Nicole Sochacki-Wójcicka
Spontaneous preterm birth prediction using convolutional neural networks
Aug 21, 2020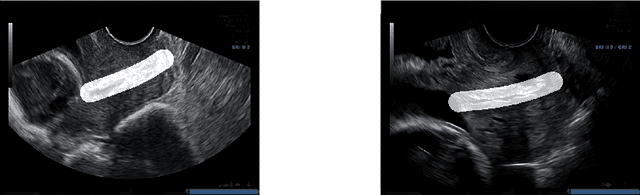
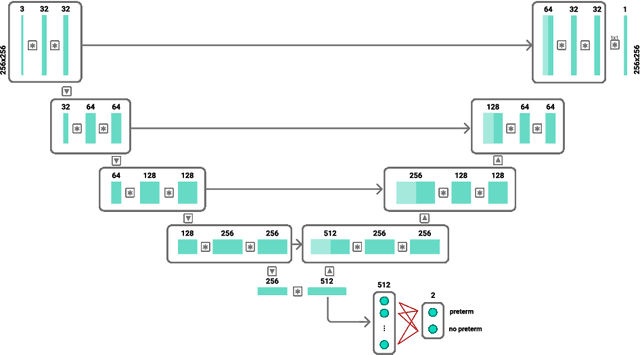
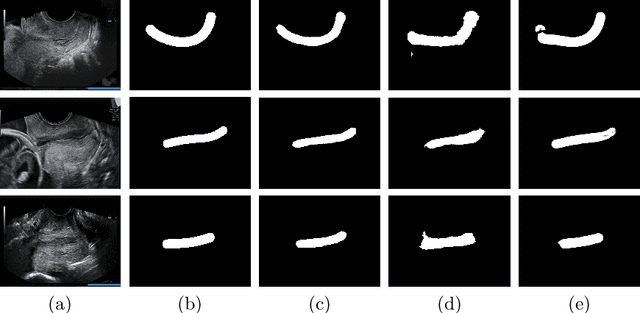
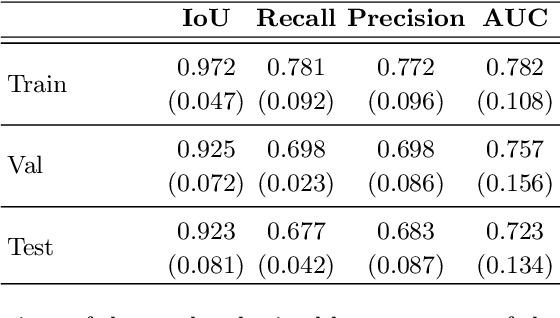
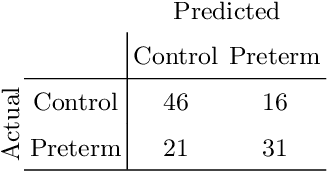
Abstract:An estimated 15 million babies are born too early every year. Approximately 1 million children die each year due to complications of preterm birth (PTB). Many survivors face a lifetime of disability, including learning disabilities and visual and hearing problems. Although manual analysis of ultrasound images (US) is still prevalent, it is prone to errors due to its subjective component and complex variations in the shape and position of organs across patients. In this work, we introduce a conceptually simple convolutional neural network (CNN) trained for segmenting prenatal ultrasound images and classifying task for the purpose of preterm birth detection. Our method efficiently segments different types of cervixes in transvaginal ultrasound images while simultaneously predicting a preterm birth based on extracted image features without human oversight. We employed three popular network models: U-Net, Fully Convolutional Network, and Deeplabv3 for the cervix segmentation task. Based on the conducted results and model efficiency, we decided to extend U-Net by adding a parallel branch for classification task. The proposed model is trained and evaluated on a dataset consisting of 354 2D transvaginal ultrasound images and achieved a segmentation accuracy with a mean Jaccard coefficient index of 0.923 $\pm$ 0.081 and a classification sensitivity of 0.677 $\pm$ 0.042 with a 3.49\% false positive rate. Our method obtained better results in the prediction of preterm birth based on transvaginal ultrasound images compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Estimation of preterm birth markers with U-Net segmentation network
Aug 24, 2019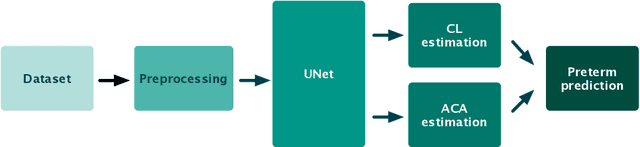
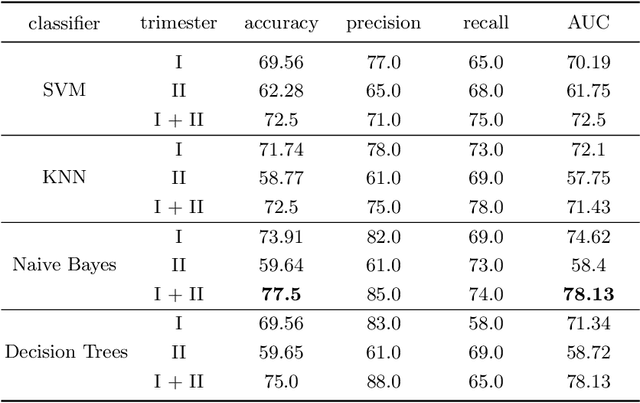
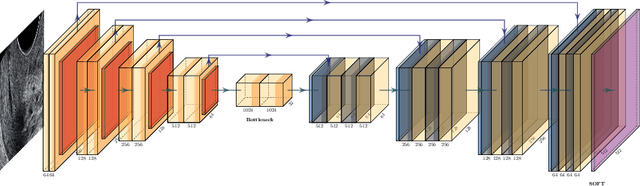
Abstract:Preterm birth is the most common cause of neonatal death. Current diagnostic methods that assess the risk of preterm birth involve the collection of maternal characteristics and transvaginal ultrasound imaging conducted in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. Analysis of the ultrasound data is based on visual inspection of images by gynaecologist, sometimes supported by hand-designed image features such as cervical length. Due to the complexity of this process and its subjective component, approximately 30% of spontaneous preterm deliveries are not correctly predicted. Moreover, 10% of the predicted preterm deliveries are false-positives. In this paper, we address the problem of predicting spontaneous preterm delivery using machine learning. To achieve this goal, we propose to first use a deep neural network architecture for segmenting prenatal ultrasound images and then automatically extract two biophysical ultrasound markers, cervical length (CL) and anterior cervical angle (ACA), from the resulting images. Our method allows to estimate ultrasound markers without human oversight. Furthermore, we show that CL and ACA markers, when combined, allow us to decrease false-negative ratio from 30% to 18%. Finally, contrary to the current approaches to diagnostics methods that rely only on gynaecologist's expertise, our method introduce objectively obtained results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge