Nitin Satpute
Polynomial Time Cryptanalytic Extraction of Neural Network Models
Oct 12, 2023

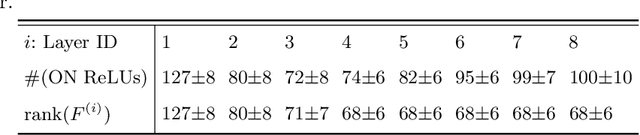

Abstract:Billions of dollars and countless GPU hours are currently spent on training Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for a variety of tasks. Thus, it is essential to determine the difficulty of extracting all the parameters of such neural networks when given access to their black-box implementations. Many versions of this problem have been studied over the last 30 years, and the best current attack on ReLU-based deep neural networks was presented at Crypto 2020 by Carlini, Jagielski, and Mironov. It resembles a differential chosen plaintext attack on a cryptosystem, which has a secret key embedded in its black-box implementation and requires a polynomial number of queries but an exponential amount of time (as a function of the number of neurons). In this paper, we improve this attack by developing several new techniques that enable us to extract with arbitrarily high precision all the real-valued parameters of a ReLU-based DNN using a polynomial number of queries and a polynomial amount of time. We demonstrate its practical efficiency by applying it to a full-sized neural network for classifying the CIFAR10 dataset, which has 3072 inputs, 8 hidden layers with 256 neurons each, and over million neuronal parameters. An attack following the approach by Carlini et al. requires an exhaustive search over 2 to the power 256 possibilities. Our attack replaces this with our new techniques, which require only 30 minutes on a 256-core computer.
Workload-Balanced Pruning for Sparse Spiking Neural Networks
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Pruning for Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) has emerged as a fundamental methodology for deploying deep SNNs on resource-constrained edge devices. Though the existing pruning methods can provide extremely high weight sparsity for deep SNNs, the high weight sparsity brings a workload imbalance problem. Specifically, the workload imbalance happens when a different number of non-zero weights are assigned to hardware units running in parallel, which results in low hardware utilization and thus imposes longer latency and higher energy costs. In preliminary experiments, we show that sparse SNNs ($\sim$98% weight sparsity) can suffer as low as $\sim$59% utilization. To alleviate the workload imbalance problem, we propose u-Ticket, where we monitor and adjust the weight connections of the SNN during Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (LTH) based pruning, thus guaranteeing the final ticket gets optimal utilization when deployed onto the hardware. Experiments indicate that our u-Ticket can guarantee up to 100% hardware utilization, thus reducing up to 76.9% latency and 63.8% energy cost compared to the non-utilization-aware LTH method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge