Olga Kovaleva
Down and Across: Introducing Crossword-Solving as a New NLP Benchmark
May 20, 2022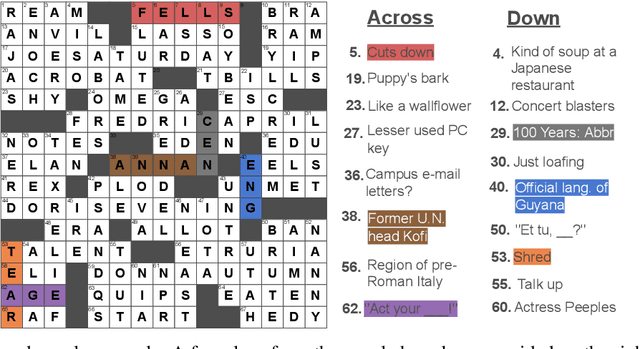
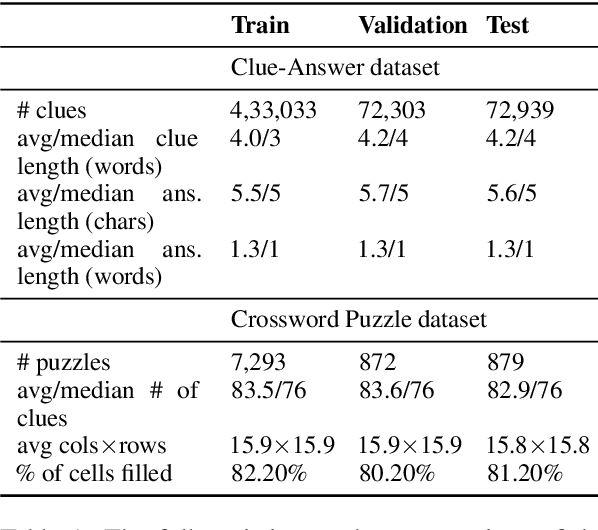
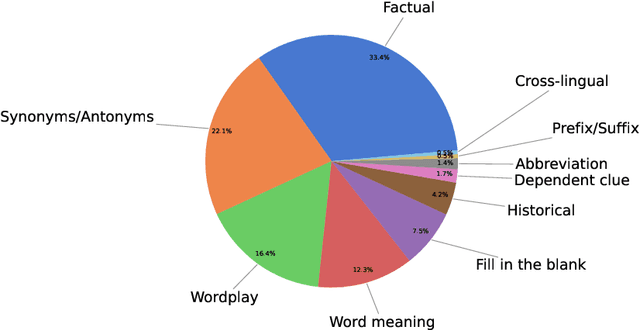
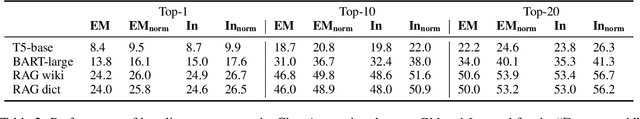
Abstract:Solving crossword puzzles requires diverse reasoning capabilities, access to a vast amount of knowledge about language and the world, and the ability to satisfy the constraints imposed by the structure of the puzzle. In this work, we introduce solving crossword puzzles as a new natural language understanding task. We release the specification of a corpus of crossword puzzles collected from the New York Times daily crossword spanning 25 years and comprised of a total of around nine thousand puzzles. These puzzles include a diverse set of clues: historic, factual, word meaning, synonyms/antonyms, fill-in-the-blank, abbreviations, prefixes/suffixes, wordplay, and cross-lingual, as well as clues that depend on the answers to other clues. We separately release the clue-answer pairs from these puzzles as an open-domain question answering dataset containing over half a million unique clue-answer pairs. For the question answering task, our baselines include several sequence-to-sequence and retrieval-based generative models. We also introduce a non-parametric constraint satisfaction baseline for solving the entire crossword puzzle. Finally, we propose an evaluation framework which consists of several complementary performance metrics.
BERT Busters: Outlier Dimensions that Disrupt Transformers
Jun 02, 2021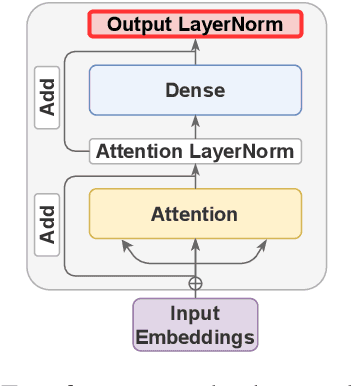
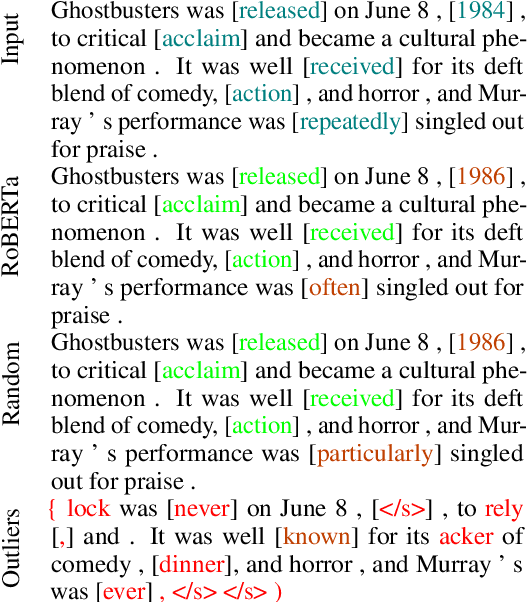
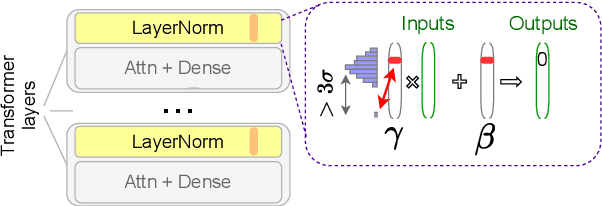
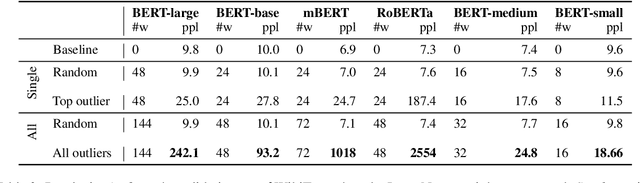
Abstract:Multiple studies have shown that Transformers are remarkably robust to pruning. Contrary to this received wisdom, we demonstrate that pre-trained Transformer encoders are surprisingly fragile to the removal of a very small number of features in the layer outputs (<0.0001% of model weights). In case of BERT and other pre-trained encoder Transformers, the affected component is the scaling factors and biases in the LayerNorm. The outliers are high-magnitude normalization parameters that emerge early in pre-training and show up consistently in the same dimensional position throughout the model. We show that disabling them significantly degrades both the MLM loss and the downstream task performance. This effect is observed across several BERT-family models and other popular pre-trained Transformer architectures, including BART, XLNet and ELECTRA; we also show a similar effect in GPT-2.
A Primer in BERTology: What we know about how BERT works
Feb 27, 2020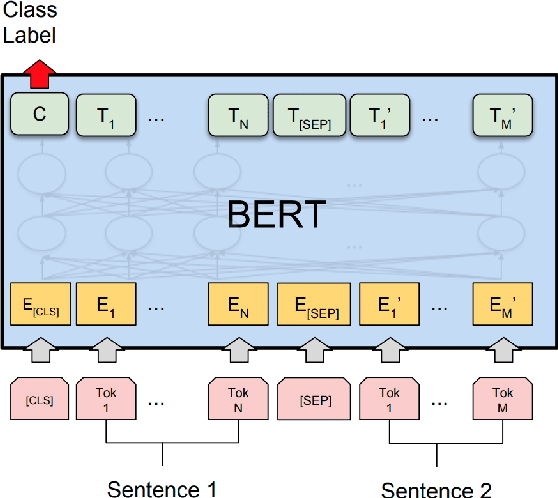
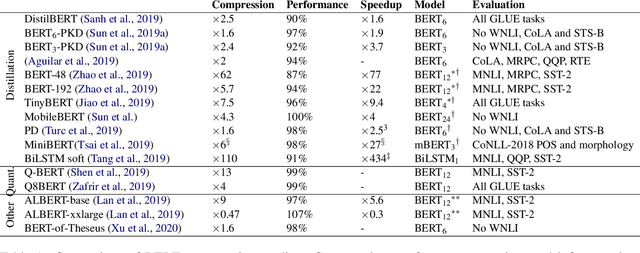
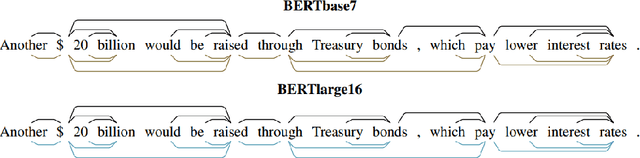
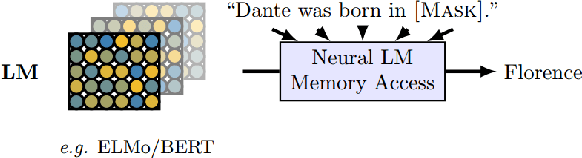
Abstract:Transformer-based models are now widely used in NLP, but we still do not understand a lot about their inner workings. This paper describes what is known to date about the famous BERT model (Devlin et al. 2019), synthesizing over 40 analysis studies. We also provide an overview of the proposed modifications to the model and its training regime. We then outline the directions for further research.
Revealing the Dark Secrets of BERT
Sep 11, 2019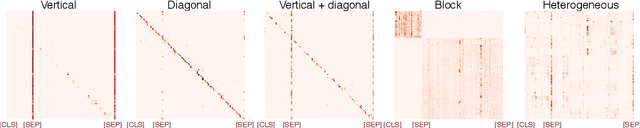
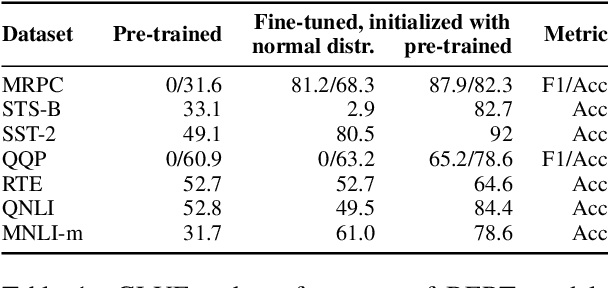
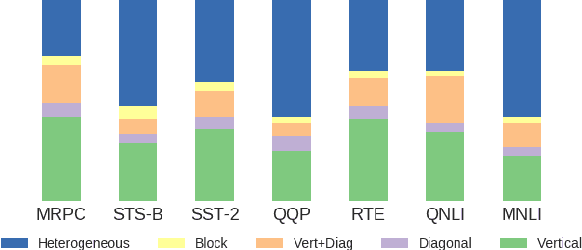
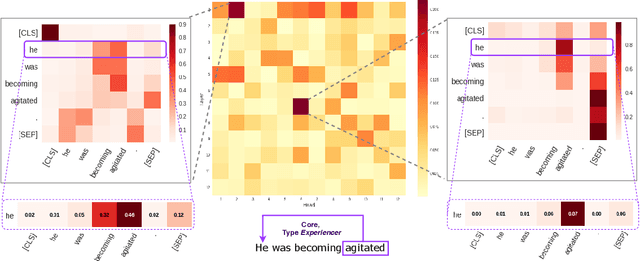
Abstract:BERT-based architectures currently give state-of-the-art performance on many NLP tasks, but little is known about the exact mechanisms that contribute to its success. In the current work, we focus on the interpretation of self-attention, which is one of the fundamental underlying components of BERT. Using a subset of GLUE tasks and a set of handcrafted features-of-interest, we propose the methodology and carry out a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the information encoded by the individual BERT's heads. Our findings suggest that there is a limited set of attention patterns that are repeated across different heads, indicating the overall model overparametrization. While different heads consistently use the same attention patterns, they have varying impact on performance across different tasks. We show that manually disabling attention in certain heads leads to a performance improvement over the regular fine-tuned BERT models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge