Ori Yonay
Myna: Masking-Based Contrastive Learning of Musical Representations
Feb 19, 2025
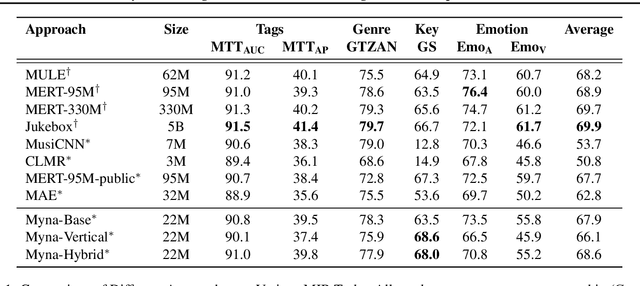


Abstract:We present Myna, a simple yet effective approach for self-supervised musical representation learning. Built on a contrastive learning framework, Myna introduces two key innovations: (1) the use of a Vision Transformer (ViT) on mel-spectrograms as the backbone and (2) a novel data augmentation strategy, token masking, that masks 90 percent of spectrogram tokens. These innovations deliver both effectiveness and efficiency: (i) Token masking enables a significant increase in per-GPU batch size, from 48 or 120 in prior methods (CLMR, MULE) to 4096. (ii) By avoiding traditional augmentations, Myna retains pitch sensitivity, enhancing performance in tasks like key detection. (iii) The use of vertical patches allows the model to better capture critical features for key detection. Our hybrid model, Myna-22M-Hybrid, processes both 16x16 and 128x2 patches, achieving state-of-the-art results. Trained on a single GPU, it outperforms MULE (62M) on average and rivals MERT-95M, which was trained on 16 and 64 GPUs, respectively. Additionally, it surpasses MERT-95M-public, establishing itself as the best-performing model trained on publicly available data. We release our code and models to promote reproducibility and facilitate future research.
FastCLIP: A Suite of Optimization Techniques to Accelerate CLIP Training with Limited Resources
Jul 01, 2024
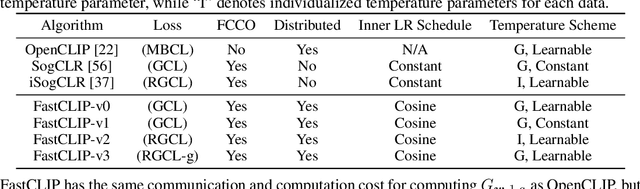
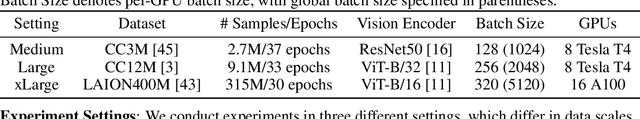
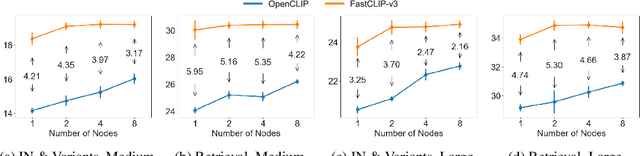
Abstract:Existing studies of training state-of-the-art Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) models on large-scale data involve hundreds of or even thousands of GPUs due to the requirement of a large batch size. However, such a large amount of resources is not accessible to most people. While advanced compositional optimization techniques for optimizing global contrastive losses have been demonstrated effective for removing the requirement of large batch size, their performance on large-scale data remains underexplored and not optimized. To bridge the gap, this paper explores several aspects of CLIP training with limited resources (e.g., up to tens of GPUs). First, we introduce FastCLIP, a general CLIP training framework built on advanced compositional optimization techniques while designed and optimized for the distributed setting. Our framework is equipped with an efficient gradient reduction strategy to reduce communication overhead. Second, to further boost training efficiency, we investigate three components of the framework from an optimization perspective: the schedule of the inner learning rate, the update rules of the temperature parameter and the model parameters, respectively. Experiments on different strategies for each component shed light on how to conduct CLIP training more efficiently. Finally, we benchmark the performance of FastCLIP and the state-of-the-art training baseline (OpenCLIP) on different compute scales up to 32 GPUs on 8 nodes, and three data scales ranging from 2.7 million, 9.1 million to 315 million image-text pairs to demonstrate the significant improvement of FastCLIP in the resource-limited setting. We release the code of FastCLIP at https://github.com/Optimization-AI/fast_clip .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge