Nicholas Kersting
Evaluating Quality of Answers for Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Strong LLM Is All You Need
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:We present a comprehensive evaluation of answer quality in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications using vRAG-Eval, a novel grading system that is designed to assess correctness, completeness, and honesty. We further map the grading of quality aspects aforementioned into a binary score, indicating an accept or reject decision, mirroring the intuitive "thumbs-up" or "thumbs-down" gesture commonly used in chat applications. This approach suits factual business settings where a clear decision opinion is essential. Our assessment applies vRAG-Eval to two Large Language Models (LLMs), evaluating the quality of answers generated by a vanilla RAG application. We compare these evaluations with human expert judgments and find a substantial alignment between GPT-4's assessments and those of human experts, reaching 83% agreement on accept or reject decisions. This study highlights the potential of LLMs as reliable evaluators in closed-domain, closed-ended settings, particularly when human evaluations require significant resources.
ONNXExplainer: an ONNX Based Generic Framework to Explain Neural Networks Using Shapley Values
Oct 03, 2023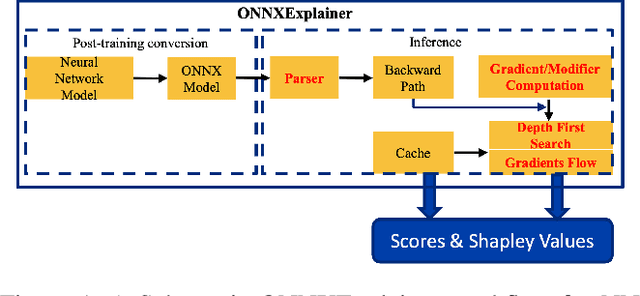
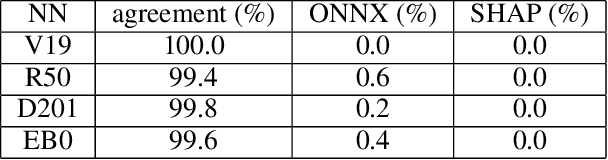
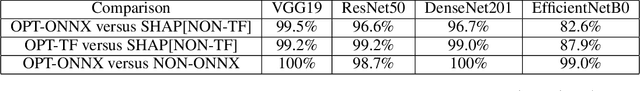
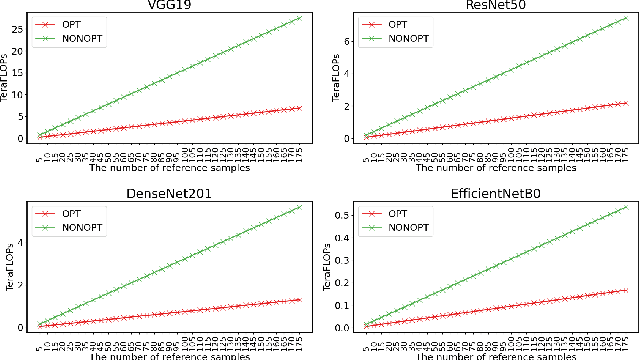
Abstract:Understanding why a neural network model makes certain decisions can be as important as the inference performance. Various methods have been proposed to help practitioners explain the prediction of a neural network model, of which Shapley values are most popular. SHAP package is a leading implementation of Shapley values to explain neural networks implemented in TensorFlow or PyTorch but lacks cross-platform support, one-shot deployment and is highly inefficient. To address these problems, we present the ONNXExplainer, which is a generic framework to explain neural networks using Shapley values in the ONNX ecosystem. In ONNXExplainer, we develop its own automatic differentiation and optimization approach, which not only enables One-Shot Deployment of neural networks inference and explanations, but also significantly improves the efficiency to compute explanation with less memory consumption. For fair comparison purposes, we also implement the same optimization in TensorFlow and PyTorch and measure its performance against the current state of the art open-source counterpart, SHAP. Extensive benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed optimization approach improves the explanation latency of VGG19, ResNet50, DenseNet201, and EfficientNetB0 by as much as 500%.
Fast and Fuzzy Private Set Intersection
May 21, 2014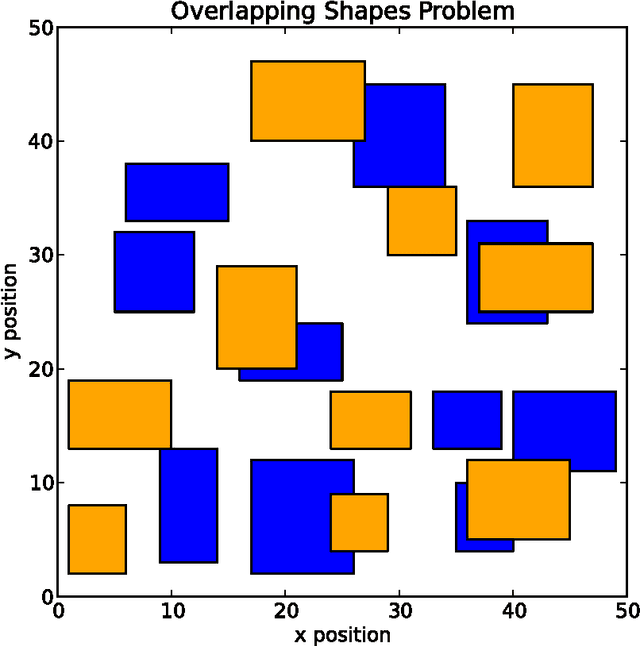
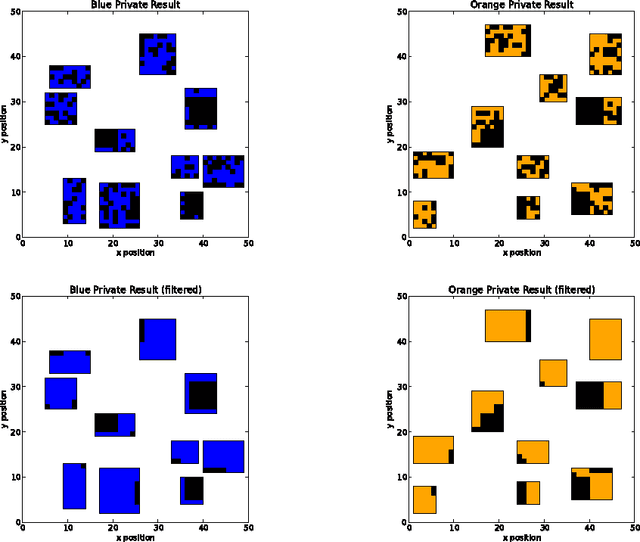
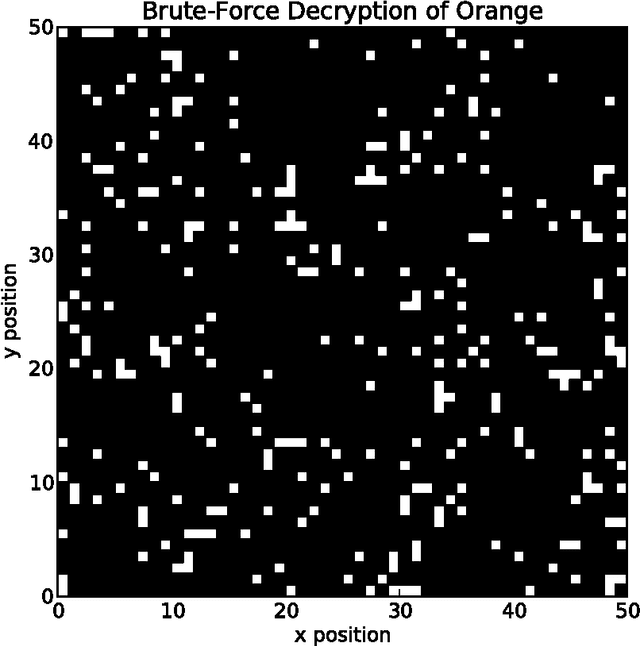
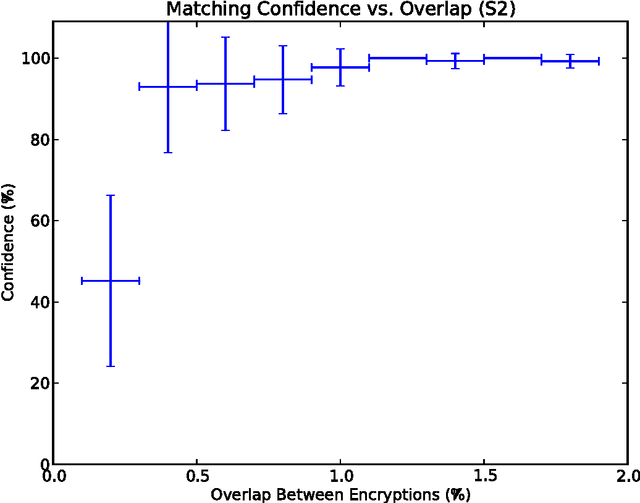
Abstract:Private Set Intersection (PSI) is usually implemented as a sequence of encryption rounds between pairs of users, whereas the present work implements PSI in a simpler fashion: each set only needs to be encrypted once, after which each pair of users need only one ordinary set comparison. This is typically orders of magnitude faster than ordinary PSI at the cost of some ``fuzziness" in the matching, which may nonetheless be tolerable or even desirable. This is demonstrated in the case where the sets consist of English words processed with WordNet.
A Secure and Comparable Text Encryption Algorithm
Aug 15, 2013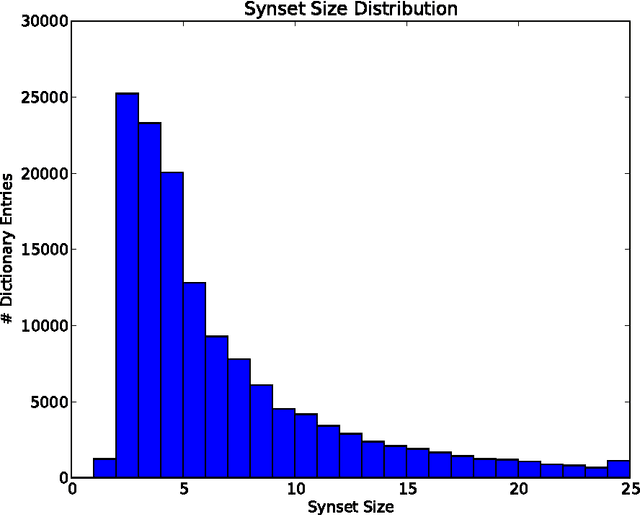
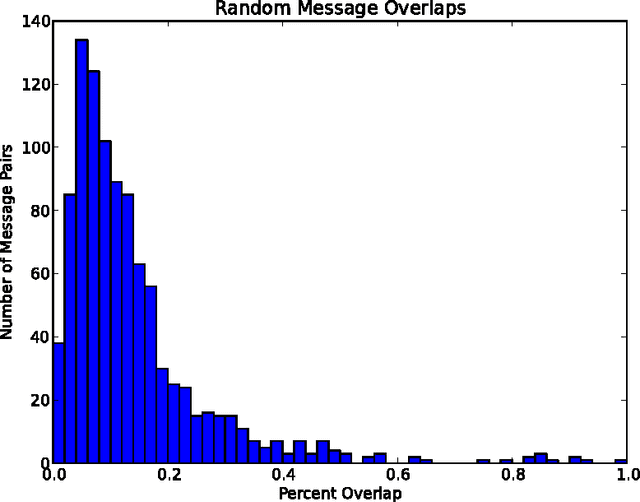
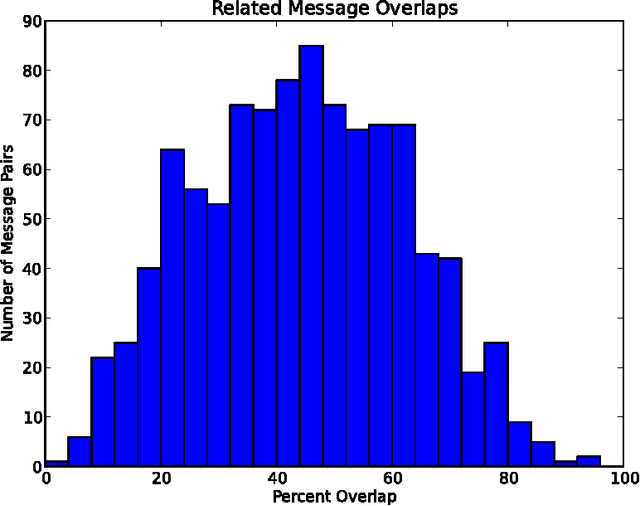
Abstract:This paper discloses a simple algorithm for encrypting text messages, based on the NP-completeness of the subset sum problem, such that the similarity between encryptions is roughly proportional to the semantic similarity between their generating messages. This allows parties to compare encrypted messages for semantic overlap without trusting an intermediary and might be applied, for example, as a means of finding scientific collaborators over the Internet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge