Nora Jarrett Forbes
RootPainter3D: Interactive-machine-learning enables rapid and accurate contouring for radiotherapy
Jun 22, 2021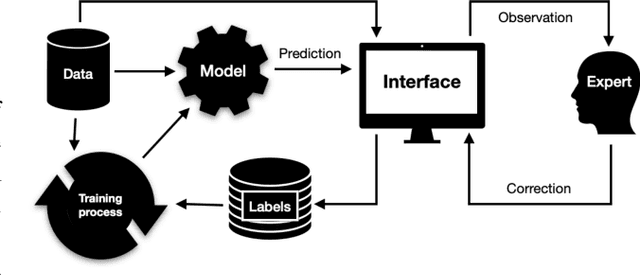
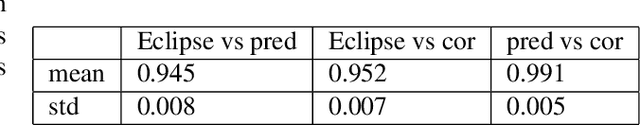
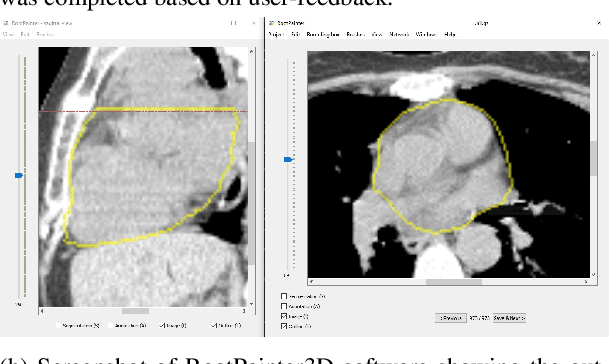
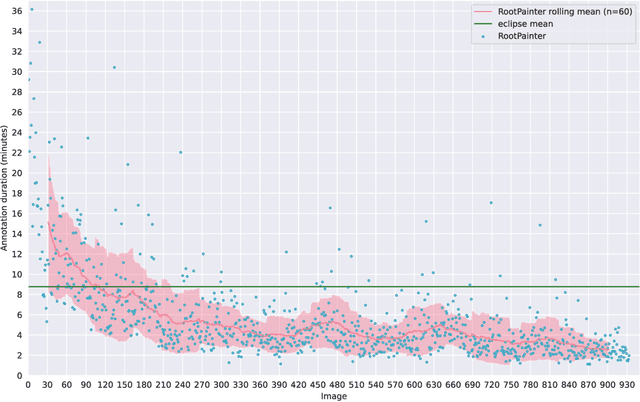
Abstract:Organ-at-risk contouring is still a bottleneck in radiotherapy, with many deep learning methods falling short of promised results when evaluated on clinical data. We investigate the accuracy and time-savings resulting from the use of an interactive-machine-learning method for an organ-at-risk contouring task. We compare the method to the Eclipse contouring software and find strong agreement with manual delineations, with a dice score of 0.95. The annotations created using corrective-annotation also take less time to create as more images are annotated, resulting in substantial time savings compared to manual methods, with hearts that take 2 minutes and 2 seconds to delineate on average, after 923 images have been delineated, compared to 7 minutes and 1 seconds when delineating manually. Our experiment demonstrates that interactive-machine-learning with corrective-annotation provides a fast and accessible way for non computer-scientists to train deep-learning models to segment their own structures of interest as part of routine clinical workflows. Source code is available at \href{https://github.com/Abe404/RootPainter3D}{this HTTPS URL}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge