Osman Tursun
PDV: Prompt Directional Vectors for Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot composed image retrieval (ZS-CIR) enables image search using a reference image and text prompt without requiring specialized text-image composition networks trained on large-scale paired data. However, current ZS-CIR approaches face three critical limitations in their reliance on composed text embeddings: static query embedding representations, insufficient utilization of image embeddings, and suboptimal performance when fusing text and image embeddings. To address these challenges, we introduce the Prompt Directional Vector (PDV), a simple yet effective training-free enhancement that captures semantic modifications induced by user prompts. PDV enables three key improvements: (1) dynamic composed text embeddings where prompt adjustments are controllable via a scaling factor, (2) composed image embeddings through semantic transfer from text prompts to image features, and (3) weighted fusion of composed text and image embeddings that enhances retrieval by balancing visual and semantic similarity. Our approach serves as a plug-and-play enhancement for existing ZS-CIR methods with minimal computational overhead. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that PDV consistently improves retrieval performance when integrated with state-of-the-art ZS-CIR approaches, particularly for methods that generate accurate compositional embeddings. The code will be publicly available.
Part-based Quantitative Analysis for Heatmaps
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Heatmaps have been instrumental in helping understand deep network decisions, and are a common approach for Explainable AI (XAI). While significant progress has been made in enhancing the informativeness and accessibility of heatmaps, heatmap analysis is typically very subjective and limited to domain experts. As such, developing automatic, scalable, and numerical analysis methods to make heatmap-based XAI more objective, end-user friendly, and cost-effective is vital. In addition, there is a need for comprehensive evaluation metrics to assess heatmap quality at a granular level.
Towards Self-Explainability of Deep Neural Networks with Heatmap Captioning and Large-Language Models
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Heatmaps are widely used to interpret deep neural networks, particularly for computer vision tasks, and the heatmap-based explainable AI (XAI) techniques are a well-researched topic. However, most studies concentrate on enhancing the quality of the generated heatmap or discovering alternate heatmap generation techniques, and little effort has been devoted to making heatmap-based XAI automatic, interactive, scalable, and accessible. To address this gap, we propose a framework that includes two modules: (1) context modelling and (2) reasoning. We proposed a template-based image captioning approach for context modelling to create text-based contextual information from the heatmap and input data. The reasoning module leverages a large language model to provide explanations in combination with specialised knowledge. Our qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework and heatmap captioning approach. The code for the proposed template-based heatmap captioning approach will be publicly available.
SESS: Saliency Enhancing with Scaling and Sliding
Jul 05, 2022
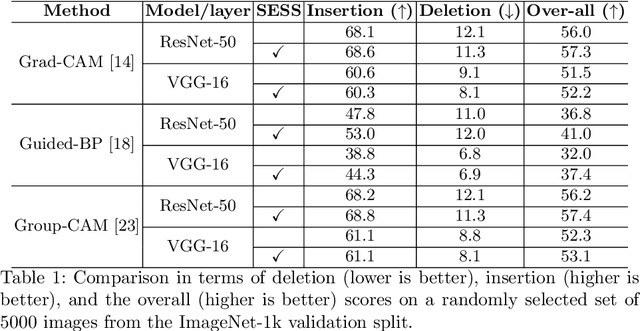
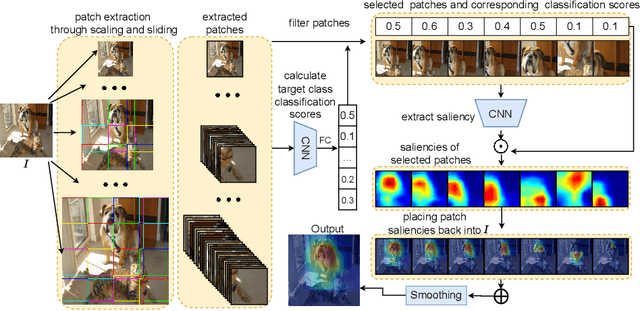

Abstract:High-quality saliency maps are essential in several machine learning application areas including explainable AI and weakly supervised object detection and segmentation. Many techniques have been developed to generate better saliency using neural networks. However, they are often limited to specific saliency visualisation methods or saliency issues. We propose a novel saliency enhancing approach called SESS (Saliency Enhancing with Scaling and Sliding). It is a method and model agnostic extension to existing saliency map generation methods. With SESS, existing saliency approaches become robust to scale variance, multiple occurrences of target objects, presence of distractors and generate less noisy and more discriminative saliency maps. SESS improves saliency by fusing saliency maps extracted from multiple patches at different scales from different areas, and combines these individual maps using a novel fusion scheme that incorporates channel-wise weights and spatial weighted average. To improve efficiency, we introduce a pre-filtering step that can exclude uninformative saliency maps to improve efficiency while still enhancing overall results. We evaluate SESS on object recognition and detection benchmarks where it achieves significant improvement. The code is released publicly to enable researchers to verify performance and further development. Code is available at: https://github.com/neouyghur/SESS
Learning Regional Attention over Multi-resolution Deep Convolutional Features for Trademark Retrieval
Apr 15, 2021



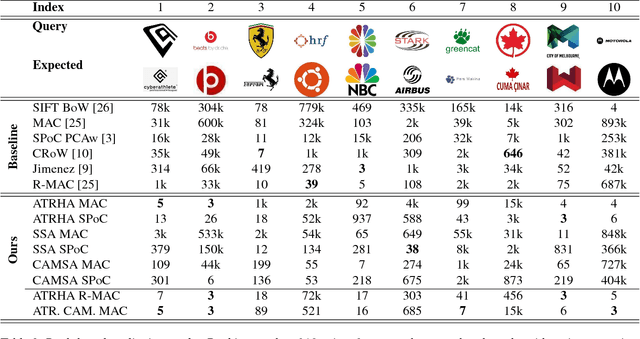
Abstract:Large-scale trademark retrieval is an important content-based image retrieval task. A recent study shows that off-the-shelf deep features aggregated with Regional-Maximum Activation of Convolutions (R-MAC) achieve state-of-the-art results. However, R-MAC suffers in the presence of background clutter/trivial regions and scale variance, and discards important spatial information. We introduce three simple but effective modifications to R-MAC to overcome these drawbacks. First, we propose the use of both sum and max pooling to minimise the loss of spatial information. We also employ domain-specific unsupervised soft-attention to eliminate background clutter and unimportant regions. Finally, we add multi-resolution inputs to enhance the scale-invariance of R-MAC. We evaluate these three modifications on the million-scale METU dataset. Our results show that all modifications bring non-trivial improvements, and surpass previous state-of-the-art results.
An Efficient Framework for Zero-Shot Sketch-Based Image Retrieval
Feb 08, 2021
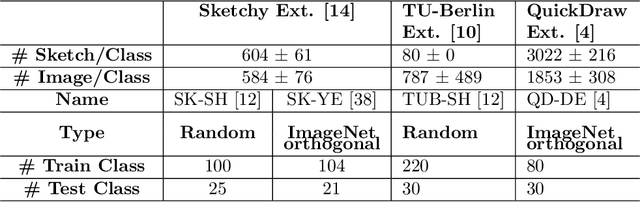
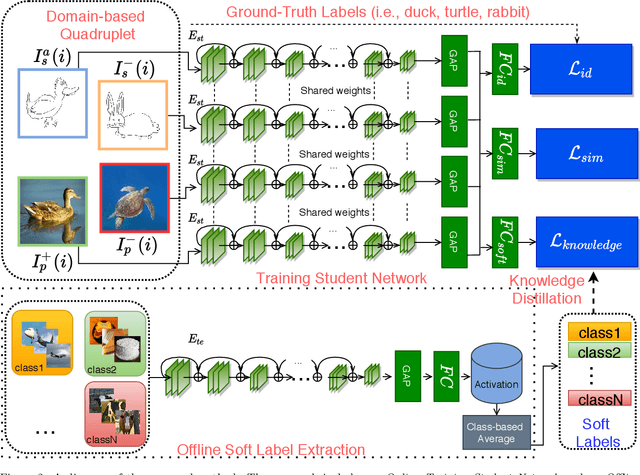
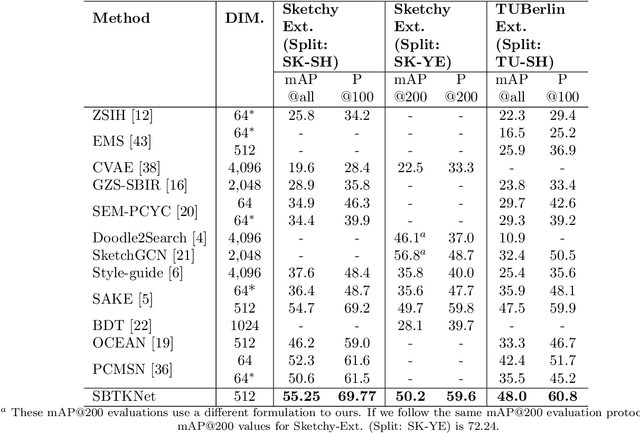
Abstract:Recently, Zero-shot Sketch-based Image Retrieval (ZS-SBIR) has attracted the attention of the computer vision community due to it's real-world applications, and the more realistic and challenging setting than found in SBIR. ZS-SBIR inherits the main challenges of multiple computer vision problems including content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR), zero-shot learning and domain adaptation. The majority of previous studies using deep neural networks have achieved improved results through either projecting sketch and images into a common low-dimensional space or transferring knowledge from seen to unseen classes. However, those approaches are trained with complex frameworks composed of multiple deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and are dependent on category-level word labels. This increases the requirements on training resources and datasets. In comparison, we propose a simple and efficient framework that does not require high computational training resources, and can be trained on datasets without semantic categorical labels. Furthermore, at training and inference stages our method only uses a single CNN. In this work, a pre-trained ImageNet CNN (e.g., ResNet50) is fine-tuned with three proposed learning objects: domain-aware quadruplet loss, semantic classification loss, and semantic knowledge preservation loss. The domain-aware quadruplet and semantic classification losses are introduced to learn discriminative, semantic and domain invariant features through considering ZS-SBIR as object detection and verification problem. ...
Enhancing Feature Invariance with Learned Image Transformations for Image Retrieval
Feb 05, 2020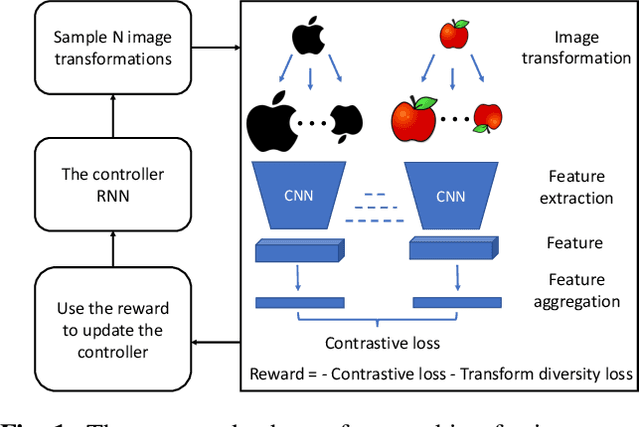


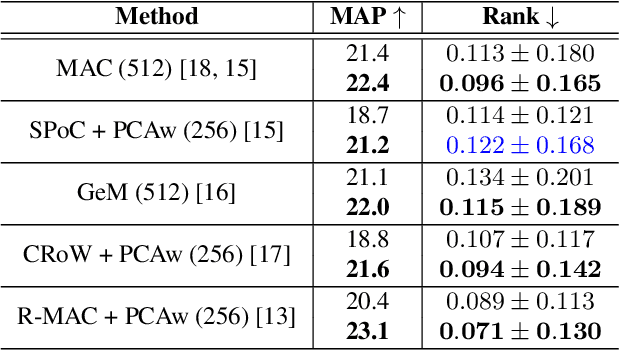
Abstract:Off-the-shelf convolutional neural network features achieve state-of-the-art results in many image retrieval tasks. However, their invariance is pre-defined by the network architecture and training data. In this work, we propose using features aggregated from transformed images to increase the invariance of off-the-shelf features without fine-tuning or modifying the network. We learn an ensemble of beneficial image transformations through reinforcement learning in an efficient way. Experiment results show the learned ensemble of transformations is effective and transferable.
MTRNet++: One-stage Mask-based Scene Text Eraser
Dec 16, 2019
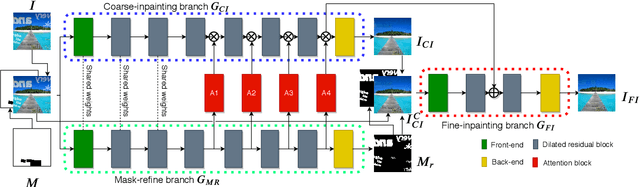

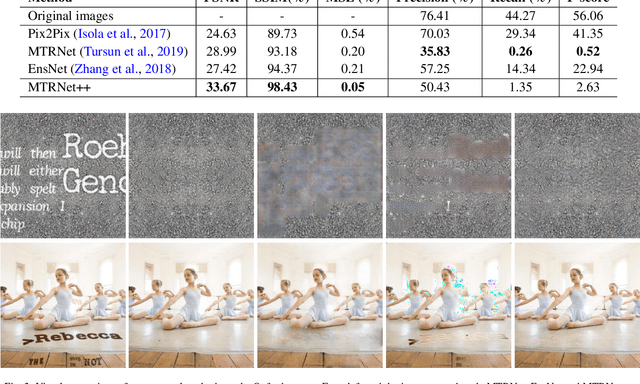
Abstract:A precise, controllable, interpretable and easily trainable text removal approach is necessary for both user-specific and large-scale text removal applications. To achieve this, we propose a one-stage mask-based text inpainting network, MTRNet++. It has a novel architecture that includes mask-refine, coarse-inpainting and fine-inpainting branches, and attention blocks. With this architecture, MTRNet++ can remove text either with or without an external mask. It achieves state-of-the-art results on both the Oxford and SCUT datasets without using external ground-truth masks. The results of ablation studies demonstrate that the proposed multi-branch architecture with attention blocks is effective and essential. It also demonstrates controllability and interpretability.
MTRNet: A Generic Scene Text Eraser
Mar 12, 2019



Abstract:Text removal algorithms have been proposed for uni-lingual scripts with regular shapes and layouts. However, to the best of our knowledge, a generic text removal method which is able to remove all or user-specified text regions regardless of font, script, language or shape is not available. Developing such a generic text eraser for real scenes is a challenging task, since it inherits all the challenges of multi-lingual and curved text detection and inpainting. To fill this gap, we propose a mask-based text removal network (MTRNet). MTRNet is a conditional adversarial generative network (cGAN) with an auxiliary mask. The introduced auxiliary mask not only makes the cGAN a generic text eraser, but also enables stable training and early convergence on a challenging large-scale synthetic dataset, initially proposed for text detection in real scenes. What's more, MTRNet achieves state-of-the-art results on several real-world datasets including ICDAR 2013, ICDAR 2017 MLT, and CTW1500, without being explicitly trained on this data, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods trained directly on these datasets.
Component-based Attention for Large-scale Trademark Retrieval
Nov 07, 2018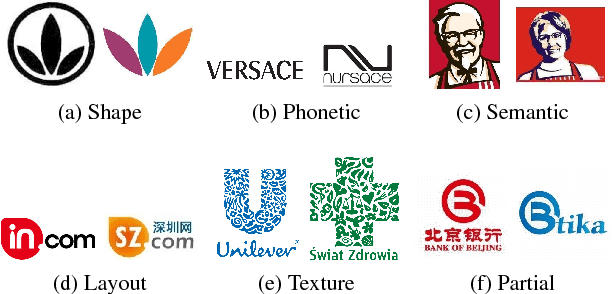


Abstract:The demand for large-scale trademark retrieval (TR) systems has significantly increased to combat the rise in international trademark infringement. Unfortunately, the ranking accuracy of current approaches using either hand-crafted or pre-trained deep convolution neural network (DCNN) features is inadequate for large-scale deployments. We show in this paper that the ranking accuracy of TR systems can be significantly improved by incorporating hard and soft attention mechanisms, which direct attention to critical information such as figurative elements and reduce attention given to distracting and uninformative elements such as text and background. Our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art results on a challenging large-scale trademark dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge