Nikita Semenov
AriGraph: Learning Knowledge Graph World Models with Episodic Memory for LLM Agents
Jul 05, 2024


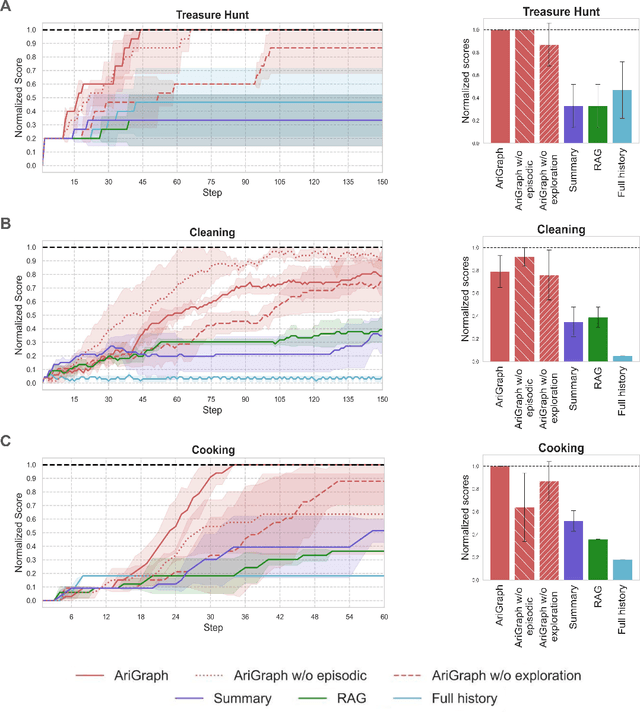
Abstract:Advancements in generative AI have broadened the potential applications of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the development of autonomous agents. Achieving true autonomy requires accumulating and updating knowledge gained from interactions with the environment and effectively utilizing it. Current LLM-based approaches leverage past experiences using a full history of observations, summarization or retrieval augmentation. However, these unstructured memory representations do not facilitate the reasoning and planning essential for complex decision-making. In our study, we introduce AriGraph, a novel method wherein the agent constructs a memory graph that integrates semantic and episodic memories while exploring the environment. This graph structure facilitates efficient associative retrieval of interconnected concepts, relevant to the agent's current state and goals, thus serving as an effective environmental model that enhances the agent's exploratory and planning capabilities. We demonstrate that our Ariadne LLM agent, equipped with this proposed memory architecture augmented with planning and decision-making, effectively handles complex tasks on a zero-shot basis in the TextWorld environment. Our approach markedly outperforms established methods such as full-history, summarization, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation in various tasks, including the cooking challenge from the First TextWorld Problems competition and novel tasks like house cleaning and puzzle Treasure Hunting.
Text Detoxification using Large Pre-trained Neural Models
Sep 18, 2021



Abstract:We present two novel unsupervised methods for eliminating toxicity in text. Our first method combines two recent ideas: (1) guidance of the generation process with small style-conditional language models and (2) use of paraphrasing models to perform style transfer. We use a well-performing paraphraser guided by style-trained language models to keep the text content and remove toxicity. Our second method uses BERT to replace toxic words with their non-offensive synonyms. We make the method more flexible by enabling BERT to replace mask tokens with a variable number of words. Finally, we present the first large-scale comparative study of style transfer models on the task of toxicity removal. We compare our models with a number of methods for style transfer. The models are evaluated in a reference-free way using a combination of unsupervised style transfer metrics. Both methods we suggest yield new SOTA results.
Methods for Detoxification of Texts for the Russian Language
May 19, 2021


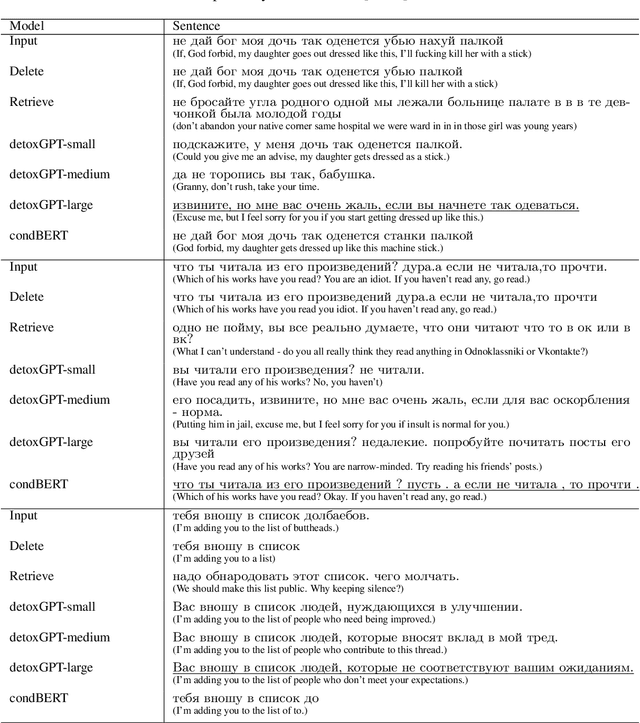
Abstract:We introduce the first study of automatic detoxification of Russian texts to combat offensive language. Such a kind of textual style transfer can be used, for instance, for processing toxic content in social media. While much work has been done for the English language in this field, it has never been solved for the Russian language yet. We test two types of models - unsupervised approach based on BERT architecture that performs local corrections and supervised approach based on pretrained language GPT-2 model - and compare them with several baselines. In addition, we describe evaluation setup providing training datasets and metrics for automatic evaluation. The results show that the tested approaches can be successfully used for detoxification, although there is room for improvement.
Detecting Inappropriate Messages on Sensitive Topics that Could Harm a Company's Reputation
Mar 09, 2021



Abstract:Not all topics are equally "flammable" in terms of toxicity: a calm discussion of turtles or fishing less often fuels inappropriate toxic dialogues than a discussion of politics or sexual minorities. We define a set of sensitive topics that can yield inappropriate and toxic messages and describe the methodology of collecting and labeling a dataset for appropriateness. While toxicity in user-generated data is well-studied, we aim at defining a more fine-grained notion of inappropriateness. The core of inappropriateness is that it can harm the reputation of a speaker. This is different from toxicity in two respects: (i) inappropriateness is topic-related, and (ii) inappropriate message is not toxic but still unacceptable. We collect and release two datasets for Russian: a topic-labeled dataset and an appropriateness-labeled dataset. We also release pre-trained classification models trained on this data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge