocessed with the CLAHE method.
A Stance Data Set on Polarized Conversations on Twitter about the Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine as a Treatment for COVID-19
Sep 05, 2020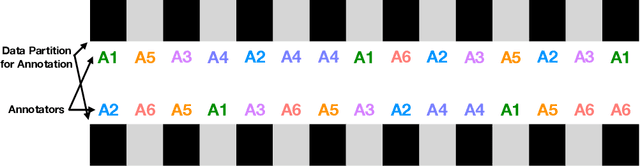
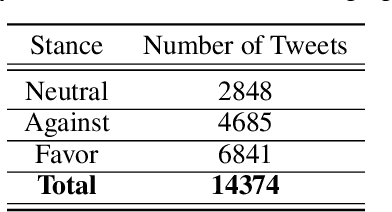

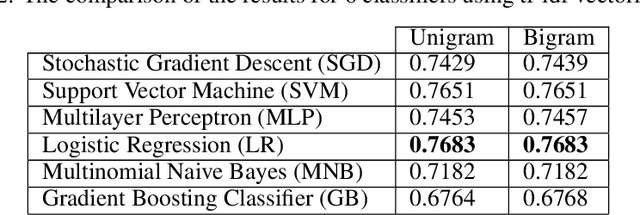
Abstract:At the time of this study, the SARS-CoV-2 virus that caused the COVID-19 pandemic has spread significantly across the world. Considering the uncertainty about policies, health risks, financial difficulties, etc. the online media, specially the Twitter platform, is experiencing a high volume of activity related to this pandemic. Among the hot topics, the polarized debates about unconfirmed medicines for the treatment and prevention of the disease have attracted significant attention from online media users. In this work, we present a stance data set, COVID-CQ, of user-generated content on Twitter in the context of COVID-19. We investigated more than 14 thousand tweets and manually annotated the opinions of the tweet initiators regarding the use of "chloroquine" and "hydroxychloroquine" for the treatment or prevention of COVID-19. To the best of our knowledge, COVID-CQ is the first data set of Twitter users' stances in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the largest Twitter data set on users' stances towards a claim, in any domain. We have made this data set available to the research community via GitHub. We expect this data set to be useful for many research purposes, including stance detection, evolution and dynamics of opinions regarding this outbreak, and changes in opinions in response to the exogenous shocks such as policy decisions and events.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge