Norbert Scherer-Negenborn
Strike the Balance: On-the-Fly Uncertainty based User Interactions for Long-Term Video Object Segmentation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a variant of video object segmentation (VOS) that bridges interactive and semi-automatic approaches, termed Lazy Video Object Segmentation (ziVOS). In contrast, to both tasks, which handle video object segmentation in an off-line manner (i.e., pre-recorded sequences), we propose through ziVOS to target online recorded sequences. Here, we strive to strike a balance between performance and robustness for long-term scenarios by soliciting user feedback's on-the-fly during the segmentation process. Hence, we aim to maximize the tracking duration of an object of interest, while requiring minimal user corrections to maintain tracking over an extended period. We propose a competitive baseline, i.e., Lazy-XMem, as a reference for future works in ziVOS. Our proposed approach uses an uncertainty estimation of the tracking state to determine whether a user interaction is necessary to refine the model's prediction. To quantitatively assess the performance of our method and the user's workload, we introduce complementary metrics alongside those already established in the field. We evaluate our approach using the recently introduced LVOS dataset, which offers numerous long-term videos. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Vujas-Eteph/LazyXMem.
READMem: Robust Embedding Association for a Diverse Memory in Unconstrained Video Object Segmentation
May 22, 2023Abstract:We present READMem (Robust Embedding Association for a Diverse Memory), a modular framework for semi-automatic video object segmentation (sVOS) methods designed to handle unconstrained videos. Contemporary sVOS works typically aggregate video frames in an ever-expanding memory, demanding high hardware resources for long-term applications. To mitigate memory requirements and prevent near object duplicates (caused by information of adjacent frames), previous methods introduce a hyper-parameter that controls the frequency of frames eligible to be stored. This parameter has to be adjusted according to concrete video properties (such as rapidity of appearance changes and video length) and does not generalize well. Instead, we integrate the embedding of a new frame into the memory only if it increases the diversity of the memory content. Furthermore, we propose a robust association of the embeddings stored in the memory with query embeddings during the update process. Our approach avoids the accumulation of redundant data, allowing us in return, to restrict the memory size and prevent extreme memory demands in long videos. We extend popular sVOS baselines with READMem, which previously showed limited performance on long videos. Our approach achieves competitive results on the Long-time Video dataset (LV1) while not hindering performance on short sequences. Our code is publicly available.
Revisiting Click-based Interactive Video Object Segmentation
Mar 03, 2022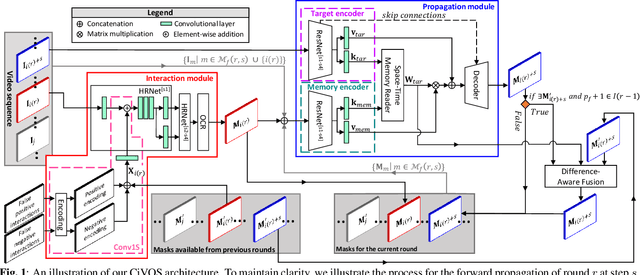
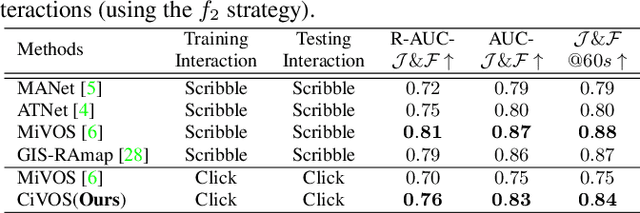
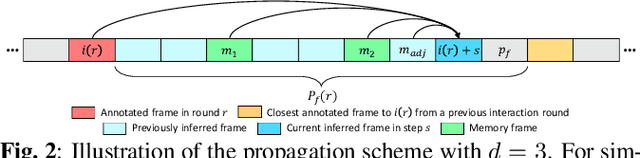
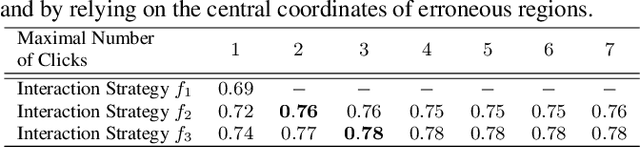
Abstract:While current methods for interactive Video Object Segmentation (iVOS) rely on scribble-based interactions to generate precise object masks, we propose a Click-based interactive Video Object Segmentation (CiVOS) framework to simplify the required user workload as much as possible. CiVOS builds on de-coupled modules reflecting user interaction and mask propagation. The interaction module converts click-based interactions into an object mask, which is then inferred to the remaining frames by the propagation module. Additional user interactions allow for a refinement of the object mask. The approach is extensively evaluated on the popular interactive~DAVIS dataset, but with an inevitable adaptation of scribble-based interactions with click-based counterparts. We consider several strategies for generating clicks during our evaluation to reflect various user inputs and adjust the DAVIS performance metric to perform a hardware-independent comparison. The presented CiVOS pipeline achieves competitive results, although requiring a lower user workload.
Integration of 3D Knowledge for On-Board UAV Visual Tracking
Aug 06, 2020



Abstract:Visual tracking from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) poses challenges such as occlusions or background clutter. In order to achieve more robust on-board UAV visual tracking, a pipeline combining information extracted from a visual tracker and a sparse 3D reconstruction of the static environment is introduced. The 3D reconstruction is based on an image-based structure-from-motion (SfM) component and thus allows to utilize a state estimator in a pseudo-3D space. Thereby improved handling of occlusion situations and background clutter is realized. Evaluation is done on prototypical image sequences captured from a UAV with low-altitude oblique views. The experimental results demonstrate the benefit of the proposed approach compared to only relying on visual cues or using a state estimation in the image space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge