Nikolaus Weichselbaumer
Combining OCR Models for Reading Early Modern Printed Books
May 11, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the usage of fine-grained font recognition on OCR for books printed from the 15th to the 18th century. We used a newly created dataset for OCR of early printed books for which fonts are labeled with bounding boxes. We know not only the font group used for each character, but the locations of font changes as well. In books of this period, we frequently find font group changes mid-line or even mid-word that indicate changes in language. We consider 8 different font groups present in our corpus and investigate 13 different subsets: the whole dataset and text lines with a single font, multiple fonts, Roman fonts, Gothic fonts, and each of the considered fonts, respectively. We show that OCR performance is strongly impacted by font style and that selecting fine-tuned models with font group recognition has a very positive impact on the results. Moreover, we developed a system using local font group recognition in order to combine the output of multiple font recognition models, and show that while slower, this approach performs better not only on text lines composed of multiple fonts but on the ones containing a single font only as well.
Proof of Concept: Automatic Type Recognition
Jul 15, 2020
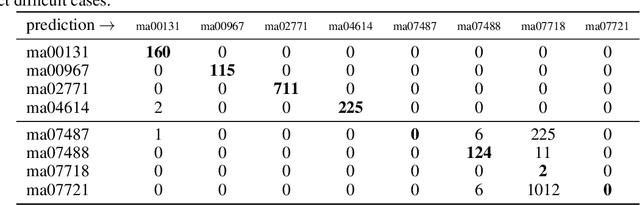
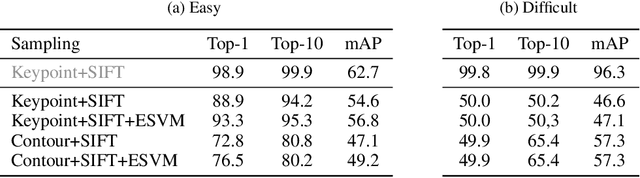
Abstract:The type used to print an early modern book can give scholars valuable information about the time and place of its production as well as the printer responsible. Currently type recognition is done manually using the shapes of `M' or `Qu' and the size of a type to look it up in a large reference work. This is reliable, but slow and requires specialized skills. We investigate the performance of type classification and type retrieval using a newly created dataset consisting of easy and difficult types used in early printed books. For type classification, we rely on a deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) originally used for font-group classification while we use a common writer identification method for the retrieval case. We show that in both scenarios, easy types can be classified/retrieved with a high accuracy while difficult cases are indeed difficult.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge